Abstract
Purpose
Soil nanoparticles (NPs) are active organic-mineral complexes and have an important impact on the migration of nutrients, organic pollutants, and heavy metals. Due to their diversity and heterogeneity, researches have mainly investigated the effect of solution chemistry on the stability of soil NPs, but little attention is paid to the influences of particle properties.
Methods
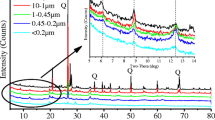
In the present study, NPs were separated from the eluviated cinnamon soil (ECS), typical cinnamon soil (TCS), and carbonate cinnamon soil (CCS), namely ECS-NP, TCS-NP, and CCS-NP. The particle composition, surface-related properties, and the aggregation kinetics of soil NPs were investigated. Correlation analyses between soil NP properties and their critical coagulation concentrations (CCCs) were further discussed.
Results
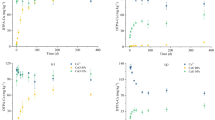
The bulk ECS, TCS, and CCS differed highly in CaCO3 content. While in soil NP fractions, the contents of soil organic matter and illite were more abundant. The particle size, specific surface area, and Hamaker constant of soil NPs followed the order of ECS-NP < TCS-NP < CCS-NP, while the yield, zeta potential (in absolute values), and the CCCs were in the reverse trend. The particle diameter, specific surface area, and zeta potential significantly correlated with the CCCs.
Conclusion
The present study revealed the important role of particle properties in dominating the stability (aggregation and dispersion) of soil NPs. Therefore, it is necessary to further systematically explore the composition of soil NPs on dominating their environmental behaviors.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afshinnia K, Sikder M, Cai B, Baalousha M (2017) Effect of nanomaterial and media physicochemical properties on Ag NM aggregation kinetics. J Colloid Interf Sci 487:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.10.037
Baalousha M (2017) Effect of nanomaterial and media physicochemical properties on nanomaterial aggregation kinetics. NanoImpact 6:55–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.impact.2016.10.005
Bagherifam S, Bowen T, Naidu R, Wijayawardena A (2021) The influence of different antimony (Sb) compounds and ageing on bioavailability and fractionation of antimony in two dissimilar soils. Environ Pollut 270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116270
Bakshi S, He ZL, Harris WG (2015) Natural nanoparticles: Implications for environment and human health. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 45:861e904. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2014.921975
Berka M, Rice JA (2004) Absolute aggregation rate constants in aggregation of kaolinite measured by simultaneous static and dynamic light scattering. Langmuir 20(15):6152–6157. https://doi.org/10.1021/la049693d
Calabi-Floody M, Bendall JS, Jara AA, Welland ME, Theng BKG, Rumpel C, Mora MDLL (2011) Nanoclays from an Andisol: Extraction, properties and carbon stabilization. Geoderma 161(3–4):159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.12.013
Chen KL, Elimelech M (2009) Relating colloidal stability of fullerene (C60) nanoparticles to nanoparticle charge and electrokinetic properties. Environ Sci Technol 43(19):7270–7276. https://doi.org/10.1021/es900185p
García-García S, Wold S, Jonsson M (2007) Kinetic determination of critical coagulation concentrations for sodium-and calcium-montmorillonite colloids in NaCl and CaCl2 aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interf Sci 315(2):512–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.07.002
Ghezzi JL, Karathanasis AD, Matocha CJ, Unrine J, Thompson YL (2014) Characterization of environmental nano-and macrocolloid particles extracted from selected soils and biosolids. Appl Environ Soil Sci 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/506482
He Y, Zeng F, Lian Z, Xu J, Brookes PC (2015) Natural soil mineral nanoparticles are novel sorbents for pentachlorophenol and phenanthrene removal. Environ Pollut 205:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.05.021
He YT, Wan JM, Tokunaga T (2008) Kinetic stability of hematite nanoparticles: The effect of particle sizes. J Nanopart Res 10(2):321–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-007-9255-1
Huang D, Zhu XY, XU BL, He Y, Zhagn MK, Liu F, Lian ZH, Dahlgren RA, Brookes PC, Xu JM (2021) Changes in profile distribution and chemical properties of natural nanoparticles in paddy soils as affected by long-term rice cultivation. Pedosphere 31(05):659–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(21)60015-2
