Abstract
Purpose
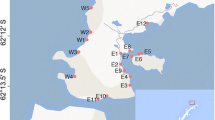
Spatial distribution on a regional scale of the rhizobacterial communities of Phragmites australis stands was investigated along the Yellow River watershed, China.
Materials and methods
Samples were collected along a secondary and the main drainage canals. Amplified ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis (ARISA) and pyrosequencing were performed to study the diversity of microbial communities. Bacterial functionality was characterized using a functional inference-based (Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States, PICRUSt) approach.
Results and discussion
Microbial community structure resulted to be primarily driven by phosphorus, nitrogen, mercury, chromium, and nickel. At genus level, taxa related to bioremediation, in particular Thiobacillus and Flavobacterium, and plant growth-promoting bacteria, such as Lysobacter, were found to be stably associated with P. australis. Genera related to fecal contamination such as Faecalibacterium, were recorded in three sampling sites. Rhizobacterial communities showed a significant fraction of taxa related to the xenobiotic metabolism and degradation.
Conclusions
Rhizobacterial communities were influenced by the multiple effects of the different environmental parameters. Moreover, the rhizosphere of P. australis can be considered potentially a source of bacterial taxa useful for bioremediation and growth-promoting activities of plants.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barton DN (2005) Report: economic analysis of the value of water in alternative uses in the Lake Wuliangsuhai catchment, Norwegian Institute of Water Research
BCPG (2010) Wuliangsuhai comprehensive treatment plan (Wuliangsuhai Zonghe Zhili Guihua). Bayannur City People’s Government, Bayannur
Besemer K (2015) Biodiversity, community structure and function of biofilms in stream ecosystems. Res Microbiol 166:774–781
Brusetti L, Borruso L (2014) Diversity and role of rhizobacteria associated to reed stands (Phragmites australis). In: Cirella GT, Zerbe S (eds) Sustainable water management and wetland restoration strategies in northern China. Bu Press, Bozen-Bolzano, pp. 83–93
Cardinale M, Brusetti L, Quatrini P, Borin S, Puglia AM, Rizzi A, Zanardini E, Sorlini C, Corselli C, Daffonchio D (2004) Comparison of different primer sets for use in automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis of complex bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6147–6156
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:33–56
Chaudhry Q, Schröder P, Werck-Reichhart D, Grajek W, Marecik R (2002) Prospects and limitations of phytoremediation for the removal of persistent pesticides in the environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 9:4–17
Clevering OA, Lissner J (1999) Taxonomy, chromosome numbers, clonal diversity and population dynamics of Phragmites australis. Aquat Bot 64:185–208
Cruz AF, Hamel C, Hanson K, Selles F, Zentner RP (2009) Thirty-seven years of soil nitrogen and phosphorus fertility management shapes the structure and function of the soil microbial community in a Brown Chernozem. Plant Soil 315:173–184
Coban O, Kuschk P, Kappelmeyer U, Spott O, Martienssen M, Jetten MS, Knoeller K (2015) Nitrogen transforming community in a horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetland. Water Res 74:203–212
Dash S, Jin C, Lee OO, Xu Y, Qian PY (2009) Antibacterial and antilarval-settlement potential and metabolite profiles of novel sponge-associated marine bacteria. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:1047–1056
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200
Ellis RJ, Neish B, Trett MW, Best JG, Weightman AJ, Morgan P, Fry JC (2001) Comparison of microbial and meiofaunal community analyses for determining impact of heavy metal contamination. J Microbiol Methods 45:171–185
Fernandes JP, Almeida CM, Pereira AC, Ribeiro IL, Reis I, Carvalho P, Basto MC, Mucha AP (2015) Microbial community dynamics associated with veterinary antibiotics removal in constructed wetlands microcosms. Bioresour Technol 182:26–33
Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. PNAS 103:626–631
Glick BR (2010) Using soil bacteria to facilitate phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 28:367–374
Gomez C, Bosecker K (1999) Leaching heavy metals from contaminated soil by using Thiobacillus ferrooxidans or Thiobacillus thiooxidans. Geomicrobiol J 16:233–244
Güsewell S, Klötzli F (2000) Assessment of aquatic and terrestrial reed (Phragmites australis) stands. Wetl Ecol Manag 8:367–373
Hazrat A, Ezzat K, Muhammad AS (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals—concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881
Hernández M, Dumont MG, Yuan Q, Conrad R (2015) Different bacterial populations associated with the roots and rhizosphere of rice incorporate plant-derived carbon. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:2244–2253
Jog R, Pandya M, Nareshkumar G, Rajkumar S (2014) Mechanism of phosphate solubilization and antifungal activity of Streptomyces spp. isolated from wheat roots and rhizosphere and their application in improving plant growth. Microbiology 160:778–788
Kleindienst S, Herbst FA, Stagars M, Frederick N, Bergen M, Seifert J, Peplies J, Amann R, Musat F, Lueders T, Knittel K (2014) Diverse sulfate-reducing bacteria of the Desulfosarcina/Desulfococcus clade are the key alkane degraders at marine seeps. Isme J 8:2029–2044
Köbbing JF, Thevs N, Zerbe S (2013) The utilisation of reed (Phragmites australis): a review. Mires Peat 13:1–14
Langille MGI, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG, McDonald D, Knights D, Reyes JA, Clemente JC, Burkepile DE, Vega Thurber RL, Knight R, Beiko RG, Huttenhower C (2013) Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat Biotechnol 31:814–821
Lauber CL, Hamady M, Knight R, Fierer N (2009) Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community composition at the continental scale. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:5111–5120
