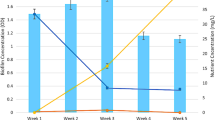
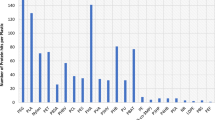
Abstract
Purpose
The objective of this study was to investigate the characteristics of sediment organic phosphorus (Po) driven by the microbial community during the ecological restoration of a plateau wetland.
Materials and methods
Twenty surface sediment samples were collected from the Caohai wetland, China. A series of analysis methods were used, including Ivanoff extraction, enzymatic hydrolysis, solution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance (31P-NMR), and high-throughput sequencing technology.
Results
The concentrations of the total Po were in the range 564.66 to 751.30 mg kg−1, among which Ful-Po was the dominant component with a proportion of 38.67–45.37%. In the enzymatically hydrolyzable Po, phosphomonoester was the main fraction accounting for 19.58–67.87%, while it made up 52.91–68.98% of the Po determined by 31P-NMR. The biogeochemical feature of Po indicated the high releasing risk of bioavailable Po from the sediment to the overlying water in the Caohai plateau wetland. Anthropogenic input was the dominant source of Po in the sediments, followed by the internal biological processes. Two thousand sixty-six OTUs were clustered in the phoD gene-harboring communities and were dominated by the Proteobacteria phylum and Rubrobacter genus. The redundancy analysis (RDA), correlation network analysis, and structural equation modeling (SEM) suggested the direct and/or indirect (coupling the C and N cycles) contribution of phoD gene communities to P fractions.
Conclusion
This study established the influence of microbes on P fractions and provided a valuable understanding of the biogeochemical cycling of P in sediment from an ecologically restored wetland.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MM, Srinivasan V, Mueller AV, Gu AZ (2021) Status and advances in technologies for phosphorus species detection and characterization in natural environment- a comprehensive review. Talanta 233:122458
Campos M, Rilling JI, Acuña JJ, Valenzuela T, Larama G, Peña-Cortés F, Ogram A, Jaisi DP, Jorquera MA (2021) Spatiotemporal variations and relationships of phosphorus, phosphomonoesterases, and bacterial communities in sediments from two Chilean rivers. Sci Total Environ 776:145782
Chen J, Gao H, Wang P, Wang C, Sun S, Wang X (2019) Effects of decabromodiphenyl ether on activity, abundance, and community composition of phosphorus mineralizing bacteria in eutrophic lake sediments. Sci Total Environ 695:133785
Chen X, Condron LM, Dunfield KE, Wakelin SA, Chen L (2021a) Impact of grassland afforestation with contrasting tree species on soil phosphorus fractions and alkaline phosphatase gene communities. Soil Biol Biochem 159:108274
Chen Z, Fang F, Shao Y, Jiang Y, Huang J, Guo J (2021b) The biotransformation of soil phosphorus in the water level fluctuation zone could increase eutrophication in reservoirs. Sci Total Environ 763:142976
Carpenter SR (2005) Eutrophication of aquatic ecosystems: bistability and soil phosphorus. PNAS 102:10002–10005
Crocker R, Blake WH, Hutchinson TH, Comber S (2021) Spatial distribution of sediment phosphorus in a Ramsar wetland. Sci Total Environ 765:142749
Doolette AL, Smernik RJ, Dougherty WJ (2009) Spiking improved solution phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance identification of soil phosphorus compounds. Soil Sci Soc Am J 73:919–927
Gao JM, Chen ZM, Wang C, Fang F, Huang JJ, Guo JS (2020) Bioavailability of organic phosphorus in the water level fluctuation zone soil and the effects of ultraviolet irradiation on it in the Three Gorges Reservoir. China Sci Total Environ 738:139912
Han JY, Kim DH, Oh S, Moon HS (2020) Effects of water level and vegetation on nitrate dynamics at varying sediment depths in laboratory-scale wetland mesocosms. Sci Total Environ 703:134741
