Abstract
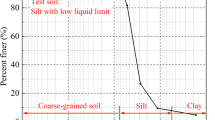
Since there is an interval time between two trains traveling in the same direction on an automatically blocked line, the dynamic loading on the railway subgrade is composed of periodic vibration when the train passes and an intermittent stage after a train has passed. Take into account this characteristic, a series of continuous-stopping repeated load triaxial tests were conducted to study deformation characteristics such as plastic strain and elastic strain of fine-grained soil under intermittent loading. Compared to continuous loading, it is found that the intermittent stage has a significant effect on the deformation characteristics of subgrade. The excess pore water pressure accumulated during the loading stage dissipated during the intermittent stage. The development of plastic strain in subsequent loading stages slowed down significantly, and the axial strain of the sample rebounded in the intermittent stage, so cumulative plastic strain was reduced. The intermittent effect on reducing elastic strain was, however, limited. An increase in intermittent time can also improve the resistance of the sample to subsequent cyclic loading. An alternating continuous-stopping loading mode can better simulate intermittent loading of trains in actual train operation and produce more practical results, providing a theoretical basis and guidance for further understanding of deformation characteristics of railway subgrade.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ρ s :
-
Particle density
- ρ dmax :
-
Maximum dry density
- w opt :
-
Optimum moisture content
- w sat :
-
Saturated moisture content
- k 20 :
-
Permeability coefficient
- w L :
-
Liquid limit
- w p :
-
Plastic limit
- I p10 :
-
Plastic index
- K :
-
Compaction coefficient
- σ 3 :
-
Confining pressure
- σ s :
-
Static deviatoric stress
- σ d :
-
Dynamic stress amplitude
- ε p :
-
Accumulated plastic strain
- ε e :
-
Resilient strain
- t :
-
Loading time
- N :
-
Number of cycles
References
Brown SF, Lashine AKF, Hyde AFL (1975) Repeated load triaxial testing of silty clay. Géotechnique 25(1):95–114
Cai Y, Guo L, Jardine RJ, Yang Z, Wang J (2016) Stress–strain response of soft clay to traffic loading. Géotechnique 67:446–451
Cerni G, Cardone F, Virgili A, Camilli S (2012) Characterisation of permanent deformation behaviour of unbound granular materials under repeated triaxial loading. Constr Build Mater 28(1):79–87
Chai JC, Miura N (2002) Traffic-load-induced permanent deformation of road on soft subsoil. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 128(11):907–916
Ding JY, Wang CL, Du YG, Li B (2017) Influence of staged cyclic loading on dynamic behavior of saturated soft clay under drained condition. World Earthq Eng 33(2):161–168
Duong TV, Cui YJ, Tang AM, Dupla JC, Canou J, Calon N, Robinet A (2016) Effects of water and fines contents on the resilient modulus of the interlayer soil of railway substructure. Acta Geotech 11(1):51–59
Erlingsson S, Magnusdottir B.(2002) Dynamic triaxial testing of unbound granular base course materials. In: Proceedings of the 6th international conference on the bearing capacity of roads and airfields, Lisbon, Portugal, pp 24–26
Gidel G, Hornych P, Chauvin J, Breysse D, Denis A (2001) A new approach for investigating the permanent deformation behaviour of unbound granular material using the repeated loading triaxial apparatus. Bulletin des laboratoires des Ponts et Chaussées 233:5–21
Gu F, Zhang Y, Luo X, Sahin H, Lytton RL (2017) Characterization and prediction of permanent deformation properties of unbound granular materials for Pavement ME Design. Constr Build Mater 155:584–592
Hou XL, Zhou JH, Zhao XB, Li XZ (2011) Research on unloading rebound deformation of muddy silty clay at Hexi district in Nanjing city. J Disaster Prev Mitig Eng 31(04):397–402
Leng WM, Zhou WQ, Nie RS, Zhao CY, Liu WJ, Yang Q (2016) Analysis of dynamic characteristics and accumulative deformation of coarse-grained soil filling of heavy-haul railway. Rock Soil Mech 37(3):728–736
Leng WM, Xiao YJ, Nie RS, Zhou WQ, Liu WJ (2017) Investigating strength and deformation characteristics of heavy-haul railway embankment materials using large-scale undrained cyclic triaxial tests. Int J Geomech 17(9):04017074
Li ZC (2000) Study on the vertical load transmision through the track structure and the characteristics of subgrade dynamic strsses. China Academy of Railway Sciences, Beijing
