Abstract
Purpose
In southern China, Cd-tainted rice produced in Cd-contaminated acidic paddy soils is a serious health concern. Thus, it is essential and urgent to remediate Cd-contaminated soils and reduce Cd accumulation in rice grains for food safety and human health.
Materials and methods
Four soil amendments (e.g., lime, biochar, soil conditioner, and seaweed organic fertilizer) combined with two rice cultivars (Yongyou17, YY-17; and Xiushui09, XS-09) with different Cd accumulation abilities were selected to evaluate the efficacy of safe utilization in a slightly moderately Cd-contaminated paddy soil.
Results and discussion
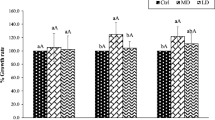
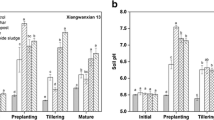
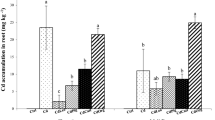
Results showed that soil amendments significantly increased soil pH and reduced Cd bioavailability compared with the control. Linear regression analysis showed that the decrease in Cd bioavailability was significantly and positively correlated with soil pH increase (P < 0.001). Soil amendments were efficient in reducing Cd uptake by rice root as well as translocation from root to aboveground plant parts. The Cd concentrations in brown rice of YY-17 and XS-09 were 0.34 and 0.22 mg kg−1 for control treatments, respectively, while the Cd concentrations of rice grain using were reduced by 45 to 88% and 55 to 88% soil amendments for two cultivars. Considering the costs and efficiency of soil amendments, the soil conditioner was the best amendment.
Conclusions
In situ immobilization combined with low-Cd-accumulation rice cultivar is an effective approach for food safety in lightly moderately Cd-contaminated acidic paddy soils.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad-Valle P, Iglesias-Jimenez E, Alvarez-Ayuso E (2017) A comparative study on the influence of different organic amendments on trace element mobility and microbial functionality of a polluted mine soil. J Environ Manag 188:287–296
Ahmad M, Rajapaksha AU, Lim JE, Zhang M, Bolan N, Mohan D, Vithanage M, Lee SS, Ok YS (2014) Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: a review. Chemosphere 99:19–33
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals—concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91(7):869–881
Alloway BJ (2013) Heavy metals in soils: trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability (third edition). Springer Science+Business Media, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/9789400744707
Antoniadis V, Robinson JS, Alloway BJ (2008) Effects of short-term pH fluctuations on cadmium, nickel, lead, and zinc availability to ryegrass in a sewage sludge-amended field. Chemosphere 71(4):759–764
Bashir S, Zhu J, Fu QL, Hu HQ (2018) Comparing the adsorption mechanism of Cd by rice straw pristine and KOH-modified biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(12):11875–11883
Bian RJ, Joseph S, Cui LQ, Pan GX, Li LQ, Liu XY, Zhang AF, Rutlidge H, Wong S, Chia C, Marjo C, Gong B, Munroe P, Donne S (2014) A three-year experiment confirms continuous immobilization of cadmium and lead in contaminated paddy field with biochar amendment. J Hazard Mater 272:121–128
Bian RJ, Li LQ, Bao DD, Zheng JW, Zhang XH, Zheng JF, Liu XY, Cheng K, Pan GX (2016) Cd immobilization in a contaminated rice paddy by inorganic stabilizers of calcium hydroxide and silicon slag and by organic stabilizer of biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(10):10028–10036
Bolan NS, Adriano DC, Curtin D (2003a) Soil acidification and liming interactions with nutrient and heavy metal transformation and bioavailability. Adv Agron 78(21):215–272
Bolan NS, Adriano DC, Mani PA, Duraisamy A (2003b) Immobilization and phytoavailability of cadmium in variable charge soils. II. Effect of lime addition. Plant Soil 251(2):187–198
Bolan NS, Makino T, Kunhikrishnan A, Kim P, Ishikawa S, Murakami M, Naidu R, Kirkham MB (2013) Cadmium contamination and its risk management in rice ecosystems. In: Sparks DL (ed) Advances in agronomy. Academic, New York, pp 183–273
