Abstract
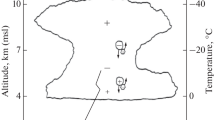
Combined with the existing stochastic lightning parameterization scheme, a classic tripole charge structure in thunderstorms is assumed in the paper, and then 2-dimensional fine-resolution lighting discharge simulations are performed to quantitatively investigate the effect of lower positive charge (LPC) on different types of lightning. The results show: (1) The LPC plays a key role in generating negative cloud-to-ground (CG) flashes and inverted intra-cloud (IC) lightning, and with the increase of charge density or distribution range of LPC region, lightning type changes from positive polarity IC lightning to negative CG flashes and then to inverted IC lightning. (2) Relative to distribution range of charge regions, the magnitude of charge density of the LPC region plays a dominant role in lightning type. Only when the maximal charge density value of LPC region is within a certain range, can negative CG flashes occur, and the occurrence probability is relatively fixed. (3) In this range, the charge density and distribution range of LPC region jointly determine the occurrence of negative CG flashes, which has a linear boundary with the trigger condition of IC lightning. (4) The common effect of charge density and distribution range of the LPC region is to change the distribution of positive potential well of bottom part of thunderstorms, and inverted IC lightning occurs when the initial reference potential is close to 0 MV, and negative CG flashes occur when the initial reference potential is far less than 0 MV.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akita M, Yoshida S, Nakamura Y, et al. 2011. Effects of charge distribution in thunderstorm on lightning propagation paths in Darwin, Australia. J Atmos Sci, 68: 719–726
Bell T F, Pasko V P, Inan U S. 1995. Runaway electrons as a source of red sprites in the mesosphere. Geophys Res Lett, 22: 2127–2130
Brown K A, Krehbiel P R, Moore C B, et al. 1971. Electrical screening layers around charged clouds. J Geophys Res, 76: 2825–2835
Bruning E C, Rust W D, Schuur T J, et al. 2007. Electrical and polarimetric radar observations of a muticell storm in TELEX. Mon Weather Rev, 135: 2525–2544
Clarence N D, Malan D J. 1957. Preliminary discharge processes in lightning flashes to ground. Q J R Meteorol Soc, 83: 161–172
Coleman L M, Marshall T C, Stolzenburg M. 2003. Effects of charge and electrostatic potential on lightning propagation. J Geophys Res, 109: 1–12
Cui H H, Qie X S, Zhang Q L, et al. 2009. Intracloud discharge and the correlated basic charge structure of a thunderstorm Zhongchuan, a Chinese Inland Plateau region. Atmos Res, 91: 425–429
Dong W S, Liu X S, Zhang Y J, et al. 2002. Broadband interferometer observations of leader-stroke of cloud-to-ground lightning discharges. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 32: 81–88
Guo F X, Zhang Y J, Qie X S, et al. 2003. Numerical simulation of different charge structures in thunderstorm (in Chinese). Pla Meteorol, 22: 268–274
Kasemir H W. 1960. A contribution to the electrostatic theory of a lightning discharges. J Geophys Res, 65: 1873–1878
Klett J D. 1972. Charge screening layers around electrified clounds. J Geophys Res, 77: 3187–3195
Krehbiel P R, Riousset J A, Pasko V P, et al. 2008. Upward electrical discharges from thunderstorm. Nat Geosci, 1: 233–237
Liu X S, Ye Z X, Shao X M. 1989. Intracloud lightning discharges in the lower part of thunderstorm. Acta Meteorol Sin, 3: 212–219
Mansell E R, Macgorman D R, Ziegler C L, et al. 2002. Simulated three-dimensional branched lightning in a numerical thunderstorm model. J Geophys Res, 107: 1–12
Mansell E R, Macgorman D R, Ziegler C L, et al. 2005. Charge structure and lightning sensitivity in a simulated multicell thunderstorm. J Geophys Res, 110: 1–24
Marshall T C, Rust W D, Winn W P, et al. 1989. Electrical structure in two thunderstorm anvil clouds. J Geophys Res, 94: 2171–2181
