Abstract
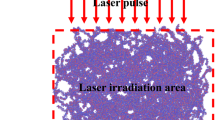
In the present work we elucidate the thermodynamic mechanisms of femtosecond (fs) laser ablation of amorphous polystyrene by means of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The effects of extrinsic parameter of laser pulse intensity and intrinsic parameter of molecular architecture on the laser ablation are further studied. Simulation results show that the laser ablation-induced polymeric material removal is achieved by evaporation from the surface and expansion within the bulk. Furthermore, inter-chain sliding and intra-chain change also play important roles in the microscopic deformation of the material. It is found that both the laser pulse intensity and the arrangement of phenyl groups have significant influence on the fs laser ablation of polystyrene.
概要
研究意义
-
1)
飞秒激光烧蚀是制备激光约束聚变快点火聚苯乙烯微球靶丸的一个重要手段
-
2)
研究聚苯乙烯飞秒激光烧蚀机理对于提高微球表面小孔加工精度具有重要的理论意义与实用价值。
创新要点
-
1)
建立了全原子模型的聚苯乙烯飞秒激光烧蚀的分子动力学仿真模型
-
2)
研究了飞秒激光烧蚀中聚苯乙烯的微观变形机理及与烧蚀加工结果的关系
-
3)
研究了外部激光强度和内部分子结构对聚苯乙烯飞秒激光烧蚀的影响规律。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gamaly E G, Rode A V, Luther-Davies B. Ablation of solids by femtosecond lasers: Ablation mechanism and ablation thresholds for metals and dielectrics. Phys Plasmas, 2002, 9: 949–957
Jiang L, Tsai H L. Energy transport and material removal in wide bandgap materials by a femtosecond laser pulse. J Heat Mass Transfer, 2005, 48: 487–499
Sahin R, Simsek E, Akturk S. Nanoscale patterning of graphene through femtosecond laser ablation. Appl Phys Lett, 2014, 104: 053118
O’Connell G, Donnelly T, Lunney J G. Nanoparticle plume dynamics in femtosecond laser ablation of gold. Appl Phys A, 2014, doi: 10..1007/s00339-013-8209-y
Lee B L P, Jeon H J, Wang A J, et al. Femtosecond laser ablation enhances cell infiltration into three-dimensional electrospun scaffolds. Acta Biomater, 2012, 8: 2648–2658
Pham D, Tonge L, Cao J N, et al. Effects of polymer properties on laser ablation behavior. Smart Mater Struct, 2002, 11: 668–674
Lippert T. Laser application of polymers. In: Advances in Polymer Science. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2004. 51–246
Suriano R, Kuznetsov A, Eaton S M, et al. Femtosecond laser ablation of polymeric substrates for the fabrication of microfluidic channels. Appl Surf Sci, 2011, 257: 6243–6250
Fernández-Pradas J M, Florian C, Caballero-Lucas F, et al. Femtosecond laser ablation of polymethyl-methacrylate with high focusing control. Appl Surf Sci, 2013, 278: 185–189
Kodama R, Norreys P A, Mima K, et al. Fast heating of ultrahigh-density plasma as a step towards laser fusion ignition. Nature, 2001, 412: 798–802
Homma H, Kodota H, Hosokawa H. Recent developments in fabrication of new conceptual gold cone and machining of polystyrene shell for fast ignition target. Fusion Sci Tech, 2011, 59: 276–278
Nagai K, Yang H, Norimatsu T. Fabrication of aerogel capsule, bromine-doped capsule and modified gold cone in modified target for the Fast Ignition Realization Experiment (FIREX) project. Nucl Fution, 2009, 49: 1–9
Reif J. Basic physics of femtosecond laser ablation. In: Miotello A, Ossi P M, eds. Laser-Surface Interactions for New Materials Production. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer, 2000. 19–41
Perez D, Lewis L J. Molecular-dynamics study of ablation of solids under femtosecond laser pulses. Phys Rev B, 2003, 67: 184102
Leveugle E, Zhigilei L V. Molecular dynamics simulation study of the ejection and transport of polymer molecules in matrix-assisted pulsed laser evaporation. J Appl Phys, 2007, 102: 074914
Wang Y, Xu X, Zhang L. Molecular dynamics simulation of ultrafast laser ablation of fused silica film. Appl Phys A, 2008, 92: 849–852
Upadhyay A K, Inogamov N A, Rethfeld B, et al. Ablation by ultrashort laser pulses: Atomistic and thermodynamic analysis of the processes at the ablation threshold. Phys Rev B, 2008, 78: 045437
Sonntag S, Paredes C T, Roth J, et al. Molecular dynamics simulations of cluster distribution from femtosecond laser ablation in aluminum. Appl Phys A, 2011, 104: 559–565
Stuart S J, Harrison J A, Tutein A B. A reactive potential for hydrocarbons with intermolecular interactions. J Chem Phys, 2000, 112: 6472–6486
Du K, Tang Y J, Zhang J J, et al. Velocity-dependent nanoscratching of amorphous polystyrene. Curr Nanosci, 2013, 9: 153–158
Bityurin N, Luk’yanchuk B S, Hong M H, et al. Models for laser ablation of polymers. Chem Rev, 2003, 103: 519–552
Plimpton S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J Comput Phys, 1995, 117: 1–19
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K. VMD-visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graphics, 1996, 14: 33–38
Stukowski A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO-the Open Visualization Tool. Modelling Simul Mater Sci Eng, 2010, 18: 015012
Itina T E, Zhigilei L V, Garrison B J. Matrix-assisted pulsed laser evaporation of polymeric materials: A molecular dynamics study. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B, 2011, 180: 238–244
Chiang W S, Lin C H, Nandan B, et al. Molecular architecture effect on the self-assembly behavior of comb-coil block copolymers displaying. Macromolecules, 2008, 41: 8138–8147
Wu J Y, He J Y, Odegard G M, et al. Effect of chain architecture on the compression behavior of nanoscale polyethylene particles. Nanoscale Res Lett, 2013, 8: 322
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Song, C., Zhang, J. et al. Atomistic investigation of ablation of amorphous polystyrene under femtosecond laser pulse. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 58, 1–7 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5587-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5587-x