Bolan N, Kunhikrishnan A, Thangarajan R, Kumpiene J, Park J, Makino T, Kirkham MB, Scheckel K (2014) Remediation of heavy metal(loid)s contaminated soils—to mobilize or to immobilize? J Hazard Mater 266:141–166
Brown S, Chaney R, Hallfrisch J, Ryan JA, Berti WR (2004) In situ soil treatments to reduce the phyto- and bioavailability of lead, zinc, and cadmium. J Environ Qual 33(2):522–531
Brown S, Christensen B, Lombi E, McLaughlin M, McGrath S, Colpaert J, Vangronsveld J (2005) An inter-laboratory study to test the ability of amendments to reduce the availability of Cd, Pb, and Zn in situ. Environ Pollut 138(1):34–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.02.020
Buekers J, Degryse F, Maes A, Smolders E (2008) Modelling the effects of ageing on Cd, Zn, Ni and Cu solubility in soils using an assemblage model. Eur J Soil Sci 59(6):1160–1170
Cao XD, Wahbi A, Ma L, Li B, Yang YL (2009) Immobilization of Zn, Cu, and Pb in contaminated soils using phosphate rock and phosphoric acid. J Hazard Mater 164(2–3):555–564
Chen SB, Xu MG, Ma YB, Yang JC (2007) Evaluation of different phosphate amendments on availability of metals in contaminated soil. Ecotox Environ Safe 67(2):278–285
Chen D, Guo H, Li RY, Li LQ, Pan GX, Chang A, Joseph S (2016) Low uptake affinity cultivars with biochar to tackle Cd-tainted rice—a field study over four rice seasons in Hunan, China. Sci Total Environ 541:1489–1498
Contin M, Mondini C, Leita L, Nobili MD (2007) Enhanced soil toxic metal fixation in iron (hydr) oxides by redox cycles. Geoderma 140(1–2):164–175
Cui HB, Fan YC, Xu L, Zhou J, Zhou DM, Mao JD, Fang GD, Cang L, Zhu ZQ (2016) Sustainability of in situ remediation of Cu- and Cd-contaminated soils with one-time application of amendments in Guixi, China. J Soils Sediments 16(5):1498–1508
Degryse F, Smolders E, Parker DR (2009) Partitioning of metals (Cd, Co, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) in soils: concepts, methodologies, prediction and applications—a review. Eur J Soil Sci 60:590–612
Doan TT, Henry-des-Tureaux T, Rumpel C, Janeau J, Jouquet P (2015) Impact of compost, vermicompost and biochar on soil fertility, maize yield and soil erosion in northern Vietnam: a three year mesocosm experiment. Sci Total Environ 514:147–154
García-Carmona M, Romero-Freire A, Sierra Aragón M, Martínez Garzón FJ, Martín Peinado FJ (2017) Evaluation of remediation techniques in soils affected by residual contamination with heavy metals and arsenic. J Environ Manag 191:228–236
Godt J, Scheidig F, Grosse-Siestrup C, Esche V, Brandenburg P, Reich A, Groneberg DA (2006) The toxicity of cadmium and resulting hazards for human health. J Occup Med Toxicol 1(1):22
Gu HL, Qiu H, Tian T, Zhan SS, Deng THB, Chaney RL, Wang SR, Tang YT, Morel JL, Qiu RL (2011) Mitigation effects of silicon rich amendments on heavy metal accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) planted on multi-metal contaminated acidic soil. Chemosphere 83(9):1234–1240
Guo JH, Liu XJ, Zhang Y, Shen JL, Han WX, Zhang WF, Christie P, Goulding KWT, Vitousek PM, Zhang FS (2010) Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 327(5968):1008–1010
Hale B, Evans L, Lambert R (2012) Effects of cement or lime on Cd, Co, Cu, Ni, Pb, Sb and Zn mobility in field-contaminated and aged soils. J Hazard Mater 199:119–127
Harter RD, Naidu R (1995) Role of metal-organic complexation in metal sorption by soils. In: Sparks DL (ed) Advances in agronomy. Academic, New York, pp 219–263
Hartley W, Edwards R, Lepp NW (2004) Arsenic and heavy metal mobility in iron oxide-amended contaminated soils as evaluated by short- and long-term leaching tests. Environ Pollut 131(3):495–504
He YB, Huang DY, Zhu QH, Wang S, Liu SL, He HB, Zhu HH, Xu C (2017) A three-season field study on the in-situ remediation of Cd-contaminated paddy soil using lime, two industrial by-products, and a low-Cd-accumulation rice cultivar. Ecotox Environ Safe 136:135–141
Houben D, Evrard L, Sonnet P (2013) Mobility, bioavailability and pH-dependent leaching of cadmium, zinc and lead in a contaminated soil amended with biochar. Chemosphere 92(11):1450–1457
Khan S, Reid BJ, Li G, Zhu YG (2014) Application of biochar to soil reduces cancer risk via rice consumption: a case study in Miaoqian village, Longyan, China. Environ Int 68:154–161
