Abstract
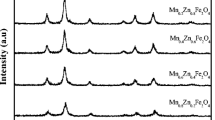
Exploring the physical properties of magnetic nanoferrites for applications in data storage media and biomedicine is a crucial step, providing new insights into the physics of nanostructured materials. Here, the focus is on studying the effect of cobalt ion concentration and thermal annealing temperature on the structural and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles (NPs) synthesized using a co-precipitation method. To this end, Co1−x(Fe2O4)x (x = 0.25, 0.5, and 0.75 M) NPs are initially prepared and then thermally annealed at different temperatures (T = 400–800 °C). X-ray diffraction patterns along with field-emission scanning electron microscopic images indicate the formation of inverse cubic spinel structure with different crystallite sizes and NP size distributions when changing the cobalt ion concentration. Based on hysteresis loop measurements, magnetic parameters such as saturation magnetization (Ms) and coercivity (Hc) show increasing trends from 5.641 emu/g and 146.246 Oe to 8.936 emu/g and 1789.555 Oe when decreasing the cobalt ion concentration. By performing the annealing process, magnetic properties are significantly enhanced in the case of x = 0.25 and 0.5 at T = 400 °C and 600 °C, achieving Ms = 129.954 emu/g and Hc = 1137.697 Oe. Meanwhile, first-order reversal curve (FORC) diagrams are employed to map magnetostatic interactions and coercivity distributions as a function of cobalt ion concentration for NPs annealed at T = 400 °C, manifesting magnetically soft and hard phases. It is found the maximum FORC distribution shifts to higher Hc values with decreasing cobalt ion concentration.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Stafford S, Garcia RS, Gun’ko YK (2018) Multimodal magnetic-plasmonic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Appl Sci 8:97
Urries I, Muñoz C, Gomez L, Marquina C, Sebastian V, Arruebo M, Santamaria J (2014) Magneto-plasmonic nanoparticles as theranostic platforms for magnetic resonance imaging, drug delivery and NIR hyperthermia applications. J Nanoscale 12:1–12
Shams SF, Ghazanfari MR, Schmitz-Antoniak C (2019) Magnetic-plasmonic heterodimer nanoparticles: Designing contemporarily features for emerging biomedical diagnosis and treatments. Nanomaterials 9:97. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010097
Kooti M, Saiahi S, Motamedi H (2013) Fabrication of silver-coated cobalt ferrite nanocomposite and the study of its antibacterial activity. J Magn Magn Mater 333:138–143
Mikalauskaite A, Kondrotas R, Niaura G, Jagminas A (2015) Gold-coated cobalt ferrite nanoparticles via methionine-induced reduction. J Phys Chem C 119:17398–17407
Yang Z, Zhang Z, Jiang Y, Chi M, Nie G, Lu X, Wang C (2016) Palladium nanoparticles modified electrospun CoFe2O4 nanotubes with enhanced peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxide. RSC Adv 6:33636–33642
Vadivel M, Babu RR, Sethuraman K, Ramamurthi K, Arivanandhan M (2014) Synthesis, structural, dielectric, magnetic and optical properties of Cr substituted CoFe2O4 nanoparticles by co-precipitation method. J Magn Magn Mater 362:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.03.016
Heydaryan K, Kashi MA, Montazer AH (2022) Tuning specific loss power of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles by changing surfactant concentration in a combined co-precipitation and thermal decomposition method. Ceram Int 48:16967–16976
Yue H, Yong L, Chunlong F, Zhi Y, Lu Z, Rui X, Di Y, Jing S (2010) J Appl Phys 108:084312
Franco A, Silva FC (2010) Appl Phys Lett 96:172505
Mohamed RM, Rashad MM, Haraz FA, Sigmund W (2010) J Magn Mag Mater 322(14):2058
Houshiar M, Zebhi F, Razi ZJ, Alidoust A, Askari Z (2014) Synthesis of cobalt ferrite(CoFe2O4) nanoparticles using combustion, co precipitation, and precipitation methods A comparison study of size structural and magnetic properties. J Magn Magn Mater 371:43–48