Lawrence JR, Chenier MR, Roy R, Beaumier D, Fortin N, Swerhone GDW, Neu TR, Greer CW (2004) Microscale and molecular assessment of impacts of nickel, nutrients, and oxygen level on structure and function of river biofilm communities microscale and molecular assessment of impacts of nickel, nutrients, and oxygen level on structure and function of river biofilm communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4326–4339
Lear G, Lewis GD (2009) Impact of catchment land use on bacterial communities within stream biofilms. Ecol Indic 9:848–855
Li YH, Zhu JN, Zhai ZH, Zhang Q (2010) Endophytic bacterial diversity in roots of Phragmites australis in constructed Beijing Cuihu wetland (China). FEMS Microbiol Lett 309:84–93
Ma Y, Prasad MNV, Rajkumar M, Freitas H (2011) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and endophytes accelerate phytoremediation of metalliferous soils. Biotechnol Adv 29:248–258
Micsinai A, Borsodi AK, Csengeri V, Horváth A, Oravecz O, Nikolausz M, Reskóné MN, Márialigeti K (2003) Rhizome-associated bacterial communities of healthy and declining reed stands in Lake Velencei, Hungary. Hydrobiologia 509:707–713
Mothes F, Reiche N, Fiedler P, Moeder M, Borsdorf H (2010) Capability of headspace based sample preparation methods for the determination of methyl tert-butyl ether and benzene in reed (Phragmites australis) from constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 80:396–403
Muhammad AQ, Khan QM, Sessitsch A (2014) Endophytic bacteria: prospects and applications for the phytoremediation of organic pollutants. Chemosphere 117:232–242
Park JH, Kim R, Aslam Z, Jeon CO, Chung YR (2008) Lysobacter capsici sp. nov., with antimicrobial activity, isolated from the rhizosphere of pepper, and emended description of the genus Lysobacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:387–392
Pernthaler J (2013) Freshwater microbial communities. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong E, Edward F, Lory S, Stephen L, Stackebrandt E, DeLong E, Fabiano T (eds) The prokaryotes. Springer, Berlin, pp. 97–112
R Core Team (2012) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. URL:http://www.R-project.org/
Rajilić-Stojanović M, de Vos WM (2014) The first 1000 cultured species of the human gastrointestinal microbiota. FEMS Microbiol Rev 38:996–1047
Ratnaweera H, Fejes J, Yawei L, Lindblim E, Faafeng B, Ruden F (2008) Report: Lake Wuliangsuhai comprehensive study extension management and control plan inner Mongolia Lake restoration project
Sun MY, Dafforn K, Brown MV, Johnston EL (2012) Bacterial communities are sensitive indicators of contaminant stress. Mar Pollut Bull 64:1029–1038
Sun Y, Wang T, Peng X, Wang P, Lu Y (2016) Bacterial community compositions in sediment polluted by perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) using Illumina high-throughput sequencing. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. doi:10.1007/s11356-016-6055-0
Thevs N, Ott K, Kerschbaumer L, He P (2014) Study areas: the Heihe River basin and Wuliangsuhai Lake at the Hetao Irrigation District. In: Cirella GT, Zerbe S (eds) Sustainable water management and wetland restoration strategies in northern China. Bu Press, Bozen-Bolzano, pp. 27–37
Vladár P, Rusznyák A, Márialigeti K, Borsodi AK (2007) Diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria inhabiting the rhizosphere of Phragmites australis in Lake Velencei (Hungary) revealed by a combined cultivation-based and molecular approach. Microb Ecol 56:64–75
Vymazal J, Kröpfelová L, Švehla J, Chrastný V, Štíchová J (2009) Trace elements in Phragmites australis growing in constructed wetlands for treatment of municipal wastewater. Ecol Eng 35:303–309
Wang GL, Wang L, Chen HH, Shen B, Li SP, Jiang JD (2011) Lysobacter ruishenii sp. nov., a chlorothalonil-degrading bacterium isolated from a long-term chlorothalonil-contaminated soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:674–679
Wang T, Wang P, Meng J, Liu S, Lu Y, Khim JS, Giesy JP (2016) A review of sources, multimedia distribution and health risks of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in China. Chemosphere 129:87–99
Whiteley AS, Bailey MJ (2000) Bacterial community structure and physiological state within an industrial phenol bioremediation system. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2400–2407
Yamian Z, Yifei J, Shengwu J, Qing Z, Duoduo F, Yumin G, Guangchun L (2012) Wuliangsuhai wetlands: a critical habitat for migratory water birds. JoRE 3:316–323
Yergeau E, Lawrence JR, Sanschagrin S, Waiser MJ, Korber DR, Greera CW (2012) Next-generation sequencing of microbial communities in the Athabasca River and its tributaries in relation to oil sands mining activities. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:7626–7637
Zhang W, Wu X, Liu G, Chen T, Zhang G, Dong Z, Yang X, Hu P (2013) Pyrosequencing reveals bacterial diversity in the rhizosphere of three Phragmites australis. Ecotypes Geomicrobiol J 30:593–599
Zheng G, Yampara-Iquise H, Jones JE, Carson CA (2009) Development of Faecalibacterium 16S rRNA gene marker for identification of human faeces. J Appl Microbiol 106:634–641
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Kurt–Eberhard–Bode Foundation within the Stifterverband für die Deutsche Wissenschaft (SuWaRest Project) (CUP n. I41J10000880007), and by the Foundation of the Free University of Bozen/Bolzano. Manuscript style has been edited end revised by Peter Brannick.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Haihan Zhang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borruso, L., Esposito, A., Bani, A. et al. Ecological diversity of sediment rhizobacteria associated with Phragmites australis along a drainage canal in the Yellow River watershed. J Soils Sediments 17, 253–265 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1498-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1498-y