Abstract
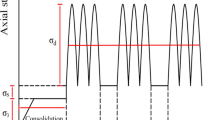
The long-term loading of the trains on the subgrade in service is the cyclic loading when the train passes and the intermittent stage when there is no train passing. However, in most studies, continuous loading was used to investigate the dynamic characteristics of a subgrade soil, which ignores the effect of loading intermittence. The aims of this research were first to study the cumulative permanent deformation behaviors under intermittent cyclic loading of trains, then to establish the classification criterion for cumulative permanent strain behaviors, and finally to propose a practical method for estimating the critical dynamic stress in the intermittent loading mode. For this purpose, according to the actual conditions of the subgrade of Shuo-Huang Heavy-Haul Railway, the monotonic triaxial test and the cyclic triaxial test with intermittent loading were performed. Based on the shakedown theory, the cumulative permanent strain behaviors under intermittent loading can be classified into three categories of plastic shakedown, plastic creep, and incremental collapse. Then, the classification criterion was established based on the permanent strain rate. Finally, an empirical formula of critical dynamic stress for intermittent loading, which could also consider the varying moisture content, was proposed.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ρs :
-
particle density
- ρdmax :
-
maximum dry density
- w opt :
-
optimum moisture content
- w int :
-
intermediate moisture content
- w sat :
-
saturated moisture content
- k :
-
permeability coefficient
- w L :
-
liquid limit
- w p :
-
plastic limit
- Ip :
-
plastic index
- K :
-
compaction coefficient
- σ3 :
-
confining pressure
- σs :
-
static deviating stress
- σd :
-
dynamic stress amplitude
- εp :
-
cumulative permanent strain
- εe :
-
resilient strain
- σ1max :
-
maximum axial stress
- q f :
-
undrained shear strength
- t :
-
loading time
- N :
-
number of loading cycles
References
Brown SF, Lashine AKF, Hyde AFL (1975) Repeated load triaxial testing of a silty clay. Géotechnique 25(1):95–114
Cerni G, Cardone F, Virgili A, Camilli S (2012) Characterisation of permanent deformation behaviour of unbound granular materials under repeated triaxial loading. Constr Build Mater 28(1):79–87
Chen C, Zhou ZM, Kong LW, Zhang XW, Yin S (2018) Undrained dynamic behaviour of peaty organic soil under long-term cyclic loading, Part I: experimental investigation. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 107:279–291
Dawson AR, Wellner F (1999) Plastic behavior of granular materials. Final Report ARC Project 933, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Nottingham
Ding JY, Wang CL, Du YG, Li B (2017) Influence of staged cyclic loading on dynamic behavior of saturated soft clay under drained condition. World Earthq Eng 33(2):161–168
Gu F, Zhang Y, Luo X, Sahin H, Lytton RL (2017) Characterization and prediction of permanent deformation properties of unbound granular materials for Pavement ME Design. Constr Build Mater 155:584–592
He S, Zheng Q, Xia T, Gan X, Shan H (2019) Experimental on long-term dynamic characteristics of marine soft soil under metro train loading considering time intermittent effect. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 38:353–364
Huang B, Ding H, Chen YM (2011) Simulation of high-speed train load by dynamic triaxial tests. Chin J Geotech Eng 33(2):195–202
Kolisoja P (1998) Large scale dynamic triaxial tests III. Ph.D. thesis, Tampere University of Technology
Leng WM, Zhou WQ, Nie RS, Zhao CY, Liu WJ, Yang Q (2016) Analysis of dynamic characteristics and cumulative deformation of coarse-grained soil filling of heavy-haul railway. Rock Soil Mech 37(3):728–736
Leng WM, Xiao YJ, Nie RS, Zhou WQ, Liu WJ (2017) Investigating strength and deformation characteristics of heavy-haul railway embankment materials using large-scale undrained cyclic triaxial tests. Int J Geomech 17(9):04017074
Li ZC (2000) Study on the vertical load transmission through the track structure and the characteristics of subgrade dynamic stresses. China academy of railway sciences, Beijing
Li DQ, Selig ET (1994) Resilient modulus for fine-grained subgrade soils. J Geotech Eng 120(6):939–957
