Abstract
Aim
For selected patients with brain metastases (BMs), the role of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) or fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (SFRT) is well recognized. The recent introduction of flattening filter free (FFF) delivery during linac-based SRS or SFRT allows shorter beam-on-time, improving patients’ comfort and facility workflow. Nevertheless, limited experiences evaluated the impact of FFF linac-based SRS and SFRT in BMs treatment. Aim of the current study was to analyze SRS/SFRT linac-based FFF delivery for BMs in terms of dosimetric and early clinical results.
Materials and methods
Patients with life expectancy >3 months, number of BMs <5, diameter <3 cm, and controlled or synchronous primary tumor received SRS/SFRT. The prescribed total dose and fractionation, based on BMs size and proximity to organs at risk, ranged from 15 Gy in 1 fraction to 30 Gy in 5 fractions. A FFF volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) plan was generated with one or two coplanar partial arcs. Toxicity was assessed according to CTCAE v4.0.
Results
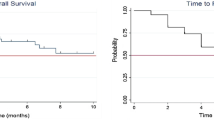
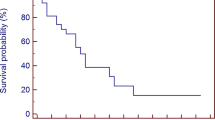
From April 2014 to February 2016, 45 patients (89 BMs) were treated with SRS/SFRT linac-based FFF delivery. The mean beam-on-time was 140 s for each lesion (range 90–290 s) and the average brain Dmean was 1 Gy (range 0.1–4.8 Gy). At the time of analysis, local control was reported in 93.2% (83/89 BMs). With a median follow-up time of 12 months (range 1–27 months), the median overall survival was 14 months and the 6-month overall survival was 77%. Finally, the median intracranial disease control was 11 months. Acute and late toxicities were acceptable without severe events (no adverse events ≥G2 were recorded).
Conclusions
These preliminary results highlighted the feasibility and safety of linac-based SRS/SFRT with FFF mode for BMs patients. A longer follow-up is necessary to confirm the efficacy of this treatment modality in BM patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mehta MP, Tsao MN, Whelan TJ et al (2005) The American society for therapeutic radiology and oncology (ASTRO) evidence-based review of the role of radiosurgery for brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:37–46. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.05.023
Patchell RA (2003) The management of brain metastases. Cancer Treat Rev 29:533–540. doi:10.1016/S0305-7372(03)00105-1
Lin X, DeAngelis LM (2015) Treatment of brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 33:3475–3484. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.60.9503
NCCN guide lines (2016) https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp. Accessed 30 Oct 2016
Kocher M, Wittig A, Piroth MD et al (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases. A report of the DEGRO Working Group on Stereotactic Radiotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol 190:521–532. doi:10.1007/s00066-014-0648-7
Soffietti R, Kocher M, Abacioglu UM et al (2013) A European organisation for research and treatment of cancer phase III trial of adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation in patients with one to three brain metastases from solid tumors after surgical resection or radiosurgery: quality-of-life result. J Clin Oncol 31:65–72. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.41.0639
Brown PD, Jaeckle K, Ballman KV et al (2016) Effect of radiosurgery alone vs radiosurgery with whole brain radiation therapy on cognitive function in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 316:401–409. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.9839
Giaj Levra N, Sicignagno G, Fiorentino A et al (2016) Whole brain radiotherapy with hippocampal avoidance and simultaneous integrated boost for brain metastases: a dosimetric volumetric-modulated arc therapy study. Radiol Med 121:60–69. doi:10.1007/s11547-015-0563-8
Nieder C, Grosu AL, Gaspar LE (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for brain metastases: a systematic review. Radiat Oncol 9:155. doi:10.1186/1748-717X-9-155
Leksell L (1951) The stereotactic method and radiosurgery of the brain. Acta Chir Scand 102:316–319
Wu A, Lindner G, Maitz AH et al (1990) Physics of Gamma Knife approach on convergent beams in stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 18:941–949
Alongi F, Fiorentino A, Mancosu P et al (2016) Stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial metastases: linac-based and gamma-dedicated unit approach. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 16:731–740. doi:10.1080/14737140.2016.1190648
Fiorentino A, Levra NG, Mazzola R et al (2015) Letter: volumetric arc therapy (RapidArc) vs Gamma Knife radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases: not only a dosimetric issue. Neurosurgery 77:E310. doi:10.1227/NEU.0000000000000796
Fiorentino A, Giaj-Levra N, Mazzola R et al (2015) Dosimetrics of intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery: only “an exercise of style”? Strahlenther Onkol 191:810–811. doi:10.1007/s00066-015-0879-2
Abacioglu U, Ozen Z, Yilmaz M et al (2014) Critical appraisal of RapidArc radiosurgery with flattening filter free photon beams for benign brain lesions in comparison to GammaKnife: a treatment planning study. Radiat Oncol 9:119. doi:10.1186/1748-717X-9-119
Kragl G, Sigamani A, Nambiraj A et al (2009) Dosimetric characteristics of 6 and 10 MV unflattened photon beams. Radiother Oncol 93:141–146. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2009.06.008
Cashmore J (2008) The characterization of unflattened photon beams from a 6 MV linear accelerator. Phys Med Biol 53:1933–1946. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/53/7/009
Vassiliev ON, Titt U, Pönisch F et al (2006) Dosimetric properties of photon beams from a flattening filter free clinical accelerator. Phys Med Biol 51:1907–1917
