Abstract
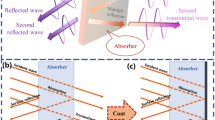
This paper presents the design and analysis of a metamaterial-based wideband microwave absorber in the C- and X-band, comprised of lumped resistors, having thicknesses of the order of 0.05 λ mm. The structure was micro-machined on the FR-4 sheet in a periodically arranged array of 15 × 15 unit cells. These unit cells have a dimension of 12 × 12 mm each. The proposed absorber design presents excellent broadband absorption characteristics with relative bandwidth (RBW) of 85.05% covering a bandwidth of 8.02 GHz ranging from 5.42 to 13.44 GHz. The absorption mechanism has been explained with the help of characteristic impedance and surface current densities in the operating region. The designed absorber shows polarization angle independency and wide incidence angle stability for the incident microwaves. The results of the prototype are compared with the simulated results illustrating excellent compatibility with the simulation results. Absorber structure may find its potential use in camouflage applications during war times.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data and Code Availability
Data underlying the results presented in this paper are not publicly available at this time but may be obtained from the authors upon reasonable request.
References
Schurig D et al (2006) Metamaterial electromagnetic cloak at microwave frequencies. Science 314(5801):977–980
Hunt J et al (2014) Metamaterial microwave holographic imaging system. JOSA A 31(10):2109–2119
Zheng Q et al (2020) Dual-broadband highly efficient reflective multi-polarisation converter based on multi-order plasmon resonant metasurface. IET Microwaves Antennas Propag 14(9):967–972
Bilal RMH et al (2020) Tunable and multiple plasmon-induced transparency in a metasurface comprised of silver S-shaped resonator and rectangular strip. IEEE Photonics J 12(3):1–13
Ding C, Liu L, Luk K-M (2019) An optically transparent dual-polarized stacked patch antenna with metal-mesh films. IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett 18(10):1981–1985
Hu D et al (2017) Optically transparent broadband microwave absorption metamaterial by standing‐up closed‐ring resonators. Adv Opt Mater 6(13):1700109
Ling Y et al (2018) Polarization-controlled dynamically switchable plasmon-induced transparency in plasmonic metamaterial. Nanoscale 10(41):19517–19523
Zhang S et al (2008) Plasmon-induced transparency in metamaterials. Phys Rev Lett 101(4):047401
Badloe T, Mun J, Rho J (2017) Metasurfaces-based absorption and reflection control: perfect absorbers and reflectors. J Nanomater 2017:1–18
Begaud X et al (2018) Ultra-wideband and wide-angle microwave metamaterial absorber. Materials (Basel) 11(10):2045
Bilal RMH et al (2020) "Elliptical metallic rings-shaped fractal metamaterial absorber in the visible regime." Sci Rep 10(1):14035
Costa F, Monorchio A, Manara G (2010) Analysis and design of ultra thin electromagnetic absorbers comprising resistively loaded high impedance surfaces. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 58(5):1551–1558
Hakim ML et al (2021) Polarization insensitivity characterization of dual-band perfect metamaterial absorber for K band sensing applications. Sci Rep 11(1):17829
Hakim ML et al (2022) Quad-band polarization-insensitive square split-ring resonator (SSRR) with an inner Jerusalem cross metamaterial absorber for Ku- and K-band sensing applications. Sensors (Basel) 22(12):4489
Jain P et al (2020) Ultra-thin metamaterial perfect absorbers for single-/dual-/multi-band microwave applications. IET Microwaves Antennas Propag 14(5):390–396
Vafapour Z (2019) Polarization-independent perfect optical metamaterial absorber as a glucose sensor in food industry applications. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience 18(4):622–627
Zou H, Cheng Y (2019) Design of a six-band terahertz metamaterial absorber for temperature sensing application. Opt Mater 88:674–679
Geffrin J-M, Eyraud C, Litman A (2015) 3-D imaging of a microwave absorber sample from microwave scattered field measurements. IEEE Microwave Wirel Compon Lett 25(7):472–474
Landy NI et al (2009) Design, theory, and measurement of a polarization-insensitive absorber for terahertz imaging. Phys Rev Appl B 79(12):125104
