Abstract
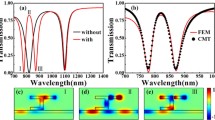
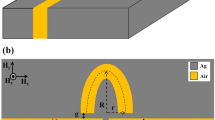
Metal–insulator–metal waveguide structure, which has a fascinating feature to confine the signal far beyond the diffraction light is numerically investigated by the finite difference time domain and the finite element methods. In this study, the MIM waveguide is both coupled with a half-elliptical groove (HEG) and an elliptical cavity resonator (ECR), and it can support the propagation of light in the nanoscale regime at the visible and near-infrared ranges. The interaction between these last elements gives rise to Fano resonance modes. Thanks to its interesting characteristics, a high sensitivity value, a factor of merit and interesting value of the group index are obtained for the proposed structure. We show that the transmission of the Fano system and the group index can reach 90% and a value of 63, respectively. We also report an investigation of the influence of the both geometrical HEG and ECR’s parameters on optical properties. Hence, the proposed structure could find a potential for applications in the integrated optical circuits such as optical storage, ultrafast plasmonic switchers, high performance filters and slow light devices.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.L. Barnes, A. Dereux, T.W. Ebbesen, Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424(6950), 824–830 (2003)
U. Fano, Effects of configuration interaction on intensities and phase shifts. Phys. Rev. 124, 1866–1878 (1961)
S. Liu, Z. Yang, R. Liu, X. Li, High sensitivity localized surface plasmon resonance sensing using a double split nanoring cavity. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(50), 24469–24477 (2011)
J.R. Lombardi, R.L. Birke, A unified view of surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Acc. Chem. Res. 42(6), 734–742 (2009)
W.S. Chang, J.B. Lassiter, P. Swanglap, H. Sobhani, S. Khatua, P. Nordlander, N.J. Halas, S. Link, A plasmonic Fano switch. Nano Lett. 12(9), 4977–4982 (2012)
N. Nordlander, J. Halas, S. Link, A plasmonic Fano switch. NanoLetter 12(9), 4977–4982 (2012)
Y. Zhang, X. Zhang, Y. Wang, R. Zhu, Reversible Fano resonance by transition from fast light to slow light in a coupled resonator-induced transparency structure. Opt. Express 21(7), 8570 (2013)
C. Wu, A.B. Khanikaev, G. Shvets, Broadband slow light metamaterial based on a double-continuum Fano resonance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106(10), 107403 (2011)
S. Zhan et al., Tunable nanoplasmonic sensor based on the asymmetric degree of Fano resonance in MDM waveguide. Nature. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22428
F. Chen, Nanosensing and slow light application based on Fano resonance in waveguide coupled equilateral triangle resonator system. Optik 171, 58–64 (2018)
X. Yi et al., Tunable Fano resonance in MDM stub waveguide coupled with a U-shaped cavity. Eur. Phys. J. D (2018). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2018-80734-6
Y. Wang et al., Ultrasharp Fano resonances based on the circular cavity optimized by a metallic nanodisk. IEEE Photonics J 8, 4502608 (2016)
B. Yun et al., Fano resonances in a plasmonic waveguide system composed of stub coupled with a square cavity resonator. J. Opt. 18, 055002 (2016)
P. Nagpal, N.C. Lindquist, S.-H. Oh, D.J. Norris, Ultrasmooth patterned metals for plasmonics and metamaterials. Science 325(5940), 594–597 (2009)
E.J.R. Vesseur, R. De Waele, H.J. Lezec, H.A. Atwater, F.J. Garcia de Abajo, A. Ploman, Surface plasmon polaritons modes in a single crystal Au nanoresonator fabricated using focused-ion-beam milling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 083110-1–083110-3 (2008)
Y. Cai, Y. Li, P. Nordlander, P.S. Cremer, Fabrication of elliptical nanorings with highly tunable and multiple plasmonic resonances. Nano Lett. 12, 4881–4888 (2012)
M.A. Yurkin, Computational approaches for plasmonics, in Handbook of Molecular Plasmonics, ed. by F. Della Sala, S. D’Agostino (Pan Stanford Publishing, Singapore, 2013), pp. 83–135
P. Panindre, S. Kumar, Effect of rounding corners on optical resonances in single-mode sharp-cornered microresonators. Opt. Lett. 41, 878–881 (2016)
