Abstract
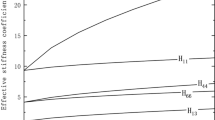
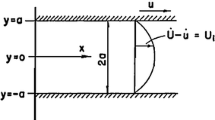
A 2.5-dimensional method in frequency wave-number domain is developed to investigate the mode waves in a deviated borehole penetrating a transversely isotropic formation. The phase velocity dispersion characteristics of the fast and slow flexural mode waves excited by a dipole source are computed accurately at various deviation angles for both hard and soft formations. The sensitivities of the flexural mode waves to all elastic constants in a transversely isotropic formation are calculated. Numerical results show that, for a soft formation, the fast flexural mode wave is dominated by c 66 at high deviation angles and low frequencies, while the slow flexural mode wave is dominated by c 44 at the same conditions. Waveforms in time domain are also presented to support the conclusions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsang L, Rader D. Numerical evaluation of the transient acoustic waveform due to a point source in a fluid-filled borehole. Geophysics, 1979, 44: 1706–1720
Kurkjian A L. Numerical computation of individual far-field arrivals excited by an acoustic source in a borehole. Geophysics, 1985, 50: 852–866
Sinha B K, Norris A N, Chang S K. Borehole flexural modes in anisotropic formations. Geophysics, 1994, 59: 1037–1052
Chi S H, Tang X M. Stoneley-wave speed modeling in general anisotropic formations. Geophysics, 2006, 71: F67–F77
Berryman J G. Long-wave elastic anisotropy in transversely isotropic media. Geophysics, 1979, 44: 896–917
Chan A K, Tsang L. Propagation of acoustic waves in a fluid-filled borehole surrounded by a concentrically layered transversely isotropic formation. J Acoust Soc Am, 1983, 74: 1605–1616
White J E, Tongtaow C. Cylindrical waves in transversely isotropic media. J Acoust Soc Am, 1981, 70: 1147–1155
Schmitt D P. Acoustic multipole logging in transversely isotropic poroelastic formations. J Acoust Soc Am, 1989, 86: 2397–2421
Zhang B X, Dong H F, Wang K X. Multipole sources in a fluid-filled borehole surrounded by a transversely isotropic elastic solid. J Acoust Soc Am, 1994, 96: 2546–2555
Ellefsen K J. Elastic Wave Propagation Along A Borehole in An Anisotropic Medium. Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree. Massachusetts: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1990. 228–231
Leslie H D, Randall C J. Multipole sources in boreholes penetrating anisotropic formations: Numerical and experimental results. J Acoust Soc Am, 1992, 91: 12–27
Wang X M, Hornby B, Dodds K. Dipole sonic response in deviated boreholes penetrating an anisotropic formation. In: SEG Annual Meeting. Salt Lake City: Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 2002. 1–4
Sinha B K, Şimşek E, Liu Q H. Elastic-wave propagation in deviated wells in anisotropic formations. Geophysics, 2006, 71: D191–D202
Lin W J, Wang X M, Zhang H L. Acoustic wave propagation in a borehole penetrating an inclined layered formation (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 2006, 49: 234–246
He X, Hu H S, Guan W. Fast and slow flexural waves in a deviated borehole in homogeneous and layered anisotropic formations. Geophys J Int, 2010, 181: 417–426
Yan S G, Song R L, Lv W G, et al. Numerical simulation of acoustic fields excited by cross-dipole source in deviated wells in transversely isotropic formation (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 2011, 54: 2412–2418
Wang R J, Qiao W X, Jv X H, et al. Acoustic multipole logging in deviated wells penetrating transversely isotropic formations: A numerical study. In: SEG Annual Meeting. Houston: Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 2013. 1–4
Kimball C V, Marzetta T L. Semblance processing of borehole acoustic array data. Geophysics, 1984, 49: 274–281
Ekstrom M P. Dispersion estimation from borehole acoustic arrays using a modified matrix pencil algorithm. In: Conference Record of the Twenty-Ninth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers. Pacific Groov: IEEE, 1995. 449–453
Ellefsen K J, Cheng C H, Toksöz M N. Applications of perturbation theory to acoustic logging. J Geophys Res, 1991, 96: 537–549
Norris A N, Sinha B K. Weak elastic anisotropy and the tube wave. Geophysics, 1993, 58: 1091–1098
Zhang B X, Wang K X. Theoretical study of perturbation method for acoustic multipole logging in anisotropic formation. J Acoust Soc Am, 1996, 99: 2674–2685
Zhu Z Y, Chi S H, Toksöz M N. Sonic logging in deviated boreholes penetrating an anisotropic formation: Laboratory study. Geophysics, 2007, 72: E125–E134
Wang R J, Qiao W X, Jv X D, et al. Experimental study of the acoustic field in the borehole surrounded by HTI formations excited by dipole sources with different orientations (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 2013, 56: 707–717
Mace B R, Duhamel D, Brennan M J, et al. Finite element prediction of wave motion in structural waveguides. J Acoust Soc Am, 2005, 117: 2835–2843
Komatitsch D, Martin R. An unsplit convolutional perfectly matched layer improved at grazing incidence for the seismic wave equation. Geophysics, 2007, 72: SM155–SM167
Li Y F, Matar O B. Convolutional perfectly matched layer for elastic second-order wave equation. J Acoust Soc Am, 2010, 127: 1318–1327
Liu L, Lin W J, Zhang H L, et al. Simulation of 2.5-dimensional borehole acoustic waves with convolutional perfectly matched layer. In: The Proceedings of Symposium on Piezoelectricity, Acoustic Waves and Device Applications (SPAWDA). Changsha: IEEE, 2013. 1–4
Ellefsen K J, Cheng C H, Toksöz M N. Effects of anisotropy upon the normal modes in a borehole. J Acoust Soc Am, 1991, 89: 2597–2616
Auld B A, Sun C P. Acoustic Fields and Waves in Solids (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 1982. 70–82
Thomsen L. Weak elastic anisotropy. Geophysics, 1986, 51: 1954–1966
Tang X M, Cheng C H, Zhao X M. Quantitative Borehole Acoustic Methods (in Chinese). Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004. 48–49
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contributed by ZHANG HaiLan (Associate Editor)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Lin, W., Zhang, H. et al. A numerical investigation of the acoustic mode waves in a deviated borehole penetrating a transversely isotropic formation. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 58, 84301 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-015-5678-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-015-5678-3