Al-badri KSL (2019) Multi band metamaterials absorber for stealth applications. Law, State and Telecommunications Review 11(1):133–144
Cheng YZ et al (2017) Ultra-thin multi-band polarization-insensitive microwave metamaterial absorber based on multiple-order responses using a single resonator structure. Materials (Basel) 10(11):1241
Gao Z et al (2021) An optically transparent broadband metamaterial absorber for radar-infrared bi-stealth. Opt Mater 112:110793
Kang J et al (2023) Multispectral flexible ultrawideband metamaterial absorbers for radar stealth and visible light transparency. Opt Mater 135:113351
Sharma A et al (2020) In-band RCS reduction and isolation enhancement of a 24 GHz radar antenna using metamaterial absorber for sensing and automotive radar applications. IEEE Sens J 20(21):13086–13093
Garg P, Jain P (2023) A review of metamaterial absorbers and their application in sensors and radar cross-section reduction. Microw Opt Technol Lett 65(2):387–411
Ramachandran T et al (2022) Radar cross-section reduction using polarisation-dependent passive metamaterial for satellite communication. Chin J Phys 76:251–268
Sharma A, Panwar R, Khanna R (2019) Design and development of low radar cross section antenna using hybrid metamaterial absorber. Microw Opt Technol Lett 61(11):2491–2499
Mishra RK, Gupta RD, Datar S (2021) Metamaterial microwave absorber (MMA) for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding in X-band. Plasmonics 16(6):2061–2071
Wu L et al (2020) Mechanical metamaterials for full-band mechanical wave shielding. Appl Mater Today 20:100671
Yang Y et al (2022) Electromagnetic shielding using flexible embroidery metamaterial absorbers: design, analysis and experiments. Mater Des 222:111079
Dincer F et al (2014) Polarization angle independent perfect metamaterial absorbers for solar cell applications in the microwave, infrared, and visible regime. Prog Electromagn Res 144:93–101
Kim K, Lee S (2019) Detailed balance analysis of plasmonic metamaterial perovskite solar cells. Opt Express 27(16):A1241–A1260
Rufangura P, Sabah C (2015) Dual-band perfect metamaterial absorber for solar cell applications. Vacuum 120:68–74
Wang Y et al (2012) Metamaterial-plasmonic absorber structure for high efficiency amorphous silicon solar cells. Nano Lett 12(1):440–445
Hossain MM, Jia B, Gu M (2015) A metamaterial emitter for highly efficient radiative cooling. Adv Opt Mater 3(8):1047–1051
Shi C et al (2018) Metamaterial-based graphene thermal emitter. Nano Res 11:3567–3573
Ashyap AYI et al (2018) Metamaterial inspired fabric antenna for wearable applications. Int J RF Microw C E 29(3):21640
Erentok A, Ziolkowski RW (2008) Metamaterial-inspired efficient electrically small antennas. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 56(3):691–707
Hasan MM, MRI Faruque, MT Islam et al (2018) Dual band metamaterial antenna for LTE/bluetooth/WiMAX system. Sci Rep 8(1):1240
Islam M et al (2015) Compact metamaterial antenna for UWB applications. Electron Lett 51(16):1222–1224
Feng Y, Qiu T, Shen C (2007) Absorbing properties and structural design of microwave absorbers based on carbonyl iron and barium ferrite. J Magn Magn Mater 318(1–2):8–13
Mu Y et al (2022) Ferrite-based composites and morphology-controlled absorbers. Rare Met 41(9):2943–2970
Sim MS et al (2018) Multiband metamaterial microwave absorbers using split ring and multiwidth slot structure. Int J RF Microw C E 28(7):21473
Ghosh S et al (2015) An ultrawideband ultrathin metamaterial absorber based on circular split rings. IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett 14:1172–1175
Amiri M, Tofigh F, Shariati N, Lipman J, Abolhasan M (2020) Review on metamaterial perfect absorbers and their applications to IoT. IEEE Internet Things J 8(6):4105–4131
Viet DT et al (2014) Perfect absorber metamaterials: peak, multi-peak and broadband absorption. Opt Commun 322:209–213
de Araujo JBO et al (2020) An ultrathin and ultrawideband metamaterial absorber and an equivalent-circuit parameter retrieval method. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 68(5):3739–3746
Chikhi N et al (2020) Pyramidal metamaterial absorber for mode damping in microwave resonant structures. Sci Rep 10(1):19352
