Abstract
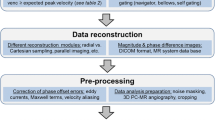
4D Flow is an emerging MR technique enabling three-dimensional and cardiac phase-resolved flowmetry with ECG-gated phase-contrast MRI that increased the speed of data acquisitions, accuracy and robustness. The method is promoting researches in areas that have not been fully addressed before in the cardiovascular system, such as flowmetry of the bloodstream across the valves, within the heart chambers, complexed flow dynamics such as vortex, helical or retrograde. Wall shear stress and other potential biomarkers derived from 4D Flow are known to be related to vascular wall diseases such as atherosclerosis. In this review, fundamental concepts of 4D Flow technique and post-processing, benefits and limitations as well as its clinical applications are discussed, and the importance of quality control and validation of the method is emphasized. New ideas inspired by 4D Flow can help clinicians and MR scientists further understand the role of flow dynamics in health sciences, diseases and various aspects of cardiovascular physiology.



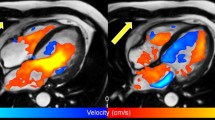
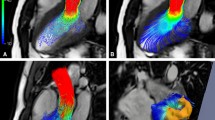
(modified from Markl M, et al. JMRI 17:500, 2003)










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wells F (2013) The heart of Leonardo. Springer, Heidelberg
Markl M, Draney MT, Hope MD, Levin JM, Chan FP, Alley MT, Pelc NJ, Herfkens RJ (2004) Time-resolved 3-dimensional velocity mapping in the thoracic aorta: visualization of 3-directional blood flow patterns in healthy volunteers and patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr 28(4):459–468
Pelc LR, Pelc NJ, Rayhill SC, Castro LJ, Glover GH, Herfkens RJ, Miller DC, Jeffrey RB (1992) Arterial and venous blood flow: noninvasive quantitation with MR imaging. Radiology 185(3):809–812. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.185.3.1438767
Markl M, Pelc NJ (2004) On flow effects in balanced steady-state free precession imaging: pictorial description, parameter dependence, and clinical implications. J Magn Res Imaging JMRI 20(4):697–705. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.20163
Motoyama D, Ishii Y, Takehara Y, Sugiyama M, Yang W, Nasu H, Ushio T, Hirose Y, Ohishi N, Wakayama T, Kabasawa H, Johnson K, Wieben O, Sakahara H, Ozono S (2017) Four-dimensional phase-contrast vastly undersampled isotropic projection reconstruction (4D PC-VIPR) MR evaluation of the renal arteries in transplant recipients: preliminary results. J Magn Res Imaging JMRI 46(2):595–603. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25607
Katahashi K, Sano M, Takehara Y, Inuzuka K, Sugiyama M, Alley MT, Takeuchi H, Unno N (2019) Flow dynamics of type II endoleaks can determine sac expansion after endovascular aneurysm repair using four-dimensional flow-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging analysis. J Vasc Surg 70(1):107e101–116e101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2018.09.048
Sakata M, Takehara Y, Katahashi K, Sano M, Inuzuka K, Yamamoto N, Sugiyama M, Sakahara H, Wakayama T, Alley MT, Konno H, Unno N (2016) Hemodynamic analysis of endoleaks after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair by using 4-dimensional flow-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging. Circ J 80(8):1715–1725. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.CJ-16-0297
Naganawa S, Cooper TG, Jenner G, Potchen EJ, Ishigaki T (1994) Flow velocity and volume measurement of superior and inferior mesenteric artery with cine phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging. Radiat Med 12(5):213–220
Ayukawa Y, Murayama S, Tsuchiya N, Yara S, Fujita J (2011) Estimation of pulmonary vascular resistance in patients with pulmonary fibrosis by phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging. Jpn J Radiol 29(8):563–569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-011-0598-2
Barthelmes D, Parviainen I, Vainio P, Vanninen R, Takala J, Ikonen A, Tueller D, Jakob SM (2009) Assessment of splanchnic blood flow using magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 21(6):693–700. https://doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0b013e32831a86e0
Dalman RL, Li KC, Moon WK, Chen I, Zarins CK (1996) Diminished postprandial hyperemia in patients with aortic and mesenteric arterial occlusive disease. Quantification by magnetic resonance flow imaging. Circulation 94(9 Suppl):II206–II210
Jeays AD, Lawford PV, Gillott R, Spencer P, Barber DC, Bardhan KD, Hose DR (2007) Characterisation of the haemodynamics of the superior mesenteric artery. J Biomech 40(9):1916–1926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2006.09.009
Machida H, Komori Y, Ueno E, Shen Y, Hirata M, Kojima S, Morita S, Sato M, Okazaki T (2009) Spatial factors for quantifying constant flow velocity in a small tube phantom: comparison of phase-contrast cine-magnetic resonance imaging and the intraluminal Doppler guidewire method. Jpn J Radiol 27(9):335–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-009-0349-9
Machida H, Komori Y, Ueno E, Shen Y, Hirata M, Kojima S, Sato M, Okazaki T, Masukawa A, Morita S, Suzuki K (2010) Accurate measurement of pulsatile flow velocity in a small tube phantom: comparison of phase-contrast cine magnetic resonance imaging and intraluminal Doppler guidewire. Jpn J Radiol 28(8):571–577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-010-0472-7
