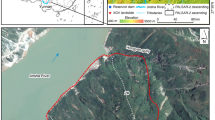
Abstract
Purpose
There are a large number of open-pit coal mines in the world, and their dependent, heterogeneous dump sites are one of the world’s largest chronic waste concerns. The long-term existence of dumps is vulnerable to non-uniform deformation and erosion simultaneously, seriously threatening also the surrounding geological and ecological security. Hence, it is critical to monitor the potential geologic hazards erosion activity of such a large, unstable accumulation.
Materials and methods
In this study, topographic observations were performed using the Terrain Observation by Progressive Scans (TOPS) mode of the up-to-date high-quality synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images from the Sentinel-1B (S-1B) satellite, while unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) photogrammetric data were used to assist in phase unwrapping, showing the deformation and soil erosion of the Baorixile open-pit coal mine dump in China from September 2016 to September 2019. At the same time, the possible areas of geological disasters were predicted, and the formation mechanism of different types of erosion was analyzed.
Results and discussion
The validation indicates that the deformation monitoring results by S-1B data matched well with the measured value. The soil consolidation has a positive effect on improving dump geological stability, while soil erosion has the opposite effect. The high correlation between accumulation consolidation and stacking height was used to distinguish soil consolidation and soil erosion from total deformation. The dump has undergone subsidence and/or erosion under gravity and non-gravity factors. The overall cumulative vertical subsidence and slope deformation ranged from 12 to − 298 mm (negative values indicate that the target moved away from the sensor) and from 4 to 365 mm, respectively. The deformation was aggravated with the increase of the stacking height of the dump site, especially at the edge of the top area. Soil erosion and slope instability were the results of the combined action of multiple factors, such as spring snowmelt erosion, summer (rainy season) surface runoff erosion and internal seepage erosion, autumn wind erosion, and winter frost heaving erosion. Potential slope destabilization hazards and hidden danger areas of slope instability need continuous attention.
Conclusion
In summary, the deformation analysis suggests that the collaborative application of S-1B SAR image and UAV photogrammetric data demonstrates the practicability of the fine deformation monitoring service in the dump site and can be a useful tool for long-term continuous deformation and soil erosion monitoring.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ban YY, Lei TW, Liu ZQ, Chen C (2017) Comparative study of erosion processes of thawed and non-frozen soil by concentrated meltwater flow. Catena 148:153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.06.019
Berardino P, Fornaro G, Lanari R, Sansosti E (2002) A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 40:2375–2383. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792
Bian Z, Dong J, Lei S, Leng H, Mu S, Wang H (2009) The impact of disposal and treatment of coal mining wastes on environment and farmland. Environ Geol 58:625–634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1537-0
Bian Z, Miao X, Lei S, Chen SE, Wang W (2012) The challenges of reusing mining and mineral-processing wastes. Science 337:702–703. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1224757
Brooks SM, Crozier MJ, Preston NJ, Anderson MG (2002) Regolith stripping and the control of shallow translational hillslope failure: application of a two-dimensional coupled soil hydrology-slope stability model, Hawke’s Bay, New Zealand. Geomorphology 45:165–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-555X(01)00153-2
Cascini L, Fornaro G, Peduto D (2010) Advanced low- and full-resolution DInSAR map generation for slow-moving landslide analysis at different scales. Eng Geol 112:29–42
Caviezel C, Hunziker M, Schaffner M, Kuhn NJ (2014) Soil-vegetation interaction on slopes with bush encroachment in the central Alps - adapting slope stability measurements to shifting process domains. Earth Surf Proc Land 39:509–521. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3513