Hu J, Long YC, Zhou W, Zhu CB, Yang Q, Zhou SQ, Wu P (2020a) Influence of different land use types on hydrochemistry and heavy metals in surface water in the lakeshore zone of the Caohai wetland. China Environ Pollut 267:115454
Hu M, Peñuelas J, Sardans J, Tong C, Chang CT, Cao W (2020b) Dynamics of phosphorus speciation and the phoD phosphatase gene community in the rhizosphere and bulk soil along an estuarine freshwater-oligohaline gradient. Geoderma 365:114236
Huang B, Yan D, Ouyang C, Zhang D, Zhu J, Liu J, Li Y, Wang Q, Han Q, Cao A (2020) Chloropicrin fumigation alters the soil phosphorus and the composition of the encoding alkaline phosphatase PhoD gene microbial community. Sci Total Environ 711:135080
Ivanoff DB, Reddy KR, Robinson S (1998) Chemical fractionation of organic phosphorus in selected Histosols. Soil Sci 163:36–45
Kurek MR, Harir M, Shukle JT, Schroth AW, Schmitt-Kopplin P, Druschel GK (2021) Seasonal transformations of dissolved organic matter and organic phosphorus in a polymictic basin: implications for redox-driven eutrophication. Chem Geol 573:120212
Li XL, Guo ML, Duan XD, Zhao JW, Hua YM, Zhou YY, Liu GL, Dionysiou DD (2019) Distribution of organic phosphorus species in sediment profiles of shallow lakes and its effect on photo-release of phosphate during sediment resuspension. Environ Int 130:104916
Long YC, Jiang J, Hu XJ, Hu J, Ren CG, Zhou SQ (2021a) The response of microbial community structure and sediment properties to anthropogenic activities in Caohai wetland sediments. Ecotox Environ Safe 211:111936
Long YC, Hu XJ, Jiang J, Hu J, Zhu CB, Zhou SQ (2021b) Phosphorus sorption - desorption behaviors in the sediments cultured with Hydrilla verticillata and Scripus triqueter as revealed by phosphorus fraction and dissolved organic matter. Chemosphere 271:129549
Mao C, Li T, Rao W, Tang Z, Song Y, Wang S (2021) Chemical speciation of phosphorus in surface sediments from the Jiangsu Coast, East China: influences, provenances and bioavailabilities. Mar Pollut Bull 163:111961
Mohapatra M, Yadav R, Rajput V, Dharne MS, Rastogi G (2021) Metagenomic analysis reveals genetic insights on biogeochemical cycling, xenobiotic degradation, and stress resistance in mudflat microbiome. J Environ Manage 292:112738
Ni Z, Wang S, Wang Y (2016) Characteristics of bioavailable organic phosphorus in sediment and its contribution to lake eutrophication in China. Environ Pollut 219:537–544
Ni ZK, Wang SR, Wu Y, Pu J (2020) Response of phosphorus fractionation in lake sediments to anthropogenic activities in China. Sci Total Environ 699:134242
Qu Y, Wang C, Guo J, Huang J, Fang F, Xiao Y, Ouyang W, Lu L (2019) Characteristics of organic phosphorus fractions in soil from water-level fluctuation zone by solution 31P-nuclear magnetic resonance and enzymatic hydrolysis. Environ Pollut 255:113209
Reddy KR, Vardanyan L, Hu J, Villapando O, Bhomia RK, Smith T, Harris WG, Newman S (2020) Soil phosphorus forms and storage in stormwater treatment areas of the Everglades: influence of vegetation and nutrient loading. Sci Total Environ 725:138442
Reitzel K, Ahlgren J, DeBrabandere H, Waldebäck M, Gogoll A, Tranvik L, Rydin E (2007) Degradation rates of organic phosphorus in lake sediment. Biogeochemistry 82:15–28
Song B, Gong J, Tang W, Zeng G, Chen M, Xu P, Shen M, Ye S, Feng H, Zhou C, Yang Y (2020) Influence of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the microbial biomass, enzyme activity, and bacterial community structure in 2,4-dichlorophenol-contaminated sediment. Sci Total Environ 713:136645
Sundareshwar PV, Morris JT, Pellechia PJ, Cohen HJ, Porter DE, Jones BC (2001) Occurrence and ecological implications of pyrophosphate in estuaries. Limnol Oceanogr 46:1570–1577
