Abstract
Purpose
The water-level-fluctuating zone (WLFZ) is the buffer zone of energy and material exchange between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Artificial vegetation restoration of WLFZ can improve the interception capacity of P pollution. The purpose of this study is to explore the effect of artificial vegetation restoration on the bioavailability of soil phosphorus (P) in the WLFZ.
Material and methods
Soil samples from different spatial locations (natural vegetation zone, artificial vegetation restoration zone) and different altitudes of the WLFZ were collected in the Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR) region, Chongqing, China. Soil P fraction, microbial biomass P (MBP), and phosphatase activity were measured.
Results and discussion
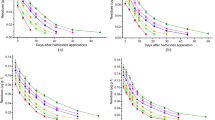
Artificial vegetation restoration changed the spatial distribution patterns of soil bioavailable P (Bio-P) in the WLFZ. The soil bioavailable inorganic P (Bio-Pi) in the artificial vegetation restoration zone was significantly higher than those at the natural vegetation zone (p < 0.05) and its content decreased with the decrease of altitude. The content of bioavailable organic P (Bio-Po) in the two transects was not significantly different in general, but was different at different altitudes. Phosphodiesterase (PDE) activity was negatively correlated with Bio-Po in artificial vegetation restoration zone (p < 0.01, R2 = 0.21), but significantly positively correlated with in natural vegetation zone (p < 0.05, R2 = 0.17); this suggests that the relationship between Bio-Po and PDE activity was altered by vegetation restoration. Moreover, the factors controlling the bioavailability of P in the WLFZ are discussed.
Conclusion
Artificial vegetation restoration and altitude are the control factors of soil P fractions and bioavailability in WLFZ. Vegetation restoration can increase soil TP and Bio-Pi in general but has little effect on Bio-Po.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MA (1992) Phosphatase activity and phosphorus fractions in karri (Eucalyptus diversicolor F. Muell.) forest soils. Biol Fertil Soils 14(3):200–204
Allison VJ, Condron LM, Peltzer DA, Richardson SJ, Turner BL (2007) Changes in enzyme activities and soil microbial community composition along carbon and nutrient gradients at the Franz Josef chronosequence. New Zealand Soil Biol Biochem 39(7):1770–1781
Bauke SL, Wang Y, Saia SM, Popp C, Tamburini F, Paetzold S, Amelung W, Sperber C (2022) Phosphate oxygen isotope ratios in vegetated riparian buffer strip soils. Vadose Zone J 21(3):e20193
Birch HF (1958) The effect of soil drying on humus decomposition and nitrogen availability. Plant Soil 10(1):9–31
Boitt G, Black A, Wakelin SA, McDowell RW, Condron LM (2018) Impacts of long-term plant biomass management on soil phosphorus under temperate grassland. Plant Soil 427(1):163–174
Brödlin D, Kaiser K, Kessler A, Hagedorn F (2019) Drying and rewetting foster phosphorus depletion of forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 128:22–34
Brookes PC, Powlson DS, Jenkinson DS (1982) Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 14(4):319–329
Bünemann EK, Keller B, Hoop D, Jud K, Boivin P, Frossard E (2013) Increased availability of phosphorus after drying and rewetting of a grassland soil: processes and plant use. Plant Soil 370(1):511–526
Burns RG, DeForest JL, Marxsen J, Sinsabaugh RL, Stromberger ME, Wallenstein MD, Weintraub MN, Zoppini A (2013) Soil enzymes in a changing environment: current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol Biochem 58:216–234
Chen CR, Condron LM, Davis MR, Sherlock RR (2003) Seasonal changes in soil phosphorus and associated microbial properties under adjacent grassland and forest in New Zealand. For Ecol Manag 177:539–557
Cheng F, Li W, Castello L, Murphy BR, Xie S (2015) Potential effects of dam cascade on fish: lessons from the Yangtze river. Rev Fish Biol Fish 25:569–585
Cleveland CC, Liptzin CD (2007) C: N: P stoichiometry in soil: is there a “redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 85:235–252
Cleveland CC, Townsend AR, Taylor P, Alvarez-Clare S, Bustamante MMC, Chuyong G, Dobrowski SZ, Grierson P, Harms KE, Houlton BZ, Marklein A, Parton W, Porder S, Reed SC, Sierra CA, Silver WL, Tanner EVJ, Wieder WR (2011) Relationships among net primary productivity, nutrients and climate in tropical rain forest: a pan-tropical analysis. Ecol Lett 14:1313–1317
Cross AF, Schlesinger WH (1995) A literature review and evaluation of the Hedley fractionation: applications to the biogeochemical cycle of soil phosphorus in natural ecosystems. Geoderma 64(3):197–214