Rieber J, Tonndorf-Martini E, Schramm O et al (2016) Radiosurgery with flattening-filter-free techniques in the treatment of brain metastases: plan comparison and early clinical evaluation. Strahlenther Onkol 192:789–796
Lohse I, Lang S, Hrbacek J et al (2011) Effect of high dose per pulse flattening filter-free beams on cancer cell survival. Radiother Oncol 101:226–232. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2011.05.072
Lai Y, Chen S, Xu C et al (2016) Dosimetric superiority of flattening filter free beams for single-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery in single brain metastasis. Oncotarget 3. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.13085 (Epub ahead of print)
Stieler F, Fleckenstein J, Simeonova A et al (2013) Intensity modulated radiosurgery of brain metastases with flattening filter-free beams. Radiother Oncol 109:448–451. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2013.10.017
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L et al (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(99)00507-6
Lischalk JW, Oermann E, Collins SP et al (2015) Five-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for single inoperable high-risk non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) brain metastases. Radiat Oncol. 10:216. doi:10.1186/s13014-015-0525-2
van Persijn van Meerten EL, Gelderblom H, Bloem JL (2010) RECIST revised: implications for the radiologist. A review article on the modified RECIST guideline. Eur Radiol 20:1456–1467. doi:10.1007/s00330-009-1685-y
Kumar AJ, Leeds NE, Fuller GN et al (2000) Malignant gliomas: MR imaging spectrum of radiation therapy- and chemotherapy-induced necrosis of the brain after treatment. Radiology 217:377–384
Koay E, Sulman EP (2012) Management of brain metastasis: past lessons, modern management, and future considerations. Curr Oncol Rep. 14:70–78. doi:10.1007/s11912-011-0205-9
Maclean J, Fersht N, Singhera M et al (2013) Multi-disciplinary management for patients with oligometastases to the brain: results of a 5 year cohort study. Radiat Oncol 8:156. doi:10.1186/1748-717X-8-156
D’Agostino GR, Autorino R, Pompucci A et al (2011) Whole-brain radiotherapy combined with surgery or stereotactic radiotherapy in patients with brain oligometastases: long-term analysis. Strahlenther Onkol 187:421–425. doi:10.1007/s00066-011-2228-4
Balducci M, Autorino R, Chiesa S et al (2015) Radiosurgery or fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy plus whole-brain radioherapy in brain oligometastases: a long-term analysis. Anticancer Res 35:3055–3059
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T et al (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol 15:387–395. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70061-0
Minniti G, Scaringi C, Paolini S et al (2016) Single-fraction versus multifraction (3 × 9 Gy) stereotactic radiosurgery for large (>2 cm) brain metastases: a comparative analysis of local control and risk of radiation-induced brain necrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 95:1142–1148. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.03.013
Croker J, Chua B, Bernard A et al (2016) Treatment of brain oligometastases with hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy utilising volumetric modulated arc therapy. Clin Exp Metastasis 33:125–132. doi:10.1007/s10585-015-9762-x
King RB, Hyland WB, Cole AJ et al (2013) An in vitro study of the radiobiological effects of flattening filter free radiotherapy treatments. Phys Med Biol 58(5):N83–N94. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/58/5/N83
Franco P, De Bari B, Ciammella P et al (2014) The role of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy in oncological and non-oncological clinical settings: highlights from the 7th meeting of AIRO–Young Members Working Group (AIRO Giovani). Tumori 100:e214–e219. doi:10.1700/1778.19280
Navarria P, Ascolese AM, Mancosu P et al (2013) Volumetric modulated arc therapy with flattening filter free (FFF) beams for stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in patients with medically inoperable early stage non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Radiother Oncol 107:414–418. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2013.04.016
Reggiori G, Mancosu P, Castiglioni S et al (2012) Can volumetric modulated arc therapy with flattening filter free beams play a role in stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver lesions? A volume-based analysis. Med Phys 39:1112–1118. doi:10.1118/1.3679858
Zwahlen DR, Lang S, Hrbacek J et al (2012) The use of photon beams of a flattening filter-free linear accelerator for hypofractionated volumetric modulated arc therapy in localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:1655–1660. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.10.019
Zhuang M, Zhang T, Chen Z et al (2012) Volumetric modulation arc radiotherapy with flattening filter-free beams compared with conventional beams for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a feasibility study. Chin J Cancer 32:397–402. doi:10.5732/cjc.012.10182
Lechner W, Kragl G, Georg D (2012) Evaluation of treatment plan quality of IMRT and VMAT with and without flattening filter using Pareto optimal fronts. Radiother Oncol 103:97. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2013.09.020
Lang S, Shrestha B, Graydon S et al (2013) Clinical application of flattening filter free beams for extracranial stereotactic radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 106:255–259. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2012.12.012
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiorentino, A., Giaj-Levra, N., Tebano, U. et al. Stereotactic ablative radiation therapy for brain metastases with volumetric modulated arc therapy and flattening filter free delivery: feasibility and early clinical results. Radiol med 122, 676–682 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-017-0768-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-017-0768-0