Huynh KA, Kai LC (2011) Aggregation kinetics of citrate and polyvinylpyrrolidone coated silver nanoparticles in monovalent and divalent electrolyte solutions. Environ Sci Technol 45(13):5564–5571. https://doi.org/10.1021/es200157h
Jonge LWD, Kjaergaard C, Moldrup P (2004) Colloids and colloid-facilitated transport of contaminants in soils. Vadose Zone J 3(2):321–325. https://doi.org/10.2113/3.2.321
Konrad A, Billiy B, Regenbogen P, Bol R, Lang F, Klumpp E, Siemens J (2021) Forest soil colloids enhance delivery of phosphorus into a diffusive gradient in thin films (DGT) sink. Front For Global Change 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/ffgc.2020.577364
Lead JR, Batley GE, Alvarez PJJ, Croteau M-N, Handy RD, McLaughlin MJ, Judy JD, Schirmer K (2018) Nanomaterials in the environment: Behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects—An updated review. Environ Toxicol Chem 37(8):2029–2063. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4147
Li R, Ren WJ, Teng Y, Sun Y, Xu YF, Zhao L, Wang XM, Christie P, Luo YM (2021) The inhibitory mechanism of natural soil colloids on the biodegradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by a degrading bacterium. J Hazard Mater 415:125687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125687
Li W, He Y, Wu J, Xu J (2012) Extraction and characterization of natural soil nanoparticles from Chinese soils. Eur J Soil Sci 63(5):754–761. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2012.01480.x
Lin D, Drew SS, Walker SL, Huang Q, Cai P (2016) Influence of extracellular polymeric substances on the aggregation kinetics of TiO2 nanoparticles. Water Res 104(1):381–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.08.044
Liu F, Xu B, He Y, Brookes PC, Tang C, Xu JM (2018) Differences in transport behavior of natural soil colloids of contrasting sizes from nanometer to micron and the environmental implications. Sci Total Environ 634:802e810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.381
Liu F, Xu B, He Y, Brookes PC, Xu JM (2019) Co-transport of phenanthrene and pentachlorophenol by natural soil nanoparticles through saturated sand columns. Environmental Pollution 249(JUN):406–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.052
Liu JB, Hwang YS, Lenhart JJ (2015) Heteroaggregation of bare silver nanoparticles with clay minerals. Environ Sci: Nano 2:528–540. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EN00130G
Mayer LM, Xing B (2001) Organic matter–surface area relationships in acid soils. Soil Sci Soc Am pro 65(1):250–258. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2001.651250x
Ndzana GM, Huang L, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Liu F, Bhattacharyya R (2019) The transformation of clay minerals in the particle size fractions of two soils from different latitude in China. CATENA 175:317–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.12.026
Pansu M, Gautheyrou J (2006) Handbook of soil analysis: Mineralogical, organic and inorganic methods. Springer
Petosa AR, Jaisi DP, Quevedo IR, Elimelech M, Tufenkji N (2010) Aggregation and deposition of engineered nanomaterials in aquatic environments: role of physicochemical interactions. Environ Sci Technol 44(17):6532–6549. https://doi.org/10.1021/es100598h
Pinchuk AO (2012) Size-dependent Hamaker constant for silver nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 116(37):20099–20102. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp3061784
Qafoku NP (2010) Terrestrial nanoparticles and their controls on soil-/geo-processes and reactions. Adv Agron 107(10):33–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(10)07002-1
Sano M, Okamura J, Seiji S (2001) Colloidal nature of single-walled carbon nanotubes in electrolyte solution: The Schulze-Hardy rule. Langmuir 17(22):7172–7173. https://doi.org/10.1021/la010698+
Song B, Chen M, Zhao L, Qiu H, Cao X (2019) Physicochemical property and colloidal stability of micron-and nano-particle biochar derived from a variety of feedstock sources. Sci Total Environ 661:685–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.193
Song T, Xiong ZY, Shi T, Yuan L (2021) Effect of glutamic acid on the preparation and characterization of Pickering emulsions stabilized by zein. Food Chem 366(1–2):130598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130598
Taghipour M, Jalali M (2018) Heavy metal release from some industrial wastes: Influence of organic and inorganic acids, clay minerals, and nanoparticles. Pedosphere 28:70–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(18)60005-0
Tang Y, Li H, Liu X, Zhu H, Tian R (2015) Unraveling the size distributions of surface properties for purple soil and yellow soil. J Environ Sci 32:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.12.011
