Abstract
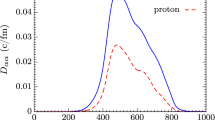
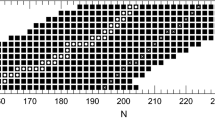
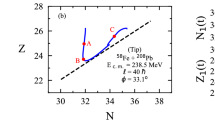
Some nearly-symmetric fusion reactions are systematically investigated with the improved quantum molecular dynamics (ImQMD) model. By introducing two-body inelastic scattering in the Fermi constraint procedure, the stability of an individual nucleus and the description of fusion cross sections at energies near the Coulomb barrier can be further improved. Simultaneously, the quasifission process in 154Sm+160Gd is also investigated with the microscopic dynamics model for the first time. We find that at energies above the Bass barrier, the fusion probability is smaller than 10-5 for this reaction, and the nuclear contact time is generally smaller than 1500 fm/c. From the central collisions of Sm+Gd, the neutron-rich fragments such as 164,165Gd, 192W can be produced in the ImQMD simulations, which implies that the quasi-fission reaction could be an alternative way to synthesize new neutron-rich heavy nuclei.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dasgupta M, Hinde D J, Diaz-Torres A, et al. Beyond the coherent coupled channels description of nuclear fusion. Phys Rev Lett, 2007, 99: 192701
Leigh J R, Dasgupta M, Hinde D J, et al. Barrier distributions from the fusion of oxygen ions with 144,148,154Sm and 186W. Phys Rev C, 1995; 52: 3151–3166
Timmers H, Ackermann D, Beghini S, et al. A case study of collectivity, transfer and fusion enhancement. Nucl Phys A, 1998, 633: 421445
Zhang H Q, Lin C J, Yang F, et al. Near-barrier fusion of 32S+90,96Zr: The effect of multi-neutron transfers in sub-barrier fusion reactions. Phys Rev C, 2010, 82: 054609
Hofmann S, Munzenberg G. The discovery of the heaviest elements. Rev Mod Phys, 2000; 72: 733–767
Oganessian Y Ts, Abdullin F Sh, Bailey D E, et al. Synthesis of a new element with atomic number Z=117. Phys Rev Lett, 2010, 104: 142502
Sobiczewski A, Pomorski K. Description of structure and properties of superheavy nuclei. Prog Part Nucl Phys, 2007; 58: 292–349
Gupta R K, Manhas M, Munzenberg G, et al. heory of the compactness of the hot fusion reaction 48Ca+244Pu292114. Phys Rev C, 2005, 72: 014607
Wong C Y. Interaction barrier in charged-particle nuclear reactions. Phys Rev Lett, 1973; 31: 766–769
Hagino K, Rowley N, Kruppa A T. A program for coupled-channel calculations with all order couplings for heavy-ion fusion reactions. Comput Phys Commun, 1999; 123: 143–152
Liu M, Wang N, Li Z X, et al. Applications of Skyrme energy-density functional to fusion reactions spanning the fusion barriers. Nucl Phys A, 2006; 768: 80–98
Wang N, Liu M, Yang Y X. Heavy-ion fusion and scattering with Skyrme energy density functional. Sci China Ser G-Phys Mech Astron, 2009; 52: 1554–1573
Wang B, Wen K, Zhao W J, et al. Systematics of capture and fusion dynamics in heavy-ion collisions. arXiv:1504.00756
Umar A S, Oberacker V E. Heavy-ion interaction potential deduced from density-constrained time-dependent Hartree-Fock calculation. Phys Rev C, 2006, 74: 021601(R)
Umar A S, Oberacker V E, Maruhn J A, et al. Microscopic composition of ion-ion interaction potentials. Phys Rev C, 2012, 85: 017602
Guo L, Maruhn J A, Reinhard P G. Boost-invariant mean field approximation and the nuclear Landau-Zener effect. Phys Rev C, 2007, 76: 014601
Dai G F, Guo L, Zhao E G, et al. Effect of tensor force on dissipation dynamics in time-dependent Hartree-Fock theory. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2014; 57: 1618–1622
Wang N, Li Z X, Wu X Z. Improved quantum molecular dynamics model and its applications to fusion reaction near barrier. Phys Rev C, 2002, 65: 064608
Wang N, Li Z, Wu X Z, et al. Further development of the improved quantum molecular dynamics model and its application to fusion reactions near the barrier. Phys Rev C, 2004, 69: 034608
Jiang Y Y, Wang N, Li Z X, et al. Dynamical nucleus-nucleus potential at short distances. Phys Rev C, 2010, 81: 044602
Zanganeh V, Wang N, Ghodsi O N. Dynamical nucleus-nucleus potential and incompressibility of nuclear matter. Phys Rev C, 2012, 85: 034601
Wang N, Ou L, Zhang Y X, et al. Microscopic dynamics simulations of heavy-ion fusion reactions induced by neutron-rich nuclei. Phys Rev C, 2014, 89: 064601
Wang N, Zhao K, Li Z X. Systematic study of 16O-induced fusion with the improved quantum molecular dynamics model. Phys Rev C, 2014, 90: 054610
Swiatecki W J. The dynamics of nuclear coalescence or reseparation. Phys Scr, 1981; 24: 113–122