Liu TJ, Ge XR, An GF (2012) Study of characteristics of saturated soft clay under uniaxial cyclic load. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 31(S1):3345–3351
Lo Presti DCF, Cavallaro A, Maugeri M, Pallara O (1999) Non-linear stress-strain modelling of geomaterials under stable and unstable cyclic loading. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering, Lisbon, pp 29–34
Mamou A, Powrie W, Priest JA, Clayton C (2017) The effects of drainage on the behaviour of railway track foundation materials during cyclic loading. Géotechnique 67(10):845–854
Mei HH, Leng WM, Nie RS, Liu WJ, Chen C, Wu XW (2019) Random distribution characteristics of peak dynamic stress on the subgrade surface of heavy-haul railways considering track irregularities. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 116:205–214
Nazzal MD, Mohammad LN, Austin A (2011) Evaluation of the shakedown behavior of unbound granular base materials. In: Geo-Frontiers 2011: Advances in Geotechnical Engineering, Texas, United States, pp 4752-4761
Nie RS, Li YF, Leng WM, Mei HH, Dong JL, Chen XX (2020) Deformation characteristics of fine-grained soil under cyclic loading with intermittence. Acta Geotech 1-14
Pérez I, Medina L, Romana MG (2006) Permanent deformation models for a granular material used in road pavements. Constr Build Mater 20(9):790–800
Rahman MS, Erlingsson S (2015) Predicting permanent deformation behaviour of unbound granular materials. Int J Pavement Eng 16(7):587–601
Raymond GP, Gaskin PN, Addo-Abedi FY (1979) Repeated compressive loading of Leda clay. Can Geotech J 16(1):1–10
Sakai A, Samang L, Miura N (2003) Partially-drained cyclic behavior and its application to the settlement of a low embankment road on silty-clay. Soils Found 43(1):33–46
Sharp R (1983) Shakedown analyses and the design of pavement under moving surface load. Ph.D. thesis, University of Sydney
Tao M, Mohammad LN, Nazzal MD, Zhang Z, Wu Z (2010) Application of shakedown theory in characterizing traditional and recycled pavement base materials. J Transp Eng 136(3):214–222
The European Standard EN 13286-7-2004. (2004) Unbound and hydraulically bound mixtures-Part 7: Cyclic load triaxial test for unbound mixtures
The First Survey & Design Institute of China (2016) Railway Code for design on subgrade of railway. China Railway Publishing House, Beijing
Wang J, Cai YQ, Lin G, Fang Y (2012) Pore pressure and strain development of Wenzhou saturated soft soil under cyclic loading by stages. Chin J Geotech Eng 34(7):1349–1354
Wang JH, Ling XC, Li QL, Zhang F, Li Y (2018) Cumulative permanent strain and critical dynamic stress of frozen silty clay under cyclic loading. Cold Reg Sci Technol 153:130–143
Werkmeister S (2003) Permanent deformation behavior of unbound granular materials in pavement constructions. Ph.D. thesis, Dresden University of Technology
Xiao YJ, Zheng KY, Chen LX, Mao JF (2018) Shakedown analysis of cyclic plastic deformation characteristics of unbound granular materials under moving wheel loads. Constr Build Mater 167:457–472
Xie D (2011) Soil dynamics. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Xu F, Zhai B, Leng WM, Yang Q, Leng HK, Nie RS (2020) Probabilistic method for evaluating the permanent strain of unbound granular materials under cyclic traffic loading. Constr Build Mater 251:118975
Yıldırım H, Erşan H (2007) Settlements under consecutive series of cyclic loading. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 27(6):577–585
Zhai B, Leng WM, Xu F, Zhang QS, Ye XY, Leng HK (2020) Critical dynamic stress and shakedown limit criterion of coarse-grained subgrade soil. Transplant Geotech 23:100354
Acknowledgements
The authors’ research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51878666, 51978672) and the Innovation Project of Central South University (Grant No. 2018zzts192).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Nie, R., Leng, W. et al. Cumulative permanent strain and critical dynamic stress of silty filler for subgrade subjected to intermittent cyclic loading of trains. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80, 3079–3096 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02125-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02125-5