Anis-ur-Rehman M, Abdullah A, Ansari M, Awan M (2011) Synthesis and thermoelectric behavior in nanoparticles of doped Co ferrites. Int J Phys Math Sci 5:568–570. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1059429
Al-Salman HS, Abdullah M (2013) Fabrication and characterization of undoped and cobalt-doped ZnO based UV photodetector prepared by RF-sputtering. J Mater Sci Technol 29:1139–1145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2013.10.007
Fahim H, Jabbar H, Al-Fregi AA (2023) Investigation on thermally induced spin crossover in Fe (Phen)molecules. JCHR 13(3):1423–1434
Arulmurugan R, Vaidyanathan G, Sendhilnathan S, Jeyadevan B (2006) J Magn Magn Mater 298:83
Goldman A (2006) Modern ferrite technology, 2nd edn. Springer, Pittsburgh, PA, USA
Al-zyadi JMK, Kadhim AA, Yao K-L (2018) Electronic and magnetic properties of the (001) surface of the CoNbMnSi Heusler alloy: First-principles calculations. J Electron Spectrosc Relat Phenom 226:17–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elspec.2018.04.005
Rajendran M, Pullar RC, Bhattacharya AK, Das D, Chintalapudi SN, Majumdar CK (2001) J Magn Magn Mater 232:71
Safi R, Ghasemi A, Shoja-Razavi R, Ghasemi E, Sodaee T (2016) Rietveld structure refinement, cations distribution and magnetic features of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation, hydrothermal, and combustion methods. Ceram Int 42:6375–6382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.01.032
Nagasa BD, Raghavender AT, Kabeta KL, Anjaneyulu T, Regasa MB (2015) Size induced structural and magnetic properties of nanostructured cobalt ferrites synthesized by co-precipitation technique. Sci Technol Arts Res J 4(1):84–87
Yakubu A, Abbas Z, Ibrahim NA, Hashim M (2015) Effect of temperature on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared via co-precipitation method. Phys Sci Int J 8:1–8. https://doi.org/10.9734/PSIJ/2015/18787
Prabhakaran T, Mangalaraja R, Denardin JC (2018) Controlling the size and magnetic properties of nano CoFe2O4 by microwave assisted co-precipitation method. Mater Res Express 5:026102. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaa73f
Zhang Y, Yang Z, Yin D, Liu Y, Fei C, Xiong R, Shi J, Yan G (2010) J Magn Magn Mater 322:3470
Peng J, Hojamberdiev M, Xu Y, Cao B, Wang J, Wu H (2011) J Magn Magn Mater 323:133
Iqbal MJ, Siddiquah MR (2008) J Alloys Compd 453:513
Hankare PP, Sankpal UB, Patil RP, Mulla IS, Lokhande PD, Gajbhiye NS (2009) J Alloys Compd 485:798
Gul IH, Maqsood A (2008) J Alloys Compd 465:227
Zi Z, Sun Y, Zhu X, Yang Z, Dai J, Song W (2009) Synthesis and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 321:1251–1255
Maaz K, Mumtaz A, Hasanain SK, Ceylan A (2007) J Magn Magn Mater 308:289
Lu RE, Chang KG, Fu B, Shen YJ, Xu MW, Yang S, Song XP, Liub M, Yang YD (2014) Magnetic properties of different CoFe2O4 nanostructures: nanofibers versus nanoparticles. J Mater Chem C 2:8578–8584
Kumar Y, Sharma A, Shirage PM (2017) The effect of calcination temperature on the structural and magnetic properties of co-precipitated CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 716:171–183
Nithiyanantham S, Viviliya S, Anandhan S, Mahalakshmi S (2021) Synthesis and characterization of cobalt ferrite through co-precipitation technique. Open-Access J 10(1):1871–1876
Heydaryan K, Mohammadalizadeh M, Montazer AH, Kashi MA (2023) Reaction time-induced improvement in hyperthermia properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with different sizes. Mater Chem Phys 303:127773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2023.127773
Elmekawy A, Iashina E, Dubitskiy I, Sotnichuk S, Bozhev I, Napolskii K et al (2020) Magnetic properties and FORC analysis of iron nanowire arrays. Mater Today Commun 25:101609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101609
Sinuhaji P, Simbolon TR, Hamid M, Hutajulu DA, Sembiring T, Rianna M et al (2021) Influences of Co compositions in CoFe2O4 on microstructures, thermal, and magnetic properties. Case Stud Therm Eng 26:101040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2021.101040