Li DQ, Selig ET (1994) Resilient modulus for fine-grained subgrade soils. J Geotech Eng 120(6):939–957
Li C, Zheng JX, Zhang Z, Sha A, Li J (2020) Morphology-based indices and recommended sampling sizes for using image-based methods to quantify degradations of compacted aggregate materials. Constr Build Mater 230:116970
Liu TJ, Ge XR, An GF (2012) Study of characteristics of saturated soft clay under uniaxial cyclic load. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 31(S1):3345–3351
Mei HH, Leng WM, Liu WJ, Nie RS, Xu XD (2017) Experimental study on accumulated plastic strain of coarse grained soil filling in subgrade bed under persistent dynamic loading. J China Railw Soc 39(2):119–126
Mei HH, Leng WM, Nie RS, Liu WJ, Chen C, Wu XW (2019) Random distribution characteristics of peak dynamic stress on the subgrade surface of heavy-haul railways considering track irregularities. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 116:205–214
Mei HH, Leng WM, Nie RS (2019) Experimental research on the dynamic response characteristics of transition subgrade induced by heavy-haul train passage. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part F J Rail Rapid Transit 233(9):974–987
Ni J, Indraratna B, Geng XY, Rujikiatkamjorn C (2012) The effect of the strain rate on soft soil behaviour under cyclic loading. In: 11th Australia-New Zealand conference on geomechanics: ground engineering in a changing world, pp 1340–1345
Pumphrey ND, Lentz RW (1986) Deformation analyses of Florida highway subgrade sand subjected to repeated load triaxial tests. Transport Res Rec 1089:49–56
Rahim AM (2005) Subgrade soil index properties to estimate resilient modulus for pavement design. Int J Pavement Eng 6(3):163–169
Rahman MS, Erlingsson S (2015) Predicting permanent deformation behaviour of unbound granular materials. Int J Pavement Eng 16(7):587–601
Salour F, Erlingsson S (2017) Permanent deformation characteristics of silty sand subgrades from multistage RLT tests. Int J Pavement Eng 18(3):236–246
Seed HB, Chan CK, Lee CE (1962) Resilience characteristics of subgrade soils and their relation to fatigue failures in asphalt pavements. In: Proceedings of the international conference on the structural design of asphalt pavements, Ann Arbor, Michigan, pp 61l–636
He SH, Zheng QQ, Xia TD, Gan XL, Shan HF (2019) Experimental on long-term dynamic characteristics of marine soft soil under metro train load considering time intermittent effect. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 38:353–364
Tang L, Yan MH, Ling XZ, Tian S (2016) Dynamic behaviours of railway’s base course materials subjected to long-term low-level cyclic loading: experimental study and empirical model. Géotechnique 67(6):537–545
Tao M, Mohammad LN, Nazzal MD, Zhang Z, Wu Z (2010) Application of shakedown theory in characterizing traditional and recycled pavement base materials. J Transp Eng 136(3):214–222
The First Survey & Design Institute of China (2016) Railway Code for design on subgrade of railway. China Railway Publishing House, Beijing
Wang SY, Lu XB, Zhao J, Wang AL (2009) Post-cyclic loading undrained strength degradation characteristics of silty clay. Rock Soil Mech 30(10):2991–2995
Wang J, Cai YQ, Lin G, Fang Y (2012) Pore pressure and strain development of Wenzhou saturated soft soil under cyclic loading by stages. Chin J Geotech Eng 34(7):1349–1354
Werkmeister S, Dawson AR, Wellner F (2001) Permanent deformation behavior of granular materials and the shakedown concept. Trans Res Rec 1757(1):75–81
Werkmeister S, Dawson AR, Wellner F (2004) Pavement design model for unbound granular materials. J Transp Eng 130(5):665–674
Yang SR, Huang WH, Liao CC (2008) Correlation between resistant modulus and plactic deformation for cohesive subgrade soil under repeated loading. Transp Res Rec 2053:72–79
Yıldırım H, Erşan H (2007) Settlements under consecutive series of cyclic loading. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 27(6):577–585
Acknowledgements
The authors’ research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51878666, 51678572) and the Innovation Project of Central South University (Grant No. 2018zzts192).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, R., Li, Y., Leng, W. et al. Deformation characteristics of fine-grained soil under cyclic loading with intermittence. Acta Geotech. 15, 3041–3054 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-020-00955-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-020-00955-3