Sun H et al (2022) Broadband and high-efficiency microwave absorbers based on pyramid structure. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 14(46):52182–52192
Shukoor MA, Dey S, Koul SK (2022) Broadband polarization insensitive wide angular stable dual-split square ring circuit analog absorber for radar cross section and electromagnetic interference shielding applications. Int J RF Microwave Comput Aided Eng 32(5):e23085
Phan DT et al (2021) Lightweight, ultra‐wideband, and polarization‐insensitive metamaterial absorber using a multilayer dielectric structure for C‐and X‐band applications. Phys Status Solidi B 258(10):2100175
Bilal RMH et al (2021) Wideband microwave absorber comprising metallic split-ring resonators surrounded with e-shaped fractal metamaterial. IEEE Access 9:5670–5677
Zou J et al (2020) Broadband mid-infrared perfect absorber using fractal Gosper curve. J Phys D Appl Phys 53(10):105106
Zhang M et al (2020) Design of wideband absorber based on dual-resistor-loaded metallic strips. Int J Antennas Propag 2020:1238656
Zhao J et al (2019) Broadband microwave metamaterial absorber with lumped resistor loading. EPJ Appl Metamaterials 6:1
Zhao J, Cheng Y (2016) Ultrabroadband microwave metamaterial absorber based on electric SRR loaded with lumped resistors. J Electron Mater 45(10):5033–5039
Ranjan P et al (2020) Wide band polarization insensitive metamaterial absorber using lumped resistors. SN Applied Sci 2(6):1061
Shukoor MA, Dey S, Koul SK et al (2022) Broadband polarization insensitive wide angular stable dual‐split square ring circuit analog absorber for radar cross section and electromagnetic interference shielding applications. Int J RF Microw C E 32(5):23085
Yoo M, Lim S (2014) Polarization-independent and ultrawideband metamaterial absorber using a hexagonal artificial impedance surface and a resistor-capacitor layer. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 62(5):2652–2658
Nguyen TKT et al (2021) Simple design of a wideband and wide-angle insensitive metamaterial absorber using lumped resistors for X- and Ku-bands. IEEE Photonics J 13(3):1–10
Nguyen TT, Lim S (2018) Design of metamaterial absorber using eight-resistive-arm cell for simultaneous broadband and wide-incidence-angle absorption. Sci Rep 8(1):6633
Nguyen TT, Lim S (2018) Angle-and polarization-insensitive broadband metamaterial absorber using resistive fan-shaped resonators. Appl Phys Lett 112(2):021605
Kalraiya S, Chaudhary RK, Abdalla MA (2019) Design and analysis of polarization independent conformal wideband metamaterial absorber using resistor loaded sector shaped resonators. J Appl Phys 125(13):134904
Nguyen TQH et al (2020) Numerical study of a broadband metamaterial absorber using a single split circle ring and lumped resistors for X-band applications. AIP Adv 10(3):035326
Zhi Cheng Y et al (2012) Design, fabrication and measurement of a broadband polarization-insensitive metamaterial absorber based on lumped elements. J Appl Phys 111(4):044902
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan under grant No. 20-17107/NRPU/R&D/HEC/2021.We are highly indebted to Dr. Muhammad Saqlain who reviewed this article and gave valuable feedback.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Khalid Majeed, Shahab Ahmad Niazi and Muhammad Abuzar Baqir conceived idea and design of the presented work. Khalid Majeed and Shahab Ahmad Niazi put forward theory and worked out results. Muhammad Abuzar Baqir, Abdul Khaliq and Muharrem Karaaslan verified the analytical methods employed. Khalid Majeed concluded the results with support of Shahab Ahmad Niazi. Moreover, Muharrem Karaaslan and Olcay Altintas fabricated the absorber and performed experimental work. Khalid Majeed. Muhammad Abuzar Baqir, Muharrem Karaaslan, Abdul Khaliq and Olcay Altintas wrote the manuscript with support of Shahab Ahmad Niazi. All authors deliberated the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Majeed, K., Niazi, S.A., Altintas, O. et al. Polarization-Insensitive Ultra-wideband Metamaterial Absorber for C- and X-bands. Plasmonics (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02165-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02165-5