Abstract
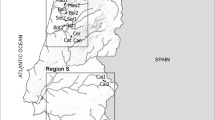
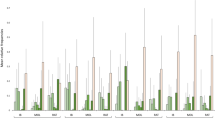
Hyporheic water exchange driven by groundwater-surface water interactions constitutes habitat conditions for aquatic biota. In our study, we conducted a field-research-based analysis of hyporheic water exchange to reveal whether the hyporheic water exchange differentiates particular Ranunculus sp. habitats. We measured the density of the stream of upwelling and hydraulic gradients of water residing in the hyporheic zone in 19 Polish rivers. We revealed that R. peltatus and R. penicillatus persist in habitats of considerably higher hyporheic water exchange upwelling flux (respectively 0.0852 m3∙d−1∙m−2 and 0.0952 m3∙d−1∙m−2) than R. circinatus, R. fluitans, and a hybrid of R. circinatus × R. fluitans (respectively m3∙d−1∙m−2; 0.0222 m3∙d−1∙m−2 and 0.0717 m3∙d−1∙m−2). The presented results can be used to indicate aquatic habitat suitability in the case of protection and management of ecosystems settled by Ranunculus sp.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data presented in the manuscript can be shared upon the written request to the corresponding author. Raw data analyzed in this study are presented in Supplementary Materials No. 2.
References
Bal K, Struyf E, Vereecken H, Viaene P, De Doncker L, de Deckere E, Mostaert F, Meire P (2011) How do macrophyte distribution patterns affect hydraulic resistances? Ecol Eng 37:529–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2010.12.018
Banks LK, Lavoie I, Robinson CE, Roy JW, Yates AG (2023) Effects of groundwater inputs on algal assemblages and cellulose decomposition differ based on habitat type in an agricultural stream. Hydrobiologia 850:3517–3537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-023-05251-1
Bączyk A, Wagner M, Okruszko T, Grygoruk M (2018) Influence of technical maintenance measures on the ecological status of agricultural lowland rivers – systematic review and implications for river management. Sci Total Environ 627:189–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.235
Bencala KE (2000) Hyporheic zone hydrological processes. Hydrol Process 14:2797–2798
Braun A, Auerswald K, Geist J (2012) Drivers and spatio-temporal extent of hyporheic patch variation: implications for sampling. PLoS ONE 7(7):e42046. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042046
Cassan L, Belaud G, Baume JP, Dejean C, Moulin F (2015) Velocity profiles in a real vegetated channel. Environ Fluid Mech 15:1263–1279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10652-015-9417-0
Gebler D, Zalewska-Gałosz J, Jopek M, Szoszkiewicz K (2022) Molecular identification and habitat requirements of the hybrid Ranunculus circinatus × R. fluitans and its parental taxa R. circinatus and R. fluitans in running waters. Hydrobiologia 849:2999–3014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-022-04909-6
Grygoruk M, Szałkiewicz E, Grodzka-Łukaszewska M, Mirosław-Świątek D, Oglęcki P, Pusłowska-Tyszewska D, Sinicyn G, Okruszko T (2021) Revealing the influence of hyporheic water exchange on the composition and abundance of bottom-dwelling macroinvertebrates in a temperate lowland river. Knowl Manag Aquat Ecosyst 422:37. https://doi.org/10.1051/kmae/2021036
Hester ET, Cardenas MB, Haggerty R, Apte SV (2017) The importance and challenge of hyporheic mixing. Water Resour Res 53:3565–3575. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016WR020005
Lawrence JE, Skold ME, Hussain FA, Silverman DR, Resh VH, Sedlak DL, Luthy RG, McCray JE (2013) Hyporheic zone in urban streams: a review and opportunities for enhancing water quality and improving aquatic habitat by active management. Environ Eng Sci 30:480–500. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2012.0235
Lewandowski J, Arnon S, Banks E, Batelaan O, Betterle A, Broecker T, Coll C, Drummond JD, Gaona Garcia J, Galloway J et al (2019) Is the hyporheic zone relevant beyond the scientific community? Water 11:2230. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112230