Dinkelaker B, Marschner H (1992) In vivo demonstration of acid-phosphatase-activity in the rhizosphere of soil-grown plants. Plant Soil 144:199–205
Evtimova VV, Donohue I (2016) Water-level fluctuations regulate the structure and functioning of natural lakes. Freshw Biol 61:251–264
Fu D, Wu X, Duan C, Chadwick DR, Jones DL (2020) Response of soil phosphorus fractions and fluxes to different vegetation restoration types in a subtropical mountain ecosystem. CATENA 193:104663
Gao YL, Fang F, Tang ZC, Zhang R, Jiang YX, Guo JS (2022) Distribution characteristics of soil phosphorus forms and phosphatase activity at different altitudes in the soil of water-level-fluctuation zone in Pengxi River, Three Gorges Reservoir. Huan Jing Ke Xue 43(10):4630–4638
George TS, Turner BL, Gregory PJ, Cademenun BJ, Richardson AE (2010) Depletion of organic phosphorus from Oxisols in relation to phosphatase activities in the rhizosphere. Eur J Soil Sci 57:47–57
Hale BW, Adams MS (2007) Ecosystem management and the conservation of river–floodplain systems. Landsc Urban Plan 80(1–2):23–33
He Z, Fortuna AM, Senwo ZN, Tazisong IA, Honeycutt CW, Griffin TS (2006) Hydrochloric fractions in Hedley fractionation may contain inorganic and organic phosphates. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70(3):893–899
Hill AR (2000) Stream chemistry and riparian zones. Streams and ground waters 83–110
Jeppesen E, Kronvang B, Meerhoff M, Søndergaard M, Hansen KM, Andersen HE, Lauridsen TL, Liboriussen L, Beklioglu M, Özen A, Olesen JE (2009) Climate change effects on runoff, catchment phosphorus loading and lake ecological state, and potential adaptations. J Environ Qual 38(5):1930–1941
Jia GM, He L, Cheng H, Wang ST, Xiang HY, Zhang XF, Xi Y (2016) Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus under different vegetation covers in three gorges reservoir area. Res Soil Water Conserv 23:23–27
Khan KS, Joergensen RG (2012) Relationships between P fractions and the microbial biomass in soils under different land use management. Geoderma 173:274–281
Khan SU, Hooda PS, Blackwell MSA, Busquets R (2022) Effects of drying and simulated flooding on soil phosphorus dynamics from two contrasting UK grassland soils. Eur J Soil Sci 73(1):e13196
Lembi CA (2001) Limnology, lake and river ecosystems. J Phycol 37(6):1146–1147
Li SZ, Deng Y, Shi FN, Hu MM, Pang BH, Wang YC, Li K, Peng WQ, Liang XD, Bao YF, Meng JJ (2019) Research progress on water-level-fluctuation zones of reservoirs: a review. Wetl Sci 17:689–696
Li JB, Xie T, Zhu H, Zhou J, Li CN, Xiong WJ, Xu L, Wu YH, He ZL, Li XZ (2021) Alkaline phosphatase activity mediates soil organic phosphorus mineralization in a subalpine forest ecosystem. Geoderma 404:115376
Ma LM, Zhang M, Teng YH, Zhao JF (2008) Characteristics of phosphorous release from soil in periodic alternately waterlogged and drained environments at WFZ of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Huan Jing Ke Xue 29(4):1035–1039
Nannipieri P, Giagnoni L, Landi L, Renella G (2011) Role of phosphatase enzymes in soil. Phosphorus in Action, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg 2011:215–243
Oehl F, Oberson A, Probst M, Fliessbach A, Roth HR, Frossard E (2001) Kinetics of microbial P uptake in cultivated soils. Biol Fert Soils 34:31–41
Perkins RG, Underwood GJC (2001) The potential for phosphorus release across the sediment–water interface in an eutrophic reservoir dosed with ferric sulphate. Water Res 35(6):1399–1406
Pulford ID, Tabatabai MA (1988) Effect of waterlogging on enzyme activities in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 20(2):215–219
Ren QS, Song H, Yuan ZX, Ni XL, Li CX (2018) Changes in soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass after revegetation in the three gorges reservoir. China Forests 9(5):249
Shen YF, Cheng RM, Xiao WF, Zeng LX, Wang LJ, Sun PF, Chen T (2022) Temporal dynamics of soil nutrients in the riparian zone: effects of water fluctuations after construction of the Three Gorges Dam. Ecol Indic 139:108865
Spohn M, Kuzyakov Y (2013) Distribution of microbial- and root-derived phosphatase activities in the rhizosphere depending on P availability and C allocation–coupling soil zymography with 14C imaging. Soil Biol Biochem 67:106–113
Tang Q, Bao Y, He X, Zhou H, Cao Z, Gao P (2014) Sedimentation and associated trace metal enrichment in the riparian zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci Total Environ 479:258–266
Tang Q, Collins AL, Wen AB, He XB, Bao YH, Yan DC, Long Y, Zhang YS (2018) Particle size differentiation explains flow regulation controls on sediment sorting in the water-level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci Total Environ 633:1114–1125