M. Tian, P. Lu, L. Chen, C. Lv, D.M. Liu, A subwavelength MIM waveguide resonator with an outer portion smooth bend structure. Opt. Commun. 284(16–17), 4078–4081 (2011)
J. Shibayama, H. Kawai, J. Yamauchi, H. Nakano, O. Communications, J. Shibayama, H. Kawai, J. Yamauchi, H. Nakano, Analysis of a 3D MIM waveguide-based plasmonic demultiplexer using the TRC-FDTD method. Opt. Commun. 452, 360–365 (2019)
Z. Han, S. He, Two-dimensional model for three-dimensional index-guided multimode plasmonic waveguides and the design of ultrasmall multimode interference splitters. Appl. Opt. 46(25), 6223–6227 (2007)
X. Yang, E. Hua, M. Wang, Y. Wang, F. Wen, S. Yan, Fano resonance in a MIM waveguide with two triangle stubs coupled with a split-ring nanocavity for sensing application. Sensors 19(22), 4972 (2019)
O. Mahboub, R. El Haffar, A. Farkhsi, Optical Fano resonance in MIM waveguides with a double splits ring resonator. Int. J. Microw. Opt. Technol. (IJMOT) 13, 181–187 (2018)
Z.H. Han, S.I. Bozhevolnyi, Plasmon-induced transparency with detuned ultracompact Fabry Perot resonators in integrated plasmonic devices. Opt. Express 19(4), 3251–3257 (2006)
F.F. Hu, H.X. Yi, Z.P. Zhou, Band-pass plasmonic slot filter with band selection and spectrally splitting capabilities. Opt. Express 19, 4848–4855 (2011)
C. Min, G. Veronis, Absorption switches in metal-dielectric-metal plasmonic waveguides. Opt. Express 17, 10757–10766 (2009)
J. Parsons, C.P. Burrows, J.R. Sambles, W.L. Barnes, A comparison of techniques used to simulate the scattering of electromagnetic radiation by metallic nanostructures. J. Mod. Opt. 57(5), 356–365 (2010)
K.H. Wen, Y.H. Hu, L. Chen, J.Y. Zhou, L. Lei, Z. Guo, Fano resonance with ultra-high figure of merits based on plasmonic metal–insulator–metal waveguide. Plasmonics 10, 27–32 (2015)
L. Hua, X. Liu, D. Mao, G. Wang, Plasmonic nanosensor based on Fano resonance in waveguide-coupled resonators. Opt. Lett. 37(18), 3780–3782 (2012)
Z. Chen, L. Yu, L.L. Wang, G.Y. Duan, Y.F. Zhao, J.H. Xiao, A refractive index nanosensor based on Fano resonance in theplasmonic waveguide system. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 27, 1695–1698 (2015)
C. Ríos, M. Stegmaier, P. Hosseini, D. Wang, T. Scherer, C.D. Wright, H. Bhaskaran, W.H.P. Pernice, Integrated all-photonic non-volatile multi-level memory. Nat. Photonics 9(11), 725 (2015)
Y. Huang, C.J. Min, G. Veronis, Subwavelength slow-light waveguide based on a plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 143117 (2011)
A. Noual, M. Amrani, E. El Boudouti, Y. Pennec, B. Djafari-Rouhani, Terahertz plasmon-induced transparency and absorption in compact graphene-based coupled nanoribbons. Appl. Phys. A (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2474-3
W. Boyd, Slow and fast light: fundamentals and applications. J. Mod. Opt. 56, 1908 (2009)
T. Baba, T. Kawasaki, H. Sasaki, J. Adachi, D. Mori, Large delay-bandwidth product and tuning of slow light pulse in photonic crystal coupled waveguide. Opt. Express 16(12), 9245–9253 (2008)
D.M. Beggs, T.P. White, L. O’Faolain, T.F. Krauss, Ultracompact and low-power optical switch based on silicon photonic crystals. Opt. Lett. 33(2), 147–149 (2008)
C. Monat, B. Corcoran et al., Slow light enhancement of nonlinear effects in silicon engineered photonic crystal waveguides. Opt. Express 17(4), 2944–2953 (2009)
H. Lu, X.M. Liu, D. Mao, Plasmonic analog of electromagnetically induced transparency in multinanoresonator-coupled waveguide systems. Phys. Rev. A 85, 053803 (2012)
Q. Wang, H. Meng, B. Huang, H. Wang, X. Zhang, W. Yu, C. Tan, X. Huang, S. Li, Dual coupled-resonator system for plasmoninduced transparency and slow light effect. Opt. Commun. 380, 95–100 (2016)
K. Totsuka, N. Kobayashi, M. Tomita, Slow light in coupled-resonator-induced transparency. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 213904–213904 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The authors would especially like to thank Pr. Mustapha Figuigue and Pr. Youssef El Hafidi for the useful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Haffar, R., Farkhsi, A. & Mahboub, O. Optical properties of MIM plasmonic waveguide with an elliptical cavity resonator. Appl. Phys. A 126, 486 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03660-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03660-w