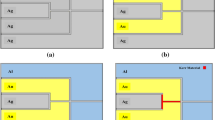
Abstract
All-optical logic gates OR, XOR, AND, and NOT based on two-dimensional (2D) plasmonic metal-insulator-metal (MIM) coupled with an elliptical ring resonator (ERR) are presented, simulated, and investigated by using the numerical method of the FEM (finite elements method). The results are compared and validated with the finite difference time domain (FDTD) method. The proposed logic gates are achieved with the same structure using the constructive and destructive optical interferences between a control signal and input signal(s). Their characterization was mainly done for two spectral regions, visible and near-infrared. A high-intensity contrast ratio (CR) between the logic states (“1” and “0”) can be achieved (28 dB) at these spectral regions. We introduce a new parameter, “gap-threshold ratio (GTR),” to characterize the gap between the maximum and minimum of the transmitted signal intensity for all logic gates. The suggested value of transmission threshold between logic “0” and logic “1” states is \(T_{th}=0.2\). A comparison of the two parameters, CR and GTR, with previous works shows that the proposed structure gives very good results for all logic gates configurations. The proposed all-optical logic gates configuration can be a key component in optical processing and telecommunication devices.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Beheshti N, Burmeister E, Ganjali Y (2010) Optical packet buffers for backbone internet routers. IEEE/ACM Trans Networking 18(5):1599–1609
Maier SA (2006) Plasmonics: the promise of highly integrated optical devices. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics In Quantum Electronics 12(6):1671–1677
Wang G, Lu H, Liu X, Mao D, Duan L (2011) Tunable multi-channel wavelength demultiplexer based on MIM plasmonic nanodisk resonators at telecommunication regime. OSA Publishing, Opt Express 19(4):3513
Zhu JH, Qi JW, Shum P, Guang Huang X (2011) A simple nanometeric plasmonic narrow-band filter structure based on metal-insulator-metal waveguide. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 10(6):1371–1376
Jonsson M (2003) Optical interconnection technology in switches, routers, and optical cross-connects. SPIE Optical Networks Magazine 4(4):20–34
Younis RM, Areed NFF, Obayya SSA (2014) Fully integrated AND and OR optical logic gates. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 26(19):1900–1903
Kirchain R, Kimerling L (2007) A roadmap for nanophotonics. Nat Photon 1:303–305
Shaik EH, Rangaswamy N (2015) Design of photonic crystal-based all-optical AND gate using T-shaped waveguide. J Mod Opt 63:941–949
Rani P, Kalra Y, Sinha RK (2013) Realization of AND gate in Y-shaped photonic crystal waveguide. Opt Commun 298–299:227–231
Pan D, Wei H, Xu HX (2013) Optical interferometric logic gates based on metal slot waveguide network realizing whole fundamental logic operations. Opt Express 21:9556–9562
Fu Y, Hu X, Lu C, Yue S, Yang H, Gong Q (2012) All-optical logic gates based on nanoscale plasmonic slot waveguides. Nano Lett 12(11):5784–5790
Chau YFC (2021) Multiple-mode bowtie cavities for refractive index and glucose sensors working in visible and near-infrared wavelength ranges. Plasmonics pp. 1557–1963
Ozbay E (2006) Plasmonics: merging photonics and electronics at nanoscale dimensions. Science 311:189–193
Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC (2008) Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater 7:442–453
Duan XF, Huang Y, Cui Y, Wang JF, Lieber CM (2001) Indium phosphide nanowires as building blocks for nanoscale electronic and optoelectronic devices. Nature 409:66–69
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424(6950):824–830
Fakhrulden FH, Mansour TS (2020) Design and simulation of plasmonic NOT gate based on insulator-metal-insulator (IMI) waveguides. Advanced Electromagnetics 9(1)
Bian Y, Gong Q (2014) Compact all-optical interferometric logic gates based on one-dimensional metal-insulator-metal structures. Opt Commun 313:27–35
Zafar R, Nawaz S, Salim M (2018) Fano resonance excited all-optical XOR, XNOR, and NOT gates with high contrast ratio. Plasmonics 13:1987–1994
Moradi M, Danaie M, Orouji AA (2019) Design of all-optical XOR and XNOR logic gates based on Fano resonance in plasmonic ring resonators. Opt Quant Electron 51(5):154
Dolatabady A, Granpayeh N (2012) All optical logic gates based on two dimensional plasmonic waveguides with nanodisk resonators. J Opt Soc Korea 16:432–442