Takahashi H, Tanaka H, Fujita N, Murase K, Tomiyama N (2011) Variation in supratentorial cerebrospinal fluid production rate in one day: measurement by nontriggered phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging. Jpn J Radiol 29(2):110–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-010-0525-y
Tsuchiya N, Ayukawa Y, Murayama S (2013) Evaluation of hemodynamic changes by use of phase-contrast MRI for patients with interstitial pneumonia, with special focus on blood flow reduction after breath-holding and bronchopulmonary shunt flow. Jpn J Radiol 31(3):197–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-012-0171-7
Li KC, Whitney WS, McDonnell CH, Fredrickson JO, Pelc NJ, Dalman RL, Jeffrey RB Jr (1994) Chronic mesenteric ischemia: evaluation with phase-contrast cine MR imaging. Radiology 190(1):175–179. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.190.1.8259400
Ishikawa T, Takehara Y, Yamashita S, Iwashima S, Sugiyama M, Wakayama T, Johnson K, Wieben O, Sakahara H, Ogata T (2015) Hemodynamic assessment in a child with renovascular hypertension using time-resolved three-dimensional cine phase-contrast MRI. J Magn Res Imaging JMRI 41(1):165–168. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.24522
Sugiyama M, Takehara Y, Kawate M, Ooishi N, Terada M, Isoda H, Sakahara H, Naganawa S, Johnson KM, Wieben O, Wakayama T, Nozaki A, Kabasawa H (2020) Optimal plane selection for measuring post-prandial blood flow increase within the superior mesenteric artery: analysis using 4D flow and computational fluid dynamics. Magn Reson Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.2463/mrms.mp.2019-0089
Suwa K, Saitoh T, Takehara Y, Sano M, Nobuhara M, Saotome M, Urushida T, Katoh H, Satoh H, Sugiyama M, Wakayama T, Alley M, Sakahara H, Hayashi H (2015) Characteristics of intra-left atrial flow dynamics and factors affecting formation of the vortex flow—analysis with phase-resolved 3-dimensional cine phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging. Circ J 79(1):144–152. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.CJ-14-0562
Suwa K, Saitoh T, Takehara Y, Sano M, Saotome M, Urushida T, Katoh H, Satoh H, Sugiyama M, Wakayama T, Alley M, Sakahara H, Hayashi H (2016) Intra-left ventricular flow dynamics in patients with preserved and impaired left ventricular function: analysis with 3D cine phase contrast MRI (4D-Flow). J Magn Res Imaging JMRI 44(6):1493–1503. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25315
Terada M, Takehara Y, Isoda H, Uto T, Matsunaga M, Alley M (2016) Low WSS and high OSI measured by 3D cine PC MRI reflect high pulmonary artery pressures in suspected secondary pulmonary arterial hypertension. Magn Reson Med Sci 15(2):193–202. https://doi.org/10.2463/mrms.mp.2015-0038
Fukuyama A, Isoda H, Morita K, Mori M, Watanabe T, Ishiguro K, Komori Y, Kosugi T (2017) Influence of spatial resolution in three-dimensional cine phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging on the accuracy of hemodynamic analysis. Magn Reson Med Sci 16(4):311–316. https://doi.org/10.2463/mrms.mp.2016-0060
Ma LE, Markl M, Chow K, Huh H, Forman C, Vali A, Greiser A, Carr J, Schnell S, Barker AJ, Jin N (2019) Aortic 4D flow MRI in 2 minutes using compressed sensing, respiratory controlled adaptive k-space reordering, and inline reconstruction. Magn Reson Med 81(6):3675–3690. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.27684
Retson TA, Besser AH, Sall S, Golden D, Hsiao A (2019) Machine learning and deep neural networks in thoracic and cardiovascular imaging. J Thorac Imaging 34(3):192–201. https://doi.org/10.1097/RTI.0000000000000385
Watanabe T, Isoda H, Takehara Y, Terada M, Naito T, Kosugi T, Onishi Y, Tanoi C, Izumi T (2018) Hemodynamic vascular biomarkers for initiation of paraclinoid internal carotid artery aneurysms using patient-specific computational fluid dynamic simulation based on magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroradiology 60(5):545–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-018-2002-8
Bratt A, Kim J, Pollie M, Beecy AN, Tehrani NH, Codella N, Perez-Johnston R, Palumbo MC, Alakbarli J, Colizza W, Drexler IR, Azevedo CF, Kim RJ, Devereux RB, Weinsaft JW (2019) Machine learning derived segmentation of phase velocity encoded cardiovascular magnetic resonance for fully automated aortic flow quantification. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 21(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12968-018-0509-0
Funding
The content of this review includes the author’s researches supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research “Kakenhi” (C) (General) (Grant No. 17K10398).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The corresponding author had the idea for the article, performed the literature search and data analysis and drafted and/or critically revised the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The corresponding author is an endowed chair of the Department of Fundamental Development for Advanced Low Invasive Diagnostic Imaging, Nagoya University, Graduate School of Medicine, and supported by a private company.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takehara, Y. 4D Flow when and how?. Radiol med 125, 838–850 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-020-01249-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-020-01249-0