Abstract
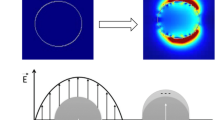
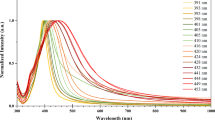
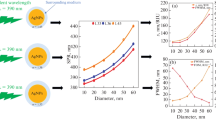
Silver nanoparticle (AgNP) has wide-spread applications in photovoltaic cell, biological sensors, biomedical devices, surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) etc. which are intricately dependent on AgNP shape, size, concentration and aggregation states. Here, the particle size, shape and aggregation dependent dipole and quadrupole surface plasmon resonances are spectroscopically investigated by preparing AgNPs (diameter 10–110nm) using silver nitrate (AgNO3) and sodium borohydride (NaBH4 as reducing agent) in aqueous environment at 0 ∘C. The AgNP UV-Visible spectra showing plasmon-induced dipole and quadrupole modes are corroborated by the theoretical framework of Mie-Gans model and discrete dipole scattering model DDSCAT and different particle sizes, shapes and possible aggregation or clusterization are predicted. All the samples show presence of spherical and nonspherical distribution of AgNP. However, the concentration of nonspherical particle is more for higher concentration of reducing agent as is evidenced by the appearance of quadrapole absorption maxima. The minimum particle size is found at a particular ratio of concentration of AgNO3 and NaBH4. The day variation of AgNP kinetics also signalled the onset of quadrupole deformation of clusters.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pinchuk A, Kreibig U (2003) Interface decay channel of particle surface plasmon resonance. New J Phys 5:151
Dahmen C, Schmidt B, von Plessen G (2007) Radiation Damping in Metal Nanoparticle Pairs. Nano Lett 7:318
Pinchuk A, Kreibig U, Hilger A (2004) Optical properties of metallic nanoparticles: influence of interface effects and interband transitions. Surf Sci 557:269
Mie G (1908) Beitrge zur Optik trber Medien, speziell kolloidaler Metallsungen. Ann Phys 25:329
Yeshchenko O A, Dmitruk I M, Alexeenko A, Yu A, Losytskyy M, Kotko A V, Pinchuk A (2009) Size-dependent surface-plasmon-enhanced photoluminescence from silver nanoparticles embedded in silica. Phys Rev B 79:235438
Oprsal J, Pouzar M, Knotek P, Slouf M, Pavlova E (2012) A study of silver nanoparticle behavior in liquid media for ecotoxicity tests. Nanocon 2012, Czech Republic
Xia Y, Halas N J (2005) Shape controlled synthesis and surface plasmonic properties of metallic nanostructures. MRS Bull 30:338–348
Jain P K, Huang X, El-Sayed I H, El-Sayed M A (2007) Noble metals on the nanoscale: optical and photothermal properties and some applications in imaging, sen sing, biology, and medicine. Plasmonics 2:107–118
Yong K T, Swihart M T, Ding H, Prasad P N (2009) Multifunctional nanoparticles as biocompatible targeted probes for human cancer diagnosis and therapy. Plasmonics 4:79–93
Ren J, Tilley R D (2007) Preparation, self-assembly, and mechanistic study of highly monodispersed nanocubes. J Am Chem Soc 129:3287–3291
Moskovits M (1985) Surface-enhanced spectroscopy. Rev Mod Phys 57:783–826
Astruc D, Lu F, Aranzaes JR, Angew J (2005) Nanoparticles as Recyclable Catalysts: The Frontier between Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis. Chem Int Ed 44:7852–7872
Riveros G, Green A, Cortes H, Gomez R, Marotti E, Dalchiele E A (2006) Size-Controlled and Optical Properties of Monodispersed Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by the Radiolytic Reduction Method. Nanotech 17:561–570
Dhar S, Reddy E M, Shiras A, Pokharkar V, Prasad B L V (2008) Natural gum reduced/stabilized gold nanoparticles for drug delivery formulations. Chem Eur J 14(2008):10244–10250
Sanpui P, Chattopadhyay A, Ghosh S S (2011) Induction of apoptosis in cancer cells at low silver nanoparticle concentrations using chitosan nanocarrier. ACS Appl Mater Int 3:218–228
Link S, El-Sayed M A (2000) Shape and size dependence of radiative, non-radiative and photothermal properties of gold nanocrystals. Int Rev Phys Chem 19(3):409
Drain B (1988) The Discrete-Dipole Approximation and its Application to Interstellar Graphite Grains. Astrophys J 333:848–872
He R, Qian X, Yin J, Zikang Z (2002) Preparation of polychrome silver nanoparticles in different solvents. J Mat Chem 12:3783–86
Raza S, Kadkhodazadeh S, Christensen T, Vece M D, Wubs M, Mortensen N, Stenger N (2015) Multipole plasmons and their disappearance in few-nanometre silver nanoparticles. Nat Comm 6:08788
Amendola V, Bakr O, Stelacci F (2010) A Study of the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Silver Nanoparticles by the Discrete Dipole Approximation Method: Effect of Shape, Size, Structure, and Assembly. Plasmonics 5:85–97
Amendola V, Polizzi S, Meneghetti M (2006) Laser ablation synthesis of gold nanoparticles in organic solvents. J Phys Chem B 110:7232–7237
Sherry L F, Jin R, Chad A, Schatz G C, Duyne R P V. (2006) Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy of single silver triangular nanoprisms. Nano Lett 6:2060
Kreibig U, Vollmer M (1995) Optical properties of metal clusters. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–134
Gans R (1915) ber die Form ultramikroskopischer Silberteilchen. Annlen Phys 47:270
Drain B T, Flatau P J (2013) User guide for the discrete dipole approximation code DDSCAT 7.3. arXiv:1305.6497 (26th May, 2013)
Palik E (1998) Handbook of optical constants of solids, 1st edn. Academic Press, Cambridge
Funding
The authors gracefully acknowledge the financial support from Department of Science and Technology (India) to procure the UV-Visible spectrophotometer under the FIST scheme at the Dept. of Physics, Barasat Government College.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, M.M., Mandal, S. & Bhattacharya, S. Investigation of the Growth Kinetics and Multipolar Plasmonic Properties of Silver Nanoparticle Cluster by Experiment and Numerical Simulations. Plasmonics 13, 1803–1810 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-018-0694-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-018-0694-6