Fakhrulden FH, Mansour TS (2018) All-optical NoT gate based on nanoring silver-air plasmonic waveguide. Int J Eng Technol 7:2818–2821
Dolatabady A, Granpayeh N (2017) All-optical logic gates in plasmonic metal-insulator-metal nanowaveguide with slot cavity resonator. J Nanophotonics 11(2):026001
Nagpal P, Lindquist NC, Oh SH, Norris DJ (2009) Ultrasmooth patterned metals for plasmonics and metamaterials. Science 325(5940):594–597
Vesseur EJR, Waele RD, Lezec HJ, Atwater HA, Garcia de Abajo FJ, Ploman A (2008) Surface plasmon polaritons modes in a single crystal Au nanoresonator fabricated using focused-ion-beam milling. Appl Phys Lett 92:083110-1-083110–3
Cai Y, Li Y, Nordlander P, Cremer PS (2012) Fabrication of elliptical nanorings with highly tunable and multiple plasmonic resonances. Nano Lett. 12:4881–4888
Yurkin MA (2013) Computational approaches for plasmonics, in Handbook of Molecular Plasmonics. ed. by F. Della Sala, S. D’Agostino. Pan Stanford Publishing, Singapore pp. 83–135
Panindre P, Kumar S (2016) Effect of rounding corners on optical resonances in single-mode sharp-cornered microresonators. Opt Lett 41:878–881
Tian M, Lu P, Chen L, Lv C, Liu DM (2011) A subwavelength MIM waveguide resonator with an outer portion smooth bend structure. Opt Commun 284(16–17):4078–4081
El Haffar R, Farkhsi A, Mahboub O (2020) Optical properties of MIM plasmonic waveguide with an elliptical cavity resonator. Appl Phys A 126:486
Veronis G, Fan SH (2005) Bends and splitters in metal-dielectric-metal subwavelength plasmonic waveguides. Appl Phys Lett 87(13):131102
Shibayama J, Kawai H, Yamauchi J, Nakano H, Shibayama J (2019) Analysis of a 3D MIM waveguide-based plasmonic demultiplexer using the TRC-FDTD method. Opt Commun 452:360–365
Han Z, He S (2007) Two-dimensional model for three-dimensional index-guided multimode plasmonic waveguides and the design of ultrasmall multimode interference split. Appl Opt 46(25)
Xiaoyu Y, Ertian H, Mengmeng W, Yifei W, Feng W, Shubin Y (2019) Fano resonance in a MIM waveguide with two triangle stubs coupled with a split-ring nanocavity for sensing application. Sensors 19(22):4972
Mahboub O, El Haffar R, Farkhsi A (2018) Optical fano resonance in MIM waveguides with a double splits ring resonator. Int J Microgr Opt Technol 13:181–187
Chen Z, Yu Y, Wang Y, Guo N, Xiao L (2020) Compact plasmonic structure induced mode excitation and Fano resonance. Plasmonics 15:2177–2183
Gao L, Lemarchand F, Lequime M (2013) Refractive index determination of SiO2 layer in the UV/Vis/NIR range: spectrophotometric reverse engineering on single and bi-layer designs. J Eur Opt Soc Rapid Publications 8:13010
Su H, Yan S, Yang X, Guo J, Wang J, Hua E (2020) Sensing features of the Fano resonance in an MIM waveguide coupled with an elliptical ring resonant cavity. Appl Sci 10:5096
Parsons J, Burrows CP, Sambles JR, Barnes WL (2010) A comparison of techniques used to simulate the scattering of electromagnetic radiation by metallic nanostructures. J Mod Opt 57(5):356–365
Abudlnabi SH, Abbas MN (2019) All-optical logic gates based on nanoring insulator-metal-insulator plasmonic waveguides at optical communications band. J Nanophotonics Opt 13:016009
Subhalakshmi G, Robinson S (2018) Design and analysis of optical logic gate using two dimension photonic crystal. IEEE International Conference on Current Trends toward Converging Technologies, Coimbatore, India
Acknowledgements
The authors would especially like to thank Pr. Youssef El Hafidi for the useful discussion
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Rida El Haffar and Oussama Mahboub conceived of the presented idea. Rida El Haffar performed the computations. Mustapha Figuigue performed the comparaison with other works. Oussama Mahboub verified the analytical methods, defined the characterization concept and supervised the findings of this work. Abdelkrim Farkhsi encouraged Rida El Haffar to investigate other logic gates configurations. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not Applicable.
Consent to Participate
All authors gave their consent to participate.
Consent for Publication
All authors gave their consent for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Haffar, R., Mahboub, O., Farkhsi, A. et al. All-Optical Logic Gates Using a Plasmonic MIM Waveguide and Elliptical Ring Resonator. Plasmonics 17, 831–842 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-021-01567-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-021-01567-7