Lin Q, Song J, Gualtieri C, Cheng D, Su P, Wang X, Fu J, Peng J (2020) Effect of hyporheic exchange on macroinvertebrate community in the Weihe River basin. China Water 12:457. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020457
Magliozzi C, Usseglio-Polatera P, Meyer A, Grabowski RC (2019) Functional traits of hyporheic and benthic invertebrates reveal the importance of wood-driven geomorphological processes in rivers. Funct Ecol 33:1758–1770. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.13381
Marciniak M, Chudziak Ł (2015) A new method of measuring the hydraulic conductivity of the bottom sediment. Przegląd Geologiczny [geological Review] 63:919–925 (In Polish)
Marciniak M, Gebler D, Grygoruk M, Zalewska-Gałosz J, Szoszkiewicz K (2023) Hyporheic flow in aquatic Ranunculus habitats in temperate lowland rivers in Central Europe. Ecol Ind 153:110422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110422
Pacioglu O, Moldovan OT (2016) Response of invertebrates from the hyporheic zone of chalk rivers to eutrophication and land use. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:4729–4740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5703-0
Pinto P, Morais M, Ilhéu M, Sandin L (2006) Relationships among biological elements (macrophytes, macroinvertebrates, and ichthyofauna) for different core river types across Europe at two different spatial scales. In: Furse MT, Hering D, Brabec K, Buffagni A, Sandin L, Verdonschot PFM (eds) The ecological status of European rivers: evaluation and intercalibration of assessment methods. Developments in Hydrobiology, vol 188. Springer, , Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-5493-8_6
Sand-Jensen K, Madsen TV (1992) Patch dynamics of the stream macrophyte, Callitriche cophocarpa. Freshw Biol 27:277–282
Schulz M, Kozerski HP, Pluntke T, Rinke K (2003) The influence of macrophytes on sedimentation and nutrient retention in the lower River Spree (Germany). Water Res 37:569–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00276-2
Vermaat JE, Santamaria L, Roos PJ (2000) Water flow across and sediment trapping in submerged macrophyte beds of contrasting growth form. Arch Hydrobiol 148:549–562
Weekes L, Fitzpatrick Ú, Kelly-Quinn M (2021) Assessment of the efficiency of river macrophytes to detect water-column nutrient levels and other environmental conditions in Irish rivers. Hydrobiologia 848:2797–2814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-021-04598-7
Wiegleb G, Bröring U, Filetti M, Brux H, Herr W (2014) Long-term dynamics of macrophyte dominance and growth form types in two northwest German lowland streams. Freshw Biol 59:1012–1025. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.1232
Wiegleb G, Bobrov AA, Zalewska-Gałosz J (2017) A taxonomic account of Ranunculus section Batrachium (Ranunculaceae). Phytotaxa 319(1):001–055. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.319.1.1
Acknowledgements
We thank Joanna Chmist-Sikorska, Stanisław Zaborowski, and the staff of Pomeranian Landscape Parks Complex for support in field sampling and laboratory work. Taxonomic issues were discussed with Gerhard Wiegleb.
Funding
The research was funded by a Grant from the National Science Centre, Poland: UMO-2016/23/B/NZ9/03600.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Marek Marciniak, Daniel Gebler, and Joanna Zalewska-Gałosz. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Marek Marciniak, Mateusz Grygoruk, and Krzysztof Szoszkiewicz. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. We thank the reviewers for their detailed and thoughtful comments that allowed us to improve this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The authors confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all authors. The authors declare that this manuscript has not been published and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Marciniak, M., Gebler, D., Grygoruk, M. et al. Different intensities and directions of hyporheic water exchange in habitats of aquatic Ranunculus species in rivers—a case study in Poland. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 26315–26319 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32924-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32924-8