Cheng W, Lei S, Bian Z, Zhao Y, Li Y, Gan Y (2020) Geographic distribution of heavy metals and identification of their sources in soils near large, open-pit coal mines using positive matrix factorization. J Hazard Mater 387:121666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121666
Costantini M (1998) A novel phase unwrapping method based on network programming. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 36:813–821. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.673674
Costantini M, Falco S, Malvarosa F, Minati F (2008) A new method for identification and analysis of persistent scatterers in series of SAR images. IEEE Int Geosci Remote Sens Symp. IEEE, pp. II-449-II-452. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2008.4779025
Dai K, Li Z, Tomás R, Liu G, Yu B, Wang X, Cheng H, Chen J, Stockamp J (2016) Monitoring activity at the Daguangbao mega-landslide (China) using Sentinel-1 TOPS time series interferometry. Remote Sens Environ 186:501–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.09.009
Dawson RF, Morgenstern NR, Stokes AW (1998) Liquefaction flowslides in Rocky Mountain coal mine waste dumps. Can Geotech J 32:328–343. https://doi.org/10.1139/t98-009
Diao X, Diao X, Wu K, Hu D, Li L, Zhou D (2016) Combining differential SAR interferometry and the probability integral method for three-dimensional deformation monitoring of mining areas. Int J Remote Sens 37:5196–5212. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2016.1230284
Du Z, Ge L, Ng AH, Zhu Q, Horgan FG, Zhang Q (2020) Risk assessment for tailings dams in Brumadinho of Brazil using InSAR time series approach. Sci Total Environ 717:137125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137125
Feng W, Lindsey E, Barbot S, Samsonov S, Dai K, Li P, Li Z, Almeida R, Chen J, Xu X (2017) Source characteristics of the 2015 MW 7.8 Gorkha (Nepal) earthquake and its MW 7.2 aftershock from space geodesy. Tectonophysics 712–713:747–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2016.02.029
Feng Y, Wang J, Bai Z, Reading L (2019) Effects of surface coal mining and land reclamation on soil properties: A review. Earth Sci Rev 191:12–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.02.015
Forkuor G, Benewinde Zoungrana J, Dimobe K, Ouattara B, Vadrevu KP, Tondoh JE (2020) Above-ground biomass mapping in West African dryland forest using Sentinel-1 and 2 datasets - a case study. Remote Sens Environ 236:111496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111496
Galloway DL, Hoffmann J (2007) The application of satellite differential SAR interferometry-derived ground displacements in hydrogeology. Hydrogeol J 15:133–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-006-0121-5
Genet M, Stokes A, Fourcaud T, Norris JE (2010) The influence of plant diversity on slope stability in a moist evergreen deciduous forest. Ecol Eng 36:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2009.05.018
Goldstein RM, Werner CL (1998) Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Geophys Res Lett 25:4035–4038. https://doi.org/10.1029/1998GL900033
Gong C, Lei S, Bian Z, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Cheng W (2019a) Analysis of the development of an erosion gully in an open-pit coal mine dump during a winter freeze-thaw cycle by using low-cost UAVs. Remote Sensing 11:1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11111356
Gong W, Darrow MM, Meyer FJ, Daanen RP (2019b) Reconstructing movement history of frozen debris lobes in northern Alaska using satellite radar interferometry. Remote Sens Environ 221:722–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2018.12.014
Haghshenas Haghighi M, Motagh M (2019) Ground surface response to continuous compaction of aquifer system in Tehran, Iran: Results from a long-term multi-sensor InSAR analysis. Remote Sens Environ 221:534–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2018.11.003
Herrera G, Gutiérrez F, García-Davalillo JC, Guerrero J, Notti D, Galve JP, Fernández-Merodo JA, Cooksley G (2013) Multi-sensor advanced DInSAR monitoring of very slow landslides: the Tena Valley case study (Central Spanish Pyrenees). Remote Sens Environ 128:31–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2012.09.020
Hess DM, Leshchinsky BA, Bunn M, Benjamin Mason H, Olsen MJ (2017) A simplified three-dimensional shallow landslide susceptibility framework considering topography and seismicity. Landslides 14:1677–1697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-017-0810-2