Tian R, Yang G, Zhu C, Liu XM, Li H (2015) Specific anion effects for aggregation of colloidal minerals: A joint experimental and theoretical study. J Phys Chem C 119:4856–4864. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp512078v
Theng BKG, Yuan GD (2008) Nanoparticles in the Soil Environment. Elements 4:395–399. https://doi.org/10.2113/gselements.4.6.395
Wang D, Chang YX, Li YR, Zhang SL, Xu SL (2021) Well-dispersed NiCoS2 nanoparticles/rGO composite with a large specific surface area as an oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalyst. Rare Met 40(11):3156–3165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01733-0
Wang Y, Li Y, Kim H, Walker SL, Abriola LM, Pennell KD (2010) Transport and retention of fullerene nanoparticles in natural soils. J Environ Qual 39(6):1925–1933. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2009.0411
Wen X, Jin X, Wang F, You Y, Joshi RK (2019) Cation-induced coagulation in graphene oxide suspensions. Mater Today Chem 13:139–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2019.06.003
Wilson MA, Tran NH, Milev AS, Kannangara G, Volk H, Lu G (2008) Nanomaterials in soils. Geoderma 146(1):291–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2008.06.004
Xu CY, Deng KY, Li JY, Xu RK (2015) Impact of environmental conditions on aggregation kinetics of hematite and goethite nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 17(10):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3198-8
Xu CY, Zhou TT, Wang CL, Liu HY, Zhang CT, Hu FN, Zhao SW, Geng ZC (2020) Aggregation of polydisperse soil colloidal particles: Dependence of Hamaker constant on particle size. Geoderma 359:113999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.113999
Young IM, Crawford JW (2004) Interactions and self-organization in the soil-microbe complex. Science 304(5677):1634–1637. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1097394
Zamanian K, Pustovoytov K, Kuzyakov Y (2016) Pedogenic carbonates: Forms and formation processes. Earth Sci Rev 157:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.03.003
Zhang J, Guo W, Li Q, Wang Z, Liu S (2018) The effects and the potential mechanism of environmental transformation of metal nanoparticles on their toxicity in organisms. Environ Sci Nano 5(11):2482–2499. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EN00688A
Zhang Q, Yu GB, Zhou QC, Li J, Peng Y (2020) Eco-friendly interpenetrating network hydrogels integrated with natural soil colloid as a green and sustainable modifier for slow release of agrochemicals. J Clean Prod 269:122060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122060
Zhang ZY, Huang L, Liu F, Wang MK, Fu QL, Zhu J (2016) Characteristics of clay minerals in soil particles of two Alfisols in China. Appl Clay Sci 120:51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.11.018
Zhang ZY, Huang L, Liu F, Wang MK, Ndzana GM, Liu ZJ (2019) Transformation of clay minerals in nanoparticles of several zonal soils in China. J Soil Sediment 19(1):211–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2013-4
Zhou D, Ji Z, Jiang X, Darren DR, Brinker J, Keller AA (2013) Influence of material properties on TiO2 nanoparticle agglomeration. PLoS ONE 8(11):e81239. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081239
Zhu M, Wang H, Keller AA, Wang T, Li FT (2014a) The effect of humic acid on the aggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles under different pH and ionic strengths. Sci Total Environ 487:375–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.036
Zhu X, Chen H, Li W, He Y, Brookes PC, Xu J (2014b) Aggregation kinetics of natural soil nanoparticles in different electrolytes. Eur J Soil Sci 65(2):206–217. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12118
Zhu X, Chen H, Li W, He Y, Brookes PC, White R, Xu JM (2017) Evaluation of the stability of soil nanoparticles: the effect of natural organic matter in electrolyte solutions. Eur J Soil Sci 68(1):105–114. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12402
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41701261 and 41977024), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2452020165).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Dong-Mei Zhou
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, N., Xu, Cy., Geng, Zc. et al. The interplay of particle properties and solution chemistry on aggregation kinetics of soil nanoparticles. J Soils Sediments 22, 1761–1772 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03176-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03176-1