Kördel W, Bernhardt C, Derz K, Hund-Rinke K, Harmsen J, Peijnenburg W, Comans R, Terytze K (2013) Incorporating availability/bioavailability in risk assessment and decision making of polluted sites, using Germany as an example. J Hazard Mater 261:854–862
Kostarelos K, Reale D, Dermatas D, Rao E, Moon DH (2006) Optimum dose of lime and fly ash for treatment of hexavalent chromium–contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 6(1–2):171–189
Lee TM, Lai HY, Chen ZS (2004) Effect of chemical amendments on the concentration of cadmium and lead in long-term contaminated soils. Chemosphere 57(10):1459–1471
Li RY, Stroud JL, Ma JF, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2009) Mitigation of arsenic accumulation in rice with water management and silicon fertilization. Environ Sci Technol 43(10):3778–3783
Li HY, Ye XX, Geng ZG, Zhou HJ, Guo XS, Zhang YX, Zhao HJ, Wang GZ (2016) The influence of biochar type on long-term stabilization for Cd and Cu in contaminated paddy soils. J Hazard Mater 304:40–48
Liang XF, Han J, Xu YM, Sun YB, Wang L, Tan X (2014) In situ field-scale remediation of Cd polluted paddy soil using sepiolite and palygorskite. Geoderma 235-236:9–18
Liu CP, Li FB, Luo CL, Liu XM, Wang SH, Liu TX, Li XD (2009) Foliar application of two silica sols reduced cadmium accumulation in rice grains. J Hazard Mater 161(2–3):1466–1472
Lombi E, Hamon RE, McGrath SP, McLaughlin MJ (2003) Lability of Cd, Cu, and Zn in polluted soils treated with lime, beringite, and red mud and identification of a non-labile colloidal fraction of metals using isotopic techniques. Environ Sci Technol 37(5):979–984
McBride MB (2002) Cadmium uptake by crops estimated from soil total Cd and pH. Soil Sci 167(1):62–67
Meers E, Samson R, Tack FMG, Ruttens A, Vandegehuchte M, Vangronsveld J, Verloo MG (2007) Phytoavailability assessment of heavy metals in soils by single extractions and accumulation by Phaseolus vulgaris. Environ Exp Bot 60(3):385–396
Meng J, Zhong LB, Wang L, Liu XM, Tang CX, Chen HJ, Xu JM (2018) Contrasting effects of alkaline amendments on the bioavailability and uptake of Cd in the rice plants in a Cd-contaminated acid paddy soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(9):8827–8835
Mignardi S, Corami A, Ferrini V (2012) Evaluation of the effectiveness of phosphate treatment for the remediation of mine waste soils contaminated with Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn. Chemosphere 86(4):354–360
Mühlbachová G, Simon T, Pechová M (2005) The availability of Cd, Pb and Zn and their relationships with soil pH and microbial biomass in soils amended by natural clinoptilolite. Plant Soil Environ 51(1):26–33
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001) Remediation technologies for metal-contaminated soils and groundwater: an evaluation. Eng Geol 60(1–4):193–207
Naidu R, Bolan NS, Kookana RS, Tiller KG (1994) Ionic strength and pH effects on surface charge and Cd sorption characteristics of soils. Eur J Soil Sci 45:419–429
Ning DF, Liang YC, Song AL, Duan AW, Liu ZD (2016) In situ stabilization of heavy metals in multiple-metal contaminated paddy soil using different steel slag-based silicon fertilizer. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(23):23638–23647
Novozamsky I, Lexmond TM, Houba VJG (1993) A single extraction procedure of soil for evaluation of uptake of some heavy metals by plants. Int J Environ An Ch 51(1–4):47–58
Pietrzykowski M, Socha J, van Doorn NS (2014) Linking heavy metal bioavailability (Cd, Cu, Zn and Pb) in scots pine needles to soil properties in reclaimed mine areas. Sci Total Environ 470-471:501–510
Porter SK, Scheckel KG, Impellitteri CA, Ryan JA (2004) Toxic metals in the environment: thermodynamic considerations for possible immobilization strategies for Pb, Cd, As, and Hg. Crit Rev Environ Sci Tec 34(6):495–604
Rafiq MT, Aziz R, Yang XE, Xiao WD, Rafiq MK, Ali B, Li TQ (2014) Cadmium phytoavailability to rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown in representative Chinese soils. A model to improve soil environmental quality guidelines for food safety. Ecotox Environ Safe 103:101–107