Tiessen HJWB, Moir JO (1993) Characterization of available P by sequential extraction. Soil Sampl Methods Anal 7:5–229
Turner BL, Haygarth PM (2005) Phosphatase activity in temperate pasture soils: potential regulation of labile organic phosphorus turnover by phosphodiesterase activity. Sci Total Environ 344(1–3):27–36
Turner BL, Driessen JP, Haygarth PM, Mckelvie ID (2003) Potential contribution of lysed bacterial cells to phosphorus solubilisation in two rewetted Australian pasture soils. Soil Biol Biochem 35:187–189
Vidon F, Allan C, Burns D, Duval TP, Gurwick N, Inamdar S, Lowrance R, Okay J, Scott D, Sebestyen S (2010) Hot spots and hot moments in riparian zones: potential for improved water quality management. J Am Water Resour Assoc 46(2):278–298
Wang Y, Zhang N, Wang D, Wu J, Zhang X (2018) Investigating the impacts of cascade hydropower development on the natural flow regime in the Yangtze River, China. Sci Total Environ 624:1187–1194
Wang C, Fang F, Yuan Z, Zhang R, Zhang W, Guo J (2020a) Spatial variations of soil phosphorus forms and the risks of phosphorus release in the water-level fluctuation zone in a tributary of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Sci Total Environ 699:134124
Wang Y, Zhang N, Wang D, Wu J (2020b) b) Impacts of cascade reservoirs on Yangtze river water temperature: assessment and ecological implications. J Hydrol 590:125240
Wang CQ, Xue L, Jiao RZ (2021) Soil phosphorus fractions, phosphatase activity, and the abundance of phoC and phoD genes vary with planting density in subtropical Chinese fir plantations. Soil till Res 209:104946
Wu JG, Huang JH, Han XG, Gao XM, He FL, Jiang MX, Jiang ZG, Primack RB, Shen ZH (2004) The Three Gorges Dam: an ecological perspective. Front Ecol Environ 2(5):241–248
Wu Y, Wang X, Zhou J, Bing H, Sun H, Wang J (2016) The fate of phosphorus in sediments after the full operation of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ Pollut 214:282–289
Xue L, Hou P, Zhang Z, Shen M, Liu F, Yang L (2020) Application of systematic strategy for agricultural non-point source pollution control in Yangtze River basin. China Agr Ecosyst Environ 304:107148
Yang WH, Qing H, Ren Q, He Y, Li X, Li C (2017) Characteristics of soil microbial biomass C and N under revegetation in the hydro-fluctuation belt of the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Acta Ecol Sin 37(23):7947–7955
Ye C, Cheng X, Zhang Q (2014) Recovery approach affects soil quality in the water level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China: implications for revegetation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(3):2018–2031
Ye C, Chen C, Butler OM, Rashti MR, Esfandbod M, Zhang DuM, Q, (2019) Spatial and temporal dynamics of nutrients in riparian soils after nine years of operation of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci Total Environ 664:841–850
Zhang B, Fang F, Guo J, Chen Y, Li Z, Guo S (2012) Phosphorus fractions and phosphate sorption-release characteristics relevant to the soil composition of water-level-fluctuating zone of Three Gorges Reservoir. Ecol Eng 40:153–159
Zhang Y, Li Y, Wang S, Umbreen S, Zhou C (2021) Soil phosphorus fractionation and its association with soil phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in a chronosequence of vegetation restoration. Ecol Eng 164:106208
Zhu J, Qu B, Li M (2017) P mobilization in the Yeyahu wetland: phosphatase enzyme activities and organic P fractions in the rhizosphere soils. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 124:304–313
Zhu K, Li W, Yang S, Ran Y, Lei X, Ma M, Wu S (2022) Intense wet-dry cycles weakened the carbon sequestration of soil aggregates in the riparian zone. CATENA 212:106117
Funding
This study was sponsored jointly by the National Key Research and Development Project (2021YFC3201002), the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS (XDB40020400), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41977296, 42277253, 51809287, U2040211), the Guizhou Science and Technology Department Fund ([2020] 4Y006, [2019]1042), the Central Leading Local Science and Technology Development Fund Project ([2021]4028), the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (No. 2019389), and the Follow-up Work of the Three Gorges Project (2136902).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Wenzhi Cao
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, S., Wang, Y., Wang, J. et al. Effects of artificial vegetation restoration on the fractions and availability of soil phosphorus in the water-level-fluctuating zone of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J Soils Sediments (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03603-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03603-x