Abstract
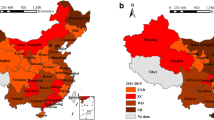
Globally, the transportation industry has become one of the leading sectors in carbon emission, and all countries are committed to environmental protection and energy conservation while experiencing rapid development. Under China’s “dual-carbon” goal, the carbon emission problem hinders the construction of China’s green transportation system and affects the high-quality development of transportation, so it is of great significance to study the spatial pattern of carbon emission efficiency in the transportation industry and the factors affecting it. Firstly, this paper measures the carbon emission value of transportation in 30 provinces in China from 2010 to 2020 based on the IPCC method and measures the carbon emission efficiency through the super-efficiency slack-based measurement model. Secondly, spatial autocorrelation analysis was conducted to determine the spatial clustering characteristics of the efficiency values. Finally, two spatial Durbin models are constructed to measure the spatial spillover effects and analyze the short-term immediate effects of each influencing factor on the static model and the long-term effects of the dynamic model considering the time lag of the transportation carbon emission efficiency. The results of the study show that (1) the average value of efficiency in the central and eastern regions is basically higher than 0.5; in the western and northeastern regions, it is basically lower than 0.3.The overall efficiency of carbon emission in the region shows a fluctuating upward trend but with increasing regional differences. (2) The number of regions with positive spatial correlation increased from 21 to 25 during the study period, and the degree of provincial transportation carbon emission efficiency agglomeration increased. (3) Although urbanization and energy intensity have a large detrimental influence on transportation carbon emission efficiency, environmental regulation has a major favorable effects on it both long and short term. Population scale, opening level, and urbanization all have significant spatial spillover effects. Accordingly, relevant policy recommendations are put forward to provide theoretical guidance for promoting the realization of low-carbon transportation.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- SBM :
-
Slack-based measurement
- SDM :
-
Spatial Dubin model
- IPCC :
-
Intergovernmental panel on climate change
- IEA :
-
International Energy Agency
- SEM :
-
Spatial error model
- SAR :
-
Spatial lag model
- DEA :
-
Data envelopment analysis
References
Aristizábal-Torres D, Castro-Peña MY, Echeverri-Gutiérrez PA, Valencia-Salazar JD (2017) Assessing the efficiency of science, technology and innovation using data envelopment analysis (DEA): the case of Colombia. Dyna 84(202):215–220. https://doi.org/10.15446/dyna.v84n202.59554
Chancel L (2022) Global carbon inequality over 1990–2019. Nat Sustain 5(11):931–938. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-022-00955-z
Chen J, Xian Q, Zhou J, Li D (2020) Impact of income inequality on CO(2) emissions in G20 countries. J Environ Manage 271:110987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110987
Chen D, Lu X, Hu W, Zhang C et al (2021) How urban sprawl influences eco-environmental quality: empirical research in China by using the spatial Durbin model. Ecol Ind 131:108113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108113
Cheng G, Zervopoulos P, Qian Z (2013) A variant of radial measure capable of dealing with negative inputs and outputs in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 225(1):100–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2012.09.031
Cheng Z, Hu X (2023) The effects of urbanization and urban sprawl on CO2 emissions in China. Environ Dev Sustain 25(2):1792–1808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02123-x
Churchill SA, Inekwe J, Ivanovski K, Smyth R (2021) Transport infrastructure and CO2 emissions in the OECD over the long run. Trans Res Part D: Trans Environ 95:102857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2021.102857
Danish, Ulucak R (2020) Relationship between energy intensity and CO2 emissions: does economic policy matter?. Sustain Dev 28(5):1457-1464. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2098
Danish Ulucak R, Khan SUD, Baloch MA et al (2020) Mitigation pathways toward sustainable development: is there any trade‐off between environmental regulation and carbon emissions reduction?. Sustain Dev 28(4):813-822. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2032
Doğan B, Chu LK, Ghosh S, Truong HHD et al (2022) How environmental taxes and carbon emissions are related in the G7 economies? Renew Energy 187:645–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.01.077
Du K, Li P, Yan Z (2019) Do green technology innovations contribute to carbon dioxide emission reduction? Empirical evidence from patent data. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 146:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.06.010
Eggleston H, Buendia L, Miwa K, Ngara T et al (2006) 2006 IPCC guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories. http://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/index.html. Accessed 23 Oct 2006
Engo J (2019) Decoupling analysis of CO2 emissions from transport sector in Cameroon. Sustain Cities Soc 51:101732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101732
Friedlingstein P, Jones MW, O’Sullivan M, Andrew RM et al (2022) Global carbon budget 2021. Earth System Science Data 14(4):1917–2005. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-14-1917-2022
Goldsmith RW (1951) A perpetual inventory of national wealth. In Studies in income and wealth, Volume 14 (pp 5–73): NBER
Grubb M, Okereke C, Arima J, Bosetti V et al. (2022) IPCC. Climate change 2022: mitigation of climate change. In. Retrieved from https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg3/. Accessed 2022-02-11
