Abstract
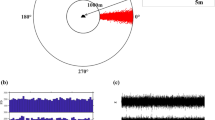
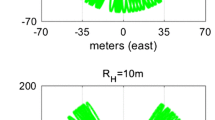
By making use of multiple acquisitions of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) observations over the same area, tomographic-SAR (tomo-SAR) technology can achieve three-dimensional (3-D) imaging of the objects of interest. The compressive sensing (CS) approach has been applied to deal with the sparseness of the elevation signals. Due to its sparsity and convexity, the L 1-norm regularization, as an approximated L 0-norm with an exact solution, has been employed in CS to reconstruct the reflectivity profile of the objects. In this paper, based on our studies on polarimetric scattering and SAR imaging simulations, we produce numerical multi-pass tomo-SAR observations of the terrain object. Then, we present the CS with novel L 1/2-norm regularization to realize 3-D reconstruction. As a non-convex optimization problem, the L 1/2-norm regularization is solved by an iterative algorithm. This numerical simulation of tomo-SAR imaging and 3-D reconstruction of the object modeling can be of great help for parameterized analysis of tomo-SAR imagery. As an example, a tomo-SAR image and 3-D reconstruction of the Beijing National Stadium model are presented.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Franceschetti G, Lanari R (1999) Synthetic aperture radar processing. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Reigber A, Moreira A (2000) First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote 38:2142–2152
Sauer S, Ferro-Famil L, Reigber A et al (2008) 3D urban remote sensing using dual-baseline POL-InSAR images at L-band. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Symp 4:IV-145
Zhu X, Bamler R (2010) Very high resolution spaceborne SAR tomography in urban environment. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote 48:4296–4308
Gini F, Lombardini F (2002) Multilook APES for multibaseline SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans Signal Process 50:1800–1803
Lombardini F, Gini F, Matteucci P et al (2001) Application of array processing techniques to multibaseline InSAR for layover solution. In: Proceeding of the radar conference 2001. IEEE, pp 210–215
Nannini M, Scheiber R, Moreira A (2009) Estimation of the minimum number of tracks for SAR tomography. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote 47:531–543
Candes EJ, Wakin MB, Boyd SP (2008) Enhancing sparsity by reweighted L1 minimization. J Fourier Anal Appl 14:877–905
Donoho DL (2006) Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans Inform Theory 52:1289–1306
Candès EJ, Romberg J, Tao T et al (2006) Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans Inform Theory 52:489–509
Xu Z, Zhang H (2010) L1/2 regularization. Sci China Inf Sci 53:1159–1169
Candès EJ (2006) Compressive sampling. In: Proceedings of the international congress of mathematicians, Madrid, Spain, August 22–30, 2006, pp 1433–1452
Chen SS, Donoho DL, Saunders MA (1998) Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM J Sci Comput 20:33–61
Candès EJ, Wakin MB (2008) An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process Mag 25:21–30
Boyd SP, Vandenberghe L (2004) Convex optimization. Cambridge university press, Cambridge
Manual, F.U.s., Suite 6.0. EM Software & Systems-SA (Pty) Ltd, 2010. p 32
Xu F, Jin YQ (2009) Bidirectional analytic ray tracing for fast computation of composite scattering from electric-large target over a randomly rough surface. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 57:1495–1505
Jin YQ, Xu F (2013) Polarimetric scattering and SAR information retrieval. Wiley, Hoboken
Munson DC Jr, O’Brien JD, Jenkins W (1983) A tomographic formulation of spotlight-mode synthetic aperture radar. Proc IEEE 71:917–925
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Xu, F. & Jin, YQ. Numerical simulation of tomographic-SAR imaging and object reconstruction using compressive sensing with L 1/2-norm regularization. Chin. Sci. Bull. 59, 4600–4607 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0554-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0554-5