Hooper A, Zebker HA (2007) Phase unwrapping in three dimensions with application to InSAR time series. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci vis 24:2737–2747. https://doi.org/10.1364/josaa.24.002737
Johansen K, Erskine PD, McCabe MF (2019) Using unmanned aerial vehicles to assess the rehabilitation performance of open cut coal mines. J Clean Prod 209:819–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.287
Kainthola A, Singh PK, Singh TN (2015) Stability investigation of road cut slope in basaltic rockmass, Mahabaleshwar, India. Geosci Front 6:837–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2014.03.002
Kim J, Lu Z, Jia Y, Shum CK (2015) Ground subsidence in Tucson, Arizona, monitored by time-series analysis using multi-sensor InSAR datasets from 1993 to 2011. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 107:126–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.03.013
Kondratyeva LM, Makhinov AN, Andreeva DV, Bashkurova AS (2020) Changes in water quality in the bureiskoe reservoir caused by a large landslide. Water Resour 47:257–268. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807820020086
Krieger L, Floricioiu D, Neckel N (2020) Drainage basin delineation for outlet glaciers of Northeast Greenland based on Sentinel-1 ice velocities and TanDEM-X elevations. Remote Sens Environ 237:111483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111483
Kværnø SH, Øygarden L (2006) The influence of freeze-thaw cycles and soil moisture on aggregate stability of three soils in Norway. CATENA 67:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2006.03.011
Ma P, Wang W, Zhang B, Wang J, Shi G, Huang G, Chen F, Jiang L, Lin H (2019) Remotely sensing large- and small-scale ground subsidence: a case study of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area of China. Remote Sens Environ 232:111–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111282
Mazzotti S, Lambert A, Van der Kooij M, Mainville A (2009) Impact of anthropogenic subsidence on relative sea-level rise in the Fraser River delta. Geology 37:771–774. https://doi.org/10.1130/G25640A.1
Nannini M, Prats-Iraola P, De Zan F, Geudtner D (2016) TOPS time series performance assessment with TerraSAR-X data. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 9:3832–3848. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2508062
Ng AH, Ge L, Du Z, Wang S, Ma C (2017) Satellite radar interferometry for monitoring subsidence induced by longwall mining activity using Radarsat-2, Sentinel-1 and ALOS-2 data. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 61:92–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2017.05.009
Notti D, Herrera G, Bianchini S, Meisina C, Garcia-Davalillo JC, Zucca F (2014) A methodology for improving landslide PSI data analysis. Int J Remote Sens 35:2186–2214
Nyssen J, Vermeersch D (2010) Slope aspect affects geomorphic dynamics of coal mining spoil heaps in Belgium. Geomorphology 123:109–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2010.07.004
Rahardjo H, Satyanaga A, Leong EC, Santoso VA, Ng YS (2014) Performance of an instrumented slope covered with shrubs and deep-rooted grass. Soils Found 54:417–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2014.04.010
Raspini F, Bianchini S, Ciampalini A, Del Soldato M, Solari L, Novali F, Del Conte S, Rucci A, Ferretti A, Casagli N (2018) Continuous, semi-automatic monitoring of ground deformation using Sentinel-1 satellites. Sci Rep 8:7253–7311. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25369-w
Rezaei A, Mousavi Z (2019) Characterization of land deformation, hydraulic head, and aquifer properties of the Gorgan confined aquifer, Iran, from InSAR observations. J Hydrol 579:124196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124196
Ribeiro J, Taffarel SR, Sampaio CH, Flores D, Silva LFO (2013) Mineral speciation and fate of some hazardous contaminants in coal waste pile from anthracite mining in Portugal. Int J Coal Geol 109–110:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2013.01.007
Rucci A, Ferretti A, Monti Guarnieri A, Rocca F (2012) Sentinel 1 SAR interferometry applications: The outlook for sub millimeter measurements. Remote Sens Environ 120:156–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.09.030
Salameh E, Frappart F, Turki I, Laignel B (2020) Intertidal topography mapping using the waterline method from Sentinel-1 & -2 images: the examples of Arcachon and Veys Bays in France. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 163:98–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.03.003