Tong T, Li R, Wu S, Xie S (2019) The distribution of sediment bacterial community in mangroves across China was governed by geographic location and eutrophication. Mar Pollut Bull 140:198–203
Turner BL, Mahieu N, Condron LM (2003) The phosphorus composition of temperate pasture soils determined by NaOH–EDTA extraction and solution 31P NMR spectroscopy. Org Geochem 34:1199–1210
Wang W, YujunYi YY, Zhou Y, Zhang S, Wang X, Yang Z (2020) Impact of anthropogenic activities on the sediment microbial communities of Baiyangdian shallow lake. Int J Sediment Res 35:180–192
Wang C, Guo J, Zhang W, Jiang Y, Fang F, He W, Jia B, Dang C (2021a) Drying-rewetting changes soil phosphorus status and enzymatically hydrolysable organic phosphorus fractions in the water-level fluctuation zone of Three Gorges reservoir. CATENA 204:105416
Wang Y, Ouyang W, He M, Han F, Lin C (2021b) Sorption dynamics, geochemical fraction and driving factors in phosphorus transport at large basin scale. J Clean Prod 294:126111
Xie F, Li L, Song K, Li G, Wu F, Giesy JP (2019) Characterization of phosphorus forms in a eutrophic lake, China. Sci Total Environ 659:1437–1447
Xie Y, Wang F, Wang K, Yue H, Lan X (2020) Responses of bacterial phoD gene abundance and diversity to crop rotation and feedbacks to phosphorus uptake in wheat. Appl Soil Ecol 154:103604
Yan D, Xia P, Song X, Lin T, Cao H (2019) Community structure and functional diversity of epiphytic bacteria and planktonic bacteria on submerged macrophytes in Caohai Lake, southwest of China. Ann Microbiol 69:933–944
Yao Q, Li Z, Song Y, Wright SJ, Guo X, Tringe SG, Tfaily MM, Paša-Tolić L, Hazen TC, Turner BL, Mayes MA, Pan C (2018) Community proteogenomics reveals the systemic impact of phosphorus availability on microbial functions in tropical soil. Nat Ecol Evol 2:499–509
Yuan H, Tai Z, Li Q, Zhang F (2020) Characterization and source identification of organic phosphorus in sediments of a hypereutrophic lake. Environ Pollut 257:113500
Zhang T, Qin M, Wei C, Li D, Lu X, Zhang L (2020) Suspended particles phoD alkaline phosphatase gene diversity in large shallow eutrophic Lake Taihu. Sci Total Environ 728:138615
Zhao G, Sheng Y, Jiang M, Zhou H, Zhang H (2019) The biogeochemical characteristics of phosphorus in coastal sediments under high salinity and dredging conditions. Chemosphere 215:681–692
Zhou J, Wu Y, Turner BL, Sun H, Wang J, Bing H, Luo J, He X, Zhu H, He Q (2019) Transformation of soil organic phosphorus along the Hailuogou post-glacial chronosequence, southeastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma 352:414–421
Zhu Y, Feng W, Liu S, He Z, Zhao X, Liu Y, Guo J, Giesy JP, Wu F (2018) Bioavailability and preservation of organic phosphorus in lake sediments: insights from enzymatic hydrolysis and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. Chemosphere 211:50–61
Acknowledgements
We thank the Guizhou Caohai National Nature Reserve Management Committee for their sampling assistance.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Fund (U1612441), the Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Projects (No. [2022] Y218, No. [2020]1Y168), and the Youth Fund from Guizhou Institute of Biology (No. [2021]08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YC L: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, writing–original draft; JJ: investigation, visualization, validation, writing–review and editing; BW: writing–review and editing; JH: investigation; ZM Z: methodology; SQ Z: funding acquisition, supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Haihan Zhang
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, Y., Jiang, J., Wu, B. et al. Phosphatase phoD gene community changes organic phosphorus in sediment from Caohai plateau wetland. J Soils Sediments 22, 2317–2328 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03245-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03245-5