Guo M, Meng J (2019) Exploring the driving factors of carbon dioxide emission from transport sector in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J Clean Prod 226:692–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.095
Guo W, Sun T, Dai H (2016) Effect of population structure change on carbon emission in China. Sustainability 8(3):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8030225
Hassan ST, Khan D, Zhu B, Batool B (2022) Is public service transportation increase environmental contamination in China? The role of nuclear energy consumption and technological change. Energy 238:121890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121890
Huang Z, Dong H, Jia S (2022) Equilibrium pricing for carbon emission in response to the target of carbon emission peaking. Energy Econ 112:106160
Jeguirim K (2021) An inquiry into the regional unemployment disparities in Tunisia: a spatial Durbin model. Middle East Dev J 13(2):265–291. https://doi.org/10.1080/17938120.2021.1958559
Jiang Z-R, Jin H-H, Wang C-J, Ye S-L et al (2020) Measurement of traffic carbon emissions and pattern of efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt (1985–2016). Environ Sci 41(6):2972–2980. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.201910221
Kazemzadeh E, Fuinhas JA, Koengkan M, Osmani F et al (2022) Do energy efficiency and export quality affect the ecological footprint in emerging countries? A two-step approach using the SBM–DEA model and panel quantile regression. J Environ Syst Decisions 42(4):608–625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-022-09846-2
Li F, Cai B, Ye Z, Wang Z et al (2019) Changing patterns and determinants of transportation carbon emissions in Chinese cities. Energy 174:562–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.02.179
Li R, Li L, Wang Q (2022) The impact of energy efficiency on carbon emissions: evidence from the transportation sector in Chinese 30 provinces. Sustain Cities Soc 82:103880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2022.103880
Liu H, Yang R, Wu D, Zhou Z (2021) Green productivity growth and competition analysis of road transportation at the provincial level employing Global Malmquist-Luenberger Index approach. J Clean Prod 279:123677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123677
Liu J, Li S, Ji Q (2021) Regional differences and driving factors analysis of carbon emission intensity from transport sector in China. Energy 224:120178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120178
Ma Q, Jia P, Kuang H (2022) Spatial imbalance and factors influencing carbon emission efficiency in China’s transport industry. Front Earth Sci 10:986467. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2022.986467
Magazzino C, Mele M (2021) On the relationship between transportation infrastructure and economic development in China. Res Transp Econ 88:100947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.retrec.2020.100947
Mashud AHM, Pervin M, Mishra U, Daryanto Y et al (2021) A sustainable inventory model with controllable carbon emissions in green-warehouse farms. J Clean Prod 298:126777
Masson-Delmotte VP, Zhai P, Pirani SL, Connors C, Péan S, Berger N, Caud Y, Chen L, Goldfarb MI, Scheel Monteiro PM (2021). IPCC, 2021: summary for policymakers. In: Climate change 2021: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the sixth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/
Meng C, Du X, Zhu M, Ren Y et al (2023) The static and dynamic carbon emission efficiency of transport industry in China. Energy 274:127297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.127297
Myovella G, Karacuka M, Haucap J (2021) Determinants of digitalization and digital divide in Sub-Saharan African economies: a spatial Durbin analysis. Telecommun Policy 45(10):102224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2021.102224
Neykov N, Krišťáková S, Hajdúchová I, Sedliačiková M et al (2021) Economic efficiency of forest enterprises—empirical study based on data envelopment analysis. J Forests 12(4):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12040462
Omri A, Hadj TB (2020) Foreign investment and air pollution: do good governance and technological innovation matter? Environ Res 185:109469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109469
Pei Y, Zhu Y, Liu S, Wang X et al (2019) Environmental regulation and carbon emission: the mediation effect of technical efficiency. J Clean Prod 236:117599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.07.074
Shao H, Wang Z (2021) Spatial network structure of transportation carbon emission efficiency in China and its influencing factors. Chin J Popul Resour Environ 19(4):295–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjpre.2022.01.002
Solaymani S (2019) CO2 emissions patterns in 7 top carbon emitter economies: the case of transport sector. Energy 168:989–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.11.145
Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner G-K, Tignor MM et al (2014) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of IPCC the intergovernmental panel on climate change. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324
Sun Y, Liu S, Li L (2022) Grey correlation analysis of transportation carbon emissions under the background of carbon peak and carbon neutrality. Energies 15(9):3064. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15093064
Tian Z, Xiao L, Liu C, Wang Y et al (2023) Study on the spatial effects of urbanization on carbon emissions from transportation in China. Techno-Econ 42(01):141–153. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-980X.2023.01.021
Tobler WR (1970) A computer movie simulating urban growth in the Detroit region. Econ Geogr 46(sup1):234–240. https://doi.org/10.2307/143141
Tone K (2001) A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 130(3):498–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(99)00407-5