Sarmap SA (2009) Synthetic aperture radar and SARscape: SAR guidebook, Purasca, Switzerland, 274 pp
Schmidt DA, Bürgmann R (2003) Time-dependent land uplift and subsidence in the Santa Clara valley, California, from a large interferometric synthetic aperture radar data set. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 108:4–1–4–13. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JB002267
Shi XS, Herle I, Muir Wood D (2018) A consolidation model for lumpy composite soils in open-pit mining. Géotechnique 68:189–204. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.16.P.054
Silvia B, Gerardo H, Rosa M, Davide N, Inmaculada G, Oscar M, Sandro M (2013) Landslide activity maps generation by means of persistent scatterer interferometry. Remote Sensing 5:6198–6222
Stokes A, Atger C, Bengough AG, Fourcaud T, Sidle RC (2009) Desirable plant root traits for protecting natural and engineered slopes against landslides. Plant Soil 324:1–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0159-y
Sun BY, Xiao JB, Li ZB, Ma B, Zhang LT, Huang YL, Bai LF (2018) An analysis of soil detachment capacity under freeze-thaw conditions using the Taguchi method. CATENA 162:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.11.025
Tarolli P, Sofia G (2016) Human topographic signatures and derived geomorphic processes across landscapes. Geomorphology 255:140–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.12.007
Torres R, Snoeij P, Geudtner D, Bibby D, Davidson M, Attema E, Potin P, Rommen B, Floury N, Brown M, Traver IN, Deghaye P, Duesmann B, Rosich B, Miranda N, Bruno C, L’Abbate M, Croci R, Pietropaolo A, Huchler M, Rostan F (2012) GMES Sentinel-1 mission. Remote Sens Environ 120:9–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.05.028
Wang J, Ouyang J, Zhang M (2020) Spatial distribution characteristics of soil and vegetation in a reclaimed area in an opencast coalmine. CATENA 195:104773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104773
Wasowski J, Bovenga F (2014) Investigating landslides and unstable slopes with satellite multi temporal interferometry: current issues and future perspectives. Eng Geol 174:103–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.03.003
Westoby MJ, Brasington J, Glasser NF, Hambrey MJ, Reynolds JM (2012) ‘Structure-from-Motion’ photogrammetry: a low-cost, effective tool for geoscience applications. Geomorphology 179:300–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.08.021
Wu Y, Ouyang W, Hao Z, Yang B, Wang L (2018) Snowmelt water drives higher soil erosion than rainfall water in a mid-high latitude upland watershed. J Hydrol 556:438–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.11.037
Xiang T, Xia G, Zhang L (2019) Mini-unmanned aerial vehicle-based remote sensing: techniques, applications, and prospects. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine 7:29–63. https://doi.org/10.1109/MGRS.2019.2918840
Yague-Martinez N, Prats-Iraola P, Rodriguez Gonzalez F, Brcic R, Shau R, Geudtner D, Eineder M, Bamler R (2016) Interferometric processing of Sentinel-1 TOPS Data. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54:2220–2234. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2015.2497902
Zhang X, Zhang H, Wang C, Tang Y, Zhang B, Wu F, Wang J, Zhang Z (2019) Time-series InSAR monitoring of permafrost freeze-thaw seasonal displacement over Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau using Sentinel-1 data. Remote Sensing 11:1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11091000
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the ongoing support provided by Shenhua Baorixile Energy Ind. Co. Ltd. And we are grateful to the European Space Agency and the US Geological Survey for their open data policy.
Funding
This research was funded by National Key Research and Development Program of China under Grant No. 2016YFC0501107.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Marcel van der Perk
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, C., Lei, S., Bian, Z. et al. Using time series InSAR to assess the deformation activity of open-pit mine dump site in severe cold area. J Soils Sediments 21, 3717–3732 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-03040-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-03040-8