Kozulin E M, Knyazheva G N, Itkis I M, et al. Fusion-fission and quasifission of superheavy systems with Z=110116 formed in 48Cainduced reactions. Phys Rev C, 2014, 90: 054608
Oberacker V E, Umar A S, Simenel C. Dissipative dynamics in quasifission. Phys Rev C, 2014, 90: 054605
Zhang H Q, Zhang C L, Lin C J, et al. Competition between fusionfission and quasifission processes in the 32S+184W reaction. Phys Rev C, 2010, 81: 034611
Shen W Q, Albinski J, Gobbi A, et al. Fission and quasifission in Uinduced reactions. Phys Rev C, 1987; 36: 115–142
Shen J J, Shen C W. Theoretical analysis of mass distribution of quasifission for 238U-induced reactions. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2014; 57: 453–457
Adamian G G, Antonenko N V, Scheid W. Model of competition between fusion and quasifission in reactions with heavy nuclei. Nucl Phys A, 1997; 618: 176–198
Diaz-Torres A, Adamian G G, Antonenko N V, et al. Quasifission process in a transport model for a dinuclear system. Phys Rev C, 2001, 64: 024604
Wang N, Zhao E G, Scheid W, et al. Theoretical study of the synthesis of superheavy nuclei with Z=119 and 120 in heavy-ion reactions with trans-uranium targets. Phys Rev C, 2012, 85: 041601(R)
Shen C, Kosenko G, Abe Y. Two-step model of fusion for the synthesis of superheavy elements. Phys Rev C, 2002, 66: 061602(R)
Zagrebaev V, Greiner W. Unified consideration of deep inelastic, quasifission and fusion-fission phenomena. J Phys G, 2005; 31: 825–844
Nasirov A K, Mandaglio G, Giardina G, et al. Effects of the entrance channel and fission barrier in the synthesis of superheavy element Z=120. Phys Rev C, 2011, 84: 044612
Bao X J, Gao Y, Li JQ, et al. Influence of nuclear basic data on the calculation of production cross sections of superheavy nuclei. Phys Rev C, 2015, 92: 014601
Choudhury R K, Gupta Y K. Revisiting the symmetric reactions for synthesis of super-heavy nuclei of Z 120. Phys Lett B, 2014; 731: 168–172
Cap T, Siwek-Wilczyńska K, Wilczński J. No chance for synthesis of super-heavy nuclei in fusion of symmetric systems. Phys Lett B, 2014; 736: 478–481
Audi G, Wang M, Wapstra A H, et al. The AME2012 atomic mass evaluation. Chin Phys C, 2012; 36: 1287–1602
Fan X H, Dong J M, Zuo W. Symmetry energy at subsaturation densities and the neutron skin thickness of 208Pb. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2015, 58(6): 062002
Papa M, Maruyama T, Bonasera A. Constrained molecular dynamics approach to fermionic systems. Phys Rev C, 2001, 64: 024612
Kolata J J, Roberts A, Howard A M, et al. Fusion of 124,132Sn with 40,48Ca. Phys Rev C, 2012, 85: 054603
Jiang C L, Back B B, Esbensen H, et al. Fusion hindrance for a positive Q-value system. Phys Rev C, 2008, 78: 017601
Gary S, Volant C. Fusion and compound nuclei decay for light and intermediate-mass systems: 24Mg, 28Si+12C, 24Mg+24,26Mg, 28Si+24Mg, 28,29,30Si. Phys Rev C, 1982; 25: 1877–1895
Montagnoli G, Stefanini A M, Esbensen H, et al. Effects of transfer channels on near- and sub-barrier fusion of 32S + 48Ca. Phys Rev C, 2013, 87: 014611
Trotta M, Stefanini A M, Corradi L, et al. Sub-barrier fusion of the magic nuclei 40,48Ca+48Ca. Phys Rev C, 2001, 65: 011601(R)
Jiang C L, Stefanini A M, Esbensen H, et al. Fusion hindrance for Ca+Ca systems: Influence of neutron excess. Phys Rev C, 2010, 82: 041601
Reisdorf W, Hessberger F P, Hildenbrand K D, et al. Fusability and fissionability in 86Kr-induced reactions near and below the fusion barrier. Nucl Phys A, 1985, 444: 154
Reisdorf W. Analysis of fissionability data at high excitation energies. Z Phys A, 1981; 300: 227–238
Wang N, Zhao K, Scheid W, et al. Fusion-fission reactions with a modified Woods-Saxon potential. Phys Rev C, 2008, 77: 014603
Wang N, Tian J L, Scheid W. Systematics of fusion probability in hot fusion reactions. Phys Rev C, 2011, 84: 061601(R)
Angeli I, Marinova K P. Table of experimental nuclear ground state charge radii: An update. At Data and Nucl Data Tables, 2013; 99: 69–95
Bass R. Nucleus-nucleus potential deduced from experimental fusion cross sections. Phys Rev Lett, 1977; 39: 265–268
Wang N, Liu M, Wu X Z, et al. Surface diffuseness correction in global mass formula. Phys Lett B, 2014; 734: 215–219
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, N., Zhao, K. & Li, Z. Fusion and quasi-fission dynamics in nearly-symmetric reactions. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 58, 112001 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-015-5726-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-015-5726-z