Marshall T C, Stolzenburg M. 1998. Estimates of cloud charge densities in thunderstorms. J Geophys Res, 103: 19769–19775
Mazur V, Ruhnke L H. 1998. Model of electric charges in thunderstorms and associated lightning. J Geophys Res, 103: 23299–23308
Nag A, Rakov V A. 2009. Some inferences on the role of lower positive charge region in facilitating different types of lightning. Geophys Res Lett, 36: 1–5
Pawar S D, Kamra A K. 2004. Evolution of lightning and the possible initiation/triggering of lightning discharges by the lower positive charge center in an isolated thundercloud in the tropics. J Geophys Res, 109: 1–12
Qie X S, Yu Y, Liu X S, et al. 2000. K-type breakdown process of intracloud discharge in Chinese inland plateau. Prog Nat Sci, 10: 607–611
Qie X S, Zhang T L, Chen C P, et al. 2005. The lower positive charge center and its effect on lightning discharges on the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys Res Lett, 32: 1–4
Qie X S, Zhang T L, Zhang G S, et al. 2009. Electrical characteristics of thunderstorms in different plateau regions of China. Atmos Res, 91: 244–249
Shao X M, Krehbiel P R. 1996. The spatial and temporal development of intracloud lightning. J Geophys Res, 101: 26641–26668
Stolzenburg M, Rust W D, Marshall T C. 1998. Electrical structure in thunderstorm convective regions, 2, isolated storms. J Geophys Res, 103: 14079–14096
Stolzenburg M, Rust W D, Marshall T C. 1998. Electrical structure in thunderstorm convective regions, 3, synthesis. J Geophys Res, 103: 14097–14108
Tan Y B, Tao S C, Zhu B Y, et al. 2006a. Numerical simulations of the bi-level and branched structure of intra-cloud lightning flashes. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 36: 486–496
Tan Y B, Tao S C, Zhu B Y, et al. 2007. A simulation of the effects of intra-cloud lightning discharges on charges and electrostatic potential distributions in a thundercloud. Chi J Geophy, 50: 916–930
Tan Y B, Tao S C, Zhu B Y. 2006b. Fine-resolution simulation of the channel structures and propagation features of intracloud lightning. Geophys Res Lett, 33: 1–4
Tao S C, Tan Y B, Zhu B Y, et al. 2009. Fine-resolution simulation of cloud-to-ground lightning and thundercloud charge transfer. Atmos Res, 91: 360–370
Tessendorf S A, Rutledge S A. 2007. Radar and lightning observations of Normal and Inverted polarity Multicellular storms from STEPS. Mon Weather Rev, 135: 3682–3706
Vonnegut B, Moore C B, Espinola R P, et al. 1966. Electric potential gradients above thunderstorms. J Atmos Sci, 23: 764–770
Wang C W, Chen Q, Liu X S, et al. 1987. The electric field produced by the lower positive charge center of thundercloud (in Chinese). Pla Meteorol, 6: 65–74
Williams. 1989. The tripole structure of thunderstorms. J Geophys Res, 94: 13151–13167
Zhang Y J, Krehbiel P R, Liu X S. 2002. Polarity inverted intracloud discharges and electric charge structure of thunderstorms. Chin Sci Bull, 47: 1725–1729
Zhang Y J, Meng Q, Lu W T, et al. 2006. Charge structures and cloud-to-ground lightning discharges characteristics in two supercell thunderstorms. Chin Sci Bull, 51: 198–212
Zhang Y J, Dong W S, Zhao Y, et al. 2004. Study of charge structure and radiation characteristic of intracloud discharge in thunderstorms of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, (Supp. l): 108–114
Zhao Z K, Qie X S, Zhang T L, et al. 2010. Electric field soundings and the charge structure within an isolated thunderstorm. Chin Sci Bull, 55: 872–876
Zheng D, Zhang Y J, Meng Q, et al. 2010. Lightning activity and electrical structure in a thunderstorm that continued for more than 24h. Atmos Res, 97: 241–256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Y., Liang, Z., Shi, Z. et al. Numerical simulation of the effect of lower positive charge region in thunderstorms on different types of lightning. Sci. China Earth Sci. 57, 2125–2134 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-014-4867-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-014-4867-7