Römkens PFAM, Brus DJ, Guo HY, Chu CL, Chiang CM, Koopmans GF (2011) Impact of model uncertainty on soil quality standards for cadmium in rice paddy fields. Sci Total Environ 409(17):3098–3105
Shaheen SM, Rinklebe J (2015) Impact of emerging and low cost alternative amendments on the (im)mobilization and phytoavailability of Cd and Pb in a contaminated floodplain soil. Ecol Eng 74:319–326
Udeigwe TK, Eze PN, Teboh JM, Stietiya MH (2011) Application, chemistry, and environmental implications of contaminant-immobilization amendments on agricultural soil and water quality. Environ Int 37(1):258–267
Wang AS, Angle JS, Chaney RL, Delorme TA, Reeves RD (2006) Soil pH effects on uptake of Cd and Zn by Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant Soil 281(1–2):325–337
Wang HY, Wen SL, Chen P, Zhang L, Cen K, Sun GX (2016) Mitigation of cadmium and arsenic in rice grain by applying different silicon fertilizers in contaminated fields. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(4):3781–3788
Williams PN, Lei M, Sun GX, Huang Q, Lu Y, Deacon C, Meharg AA, Zhu YG (2009) Occurrence and partitioning of cadmium, arsenic and lead in mine impacted paddy rice: Hunan, China. Environ Sci Technol 43(3):637–642
Wu G, Kang HB, Zhang XY, Shao HB, Chu LY, Ruan CJ (2010) A critical review on the bio-removal of hazardous heavy metals from contaminated soils: issues, progress, eco-environmental concerns and opportunities. J Hazard Mater 174(1–3):1–8
Wuana RA, Okieimen FE (2011) Heavy metals in contaminated soils: a review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. Isrn Ecology 2011:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.113
Xu XY, Cao XD, Zhao L (2013) Comparison of rice husk- and dairy manure-derived biochars for simultaneously removing heavy metals from aqueous solutions: role of mineral components in biochars. Chemosphere 92(8):955–961
Yang Y, Wang ME, Chen WP, Li YL, Peng C (2017) Cadmium accumulation risk in vegetables and rice in southern China: insights from solid-solution partitioning and plant uptake factor. J Agric Food Chem 65(27):5463–5469
Yu HY, Liu CP, Zhu JS, Li FB, Deng DM, Wang Q, Liu CS (2016) Cadmium availability in rice paddy fields from a mining area: the effects of soil properties highlighting iron fractions and pH value. Environ Pollut 209:38–45
Zeng FR, Ali S, Zhang HT, Ouyang YN, Qiu BY, Wu FB, Zhang GP (2011) The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environ Pollut 159(1):84–91
Zhang WL, Du Y, Zhai MM, Shang Q (2014) Cadmium exposure and its health effects: a 19-year follow-up study of a polluted area in China. Sci Total Environ 470-471:224–228
Zhao KL, Liu XM, Xu JM, Selim HM (2010) Heavy metal contaminations in a soil–rice system: identification of spatial dependence in relation to soil properties of paddy fields. J Hazard Mater 181(1–3):778–787
Zhao FJ, Ma YB, Zhu YG, Tang Z, McGrath SP (2015) Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation strategies. Environ Sci Technol 49(2):750–759
Zhu QH, Huang DY, Liu SL, Zhou B, Luo ZC, Zhu HH (2012) Flooding-enhanced immobilization effect of sepiolite on cadmium in paddy soil. J Soils Sediments 12(2):169–177
Zhu HH, Chen C, Xu C, Zhu QH, Huang DY (2016) Effects of soil acidification and liming on the phytoavailability of cadmium in paddy soils of central subtropical China. Environ Pollut 219:99–106
Acknowledgements
This work was jointly supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0200106) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41571450 and 41721001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ravi Naidu
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 101 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, L., Huang, T., Shi, J. et al. Decreasing cadmium uptake of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in the cadmium-contaminated paddy field through different cultivars coupling with appropriate soil amendments. J Soils Sediments 19, 1788–1798 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2186-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2186-x