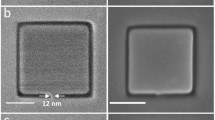
Abstract
Graphene has the advantages of high electrical conductivity, high heat conductivity, and low noise, which makes it a potential option for integrated circuits interconnection and nanoelectrodes. In this paper, we present a novel fabrication method for graphene nanoeletrodes with nanogap. First, graphene grown by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is assembled to a chip with microelectrodes. Second, an atomic force microscopy (AFM) based mechanical cutting method is developed to cut the graphene into nanoribbons and nanoeletrodes with nanogap. Then the electronic property of a single nanodot is characterized using the garphene nanoelectrodes, demonstrating the effectiveness of the graphene nanoelectrodes. The fabricated graphene nanoeletrode pairs can be used as probes to detect single molecule in micro-environment, and show an attractive prospect for future molecular electronics applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang X, Wang J, Ogorevc B, et al. Glucose nanosensor based on Prussian-blue modified carbon-fiber cone nanoelectrode and an integrated reference electrode. Electroanalysis, 1999, 11: 945–949
Koehne J, Chen H, Li J, et al. Ultrasensitive label-free DNA analysis using an electronic chip based on carbon nanotube nanoelectrode arrays. Nanotechnology, 2003, 14: 1239
Bratten C D, Cobbold P H, Cooper J M. Single-cell measurements of purine release using a micromachined electroanalytical sensor. Analytical chemistry, 1998, 70: 1164–1170
Slevin C J, Gray N J, Macpherson J V, et al. Fabrication and characterisation of nanometre-sized platinum electrodes for voltammetric analysis and imaging. Electrochem Commun, 1999, 1: 282–288
Dryfe R A, Kralj B. Voltammetric ion transfer in the presence of a nanoporous material. Electrochem Communs, 1999, 1: 128–130
Wu J, Becerril H A, Bao Z, et al. Organic solar cells with solution-processed graphene transparent electrodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92: 263302
Wu J, Agrawal M, Becerril H A, et al. Organic light-emitting diodes on solution-processed graphene transparent electrodes. ACS Nano, 2009, 4: 43–48
Bae S, Kim H, Lee Y, et al. Roll-to-roll production of 30-inch graphene films for transparent electrodes. Nat Nanotechnol, 2010, 5: 574–578
Di C A, Wei D, Yu G, et al. Patterned graphene as source/drain electrodes for bottom-contact organic field-effect transistors. Adv Mater, 2008, 20: 3289–3293
Cao Y, Wei Z, Liu S, et al. High-performance Langmuir-Blodgett monolayer transistors with high responsivity. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2010, 122: 6463–6467
Cao Y, Liu S, Shen Q, et al. High-performance photoresponsive organic nanotransistors with single-layer graphenes as two-dimensional electrodes. Adv Funct Mater, 2009, 19: 2743–2748
Tan X, Zhou Z, Cheng M M-C. Electrowetting on dielectric experiments using graphene. Nanotechnology, 2012, 23: 375501
Xu M, Fujita D, Hanagata N. Perspectives and challenges of emerging single-molecule DNA sequencing technologies. Small, 2009, 5: 2638–2649
Tung V C, Allen M J, Yang Y, et al. High-throughput solution processing of large-scale graphene. Nat Nanotechnol, 2008, 4: 25–29
Giesbers A, Zeitler U, Neubeck S, et al. Nanolithography and manipulation of graphene using an atomic force microscope. Solid State Commun, 2008, 147: 366–369
Weng L, Zhang L, Chen Y P, et al. Atomic force microscope local oxidation nanolithography of graphene. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 93: 093107
Tapaszto L, Dobrik G, Lambin P, et al. Tailoring the atomic structure of graphene nanoribbons by scanning tunnelling microscope lithography. Nat Nanotechnol, 2008, 3: 397–401
Bell D C, Lemme M C, Stern L A, et al. Precision cutting and patterning of graphene with helium ions. Nanotechnology, 2009, 20: 455301
Lemme M C, Bell D C, Williams J R, et al. Etching of graphene devices with a helium ion beam. ACS Nano, 2009, 3: 2674–2676
Ci L, Xu Z, Wang L, et al. Controlled nanocutting of graphene. Nano Research, 2008, 1: 116–122
Lu G, Zhou X, Li H, et al. Nanolithography of single-layer graphene oxide films by atomic force microscopy. Langmuir, 2010, 26: 6164–6166
He Y, Dong H, Li T, et al. Graphene and graphene oxide nanogap electrodes fabricated by atomic force microscopy nanolithography. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 97: 133301
Zhang Y, Gao Y, Liu L, et al. Cutting forces related with lattice orientations of graphene using an atomic force microscopy based nanorobot. Appl Phys Lett, 2012, 101: 213101
Gao L, Ren W, Xu H, et al. Repeated growth and bubbling transfer of graphene with millimetre-size single-crystal grains using platinum. Nat Commun, 2012, 3: 699
Wang Z, Jiao N, Tung S, et al. Research on the atomic force microscopy-based fabrication of nanochannels on silicon oxide surfaces. Chin Sci Bull, 2010, 55: 3466–3471
Bhushan B, Nosonovsky M, Jung Y C. Lotus effect: Roughness-induced superhydrophobic surfaces. In: Nanotribology and Nanomechanics. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2008. 995–1072
Wang Z, Jiao N, Tung S, et al. Atomic force microscopy-based repeated machining theory for nanochannels on silicon oxide surfaces. Appl Surf Sci, 2011, 257: 3627–3631
Liu Z, Jiao N, Xu K, et al. Nanodot deposition and its application with atomic force microscope. J Nanopart Res, 2013, 15: 1687
Areshkin D A, Gunlycke D, White C T. Ballistic transport in graphene nanostrips in the presence of disorder: Importance of edge effects. Nano Lett, 2007, 7: 204–210
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, S., Liu, Z., Jiao, N. et al. Fabrication and characteristic detection of graphene nanoelectrodes. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 57, 1950–1955 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5603-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5603-4