Esmaeili A, Almasi Kashi M, Ramazani A, Montazer AH (2016) J Magn Magn Mater 397:64–72
Roberts AP, Heslop D, Zhao X, Pike CR (2014) Rev Geophys 52:557–602
Deshmukh V, Nagaswarupa H, Raghavendra N (2021) Development of Co-doped MnFe2O4 nanoparticles for electrochemical supercapacitors. Ceram Int 47:10268–10273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.07.191
Kashi MA, Heydaryan K (2023) A comparative study on characterization and hyperthermia properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized with different surfactants. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34:2255
Standley KJ (1972) Oxide magnetic materials. Clarendon Press, Oxford
More SS, Kadam RH, Kadam AB, Mane DR, Bichile GK (2010) Cent Eur J Chem 8(2):419
Byrne J, Coker V, Moise S, Wincott P, Vaughan D, Tuna F et al (2013) Controlled cobalt doping in biogenic magnetite nanoparticles. J R Soc Interface 10:20130134. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2013.0134
Safi R, Ghasemi A, Shoja-Razavi R, Tavousi M (2015) The role of pH on the particle size and magnetic consequence of cobalt ferrite”. J Magn Magn Mater 396:288–294
Kumar Y, Sharma A, Shirage PM (2019) Impact of different morphologies of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles for tuning of structural, optical and magnetic properties. J Alloys Compds 778:398–409
Rai AK, Thi TV, Gim J, Mathew V, Kim J (2014) Co1−xFe2+xO4 (x= 0.1, 0.2) anode materials for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Solid State Sci 36:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2014.07.002
Sharifi I, Shokrollahi H, Doroodmand MM, Safi R (2012) Magnetic and structural studies on CoFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation, normal micelles and reverse micelles methods. J Magn Magn Mater 324:1854–1861
Obaidat IM, Narayanaswamy V, Alaabed S, Sambasivam S, Muralee Gopi ChVV (2019) Principles of magnetic hyperthermia: a focus on using multifunctional hybrid magnetic nanoparticles. Magnetochemistry 5(67):1–40
Kumari S, Pradhan LK, Kumar L, Manglam MK, Kar M (2019) Effect of annealing temperature on morphology and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanofibers. Mater Res Express 6:1250a3. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab5fa1
Khanahmadzadeh S, Heydaryan K (2022) Synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles and investigation of magnetic hyperthermia properties at different concentrations. J Appl Res Chem 16:64–72
Dippong T, Cadar O, Levei EA, Leostean C, Tudoran LB (2017) Effect of annealing on the structure and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4: SiO2 nanocomposites. Ceram Int 43:9145–9152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.04.063
Ayyappan S, Mahadevan S, Chandramohan P, Srinivasan MP, Philip J, Raj B (2010) Influence of Co+2 ion concentration on the size, magnetic properties, and purity of CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 114:6334–6341
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ameer F. Shamkhi wrote the main manuscript text, and Hashim Jabbar reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for Publication
The corresponding author attests that this study has been approved by all the co-authors concerned.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
By submitting the manuscript, the authors understand that the material presented in this manuscript has not been published before, nor has it been submitted for publication in another journal.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shamkhi, A.F., Jabbar, H. Effect of Cobalt Ion Concentration and Thermal Annealing Temperature on Structural and Magnetic Properties of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Plasmonics (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-024-02279-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-024-02279-4