Torres-Samuel M, Vásquez CL, Luna M, Bucci N et al (2020) Performance of education and research in Latin American countries through data envelopment analysis (DEA). Procedia Comput Sci 170:1023–1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.03.079
Waheed R, Sarwar S, Wei C (2019) The survey of economic growth, energy consumption and carbon emission. Energy Rep 5:1103–1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2019.07.006
Wang Q, Li L (2021) The effects of population aging, life expectancy, unemployment rate, population density, per capita GDP, urbanization on per capita carbon emissions. Sustain Prod Consum 28:760–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.06.029
Wang Y, Li L, Kubota J, Han R et al (2016) Does urbanization lead to more carbon emission? Evidence from a panel of BRICS countries. Appl Energy 168:375–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.01.105
Wang Y, Zhou Y, Zhu L, Zhang F et al (2018) Influencing factors and decoupling elasticity of China’s transportation carbon emissions. Energies 11(5):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051157
Wang G, Deng X, Wang J, Zhang F et al (2019) Carbon emission efficiency in China: a spatial panel data analysis. China Econ Rev 56:101313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2019.101313
Wang L, Zhao Z, Xue X, Wang Y (2019) Spillover effects of railway and road on CO2 emission in China: a spatiotemporal analysis. J Clean Prod 234:797–809
Wang C, Wood J, Wang Y, Geng X et al (2020) CO2 emission in transportation sector across 51 countries along the Belt and Road from 2000 to 2014. J Clean Prod 266:122000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122000
Wang C, Kim Y-S, Kim CY (2021) Causality between logistics infrastructure and economic development in China. Transp Policy 100:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2020.10.005
Wang C, Yao X, Sinha PN, Su H et al (2022) Why do government policy and environmental awareness matter in predicting NEVs purchase intention? Moder Role Educ Level Cities 131:103904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2022.103904
Wang C, Feng X, Woo S, Wood J et al (2023) The optimization of an EV decommissioned battery recycling network: a third-party approach. J Environ Manage 348:119299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119299
Wang C, Sinha PN, Zhang X, Wang S et al (2024) The impact of NEV users’ perceived benefits on purchase intention. Travel Behaviour 34:100681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tbs.2023.100681
Wang C, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Wood J, Kim CY, Li Y (2020) Transportation CO2 emission decoupling: an assessment of the Eurasian logistics corridor. Trans Res Part D: Transp Environ 86:102486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2020.102486
Wu H, Xu L, Ren S, Hao Y et al (2020) How do energy consumption and environmental regulation affect carbon emissions in China? New evidence from a dynamic threshold panel model. Resour Policy 67:101678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101678
Xie R, Fang J, Liu C (2017) The effects of transportation infrastructure on urban carbon emissions. Appl Energy 196:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy
Xu X, Xu H (2021) The driving factors of carbon emissions in China’s transportation sector: a spatial analysis. J Front Energy Res 9:664046. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2021.664046
Xu G, Schwarz P, Yang H (2020) Adjusting energy consumption structure to achieve China’s CO2 emissions peak. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 122:109737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.109737
Xu H, Wang Y, Liu H, Yang R (2020) Environmental efficiency measurement and convergence analysis of interprovincial road transport in China. Sustainability 12(11):4613. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114613
Yang F, Han C (2011) Empirical evidence on the relationship between transportation infrastructure and economic growth in China. Chin Popul Resour Environ 21(10):147–152. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2011.10.022
Yuan C, Zhang S, Jiao P, Wu D (2017) Study on spatial and temporal changes of total factor carbon emission efficiency and influencing factors of provincial transportation in China. Resour Sci 39(04):687–697. https://doi.org/10.18402/resci.2017.04.10
Zhang N, Wei X (2015) Dynamic total factor carbon emissions performance changes in the Chinese transportation industry. Appl Energy 146:409–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.01.072
Zhang S, Zhao T (2019) Identifying major influencing factors of CO2 emissions in China: regional disparities analysis based on STIRPAT model from 1996 to 2015. Atmos Environ 207:136–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.12.040
Zhang F, Deng X, Phillips F, Fang C et al (2020) Impacts of industrial structure and technical progress on carbon emission intensity: evidence from 281 cities in China. Technol Forecast Soc Change 154:119949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.119949
Zhang W, Li G, Uddin MK, Guo S (2020) Environmental regulation, foreign investment behavior, and carbon emissions for 30 provinces in China. J Clean Prod 248:119208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119208
Zhang GK, Li JW (2016) Estimation of capital stock and return on capital for transportation infrastructure in China. Contemporary Finance and Economics (6):3–14
Zhao J, Jiang Q, Dong X, Dong K et al (2022) How does industrial structure adjustment reduce CO2 emissions? Spatial and mediation effects analysis for China. Energy Econ 105:105704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105704
Zhao X, Wang J, Fu X, Zheng W et al (2022) Spatial–temporal characteristics and regional differences of the freight transport industry’s carbon emission efficiency in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(50):75851–75869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21101-4
Zhu C, Gao D (2019) A research on the factors influencing carbon emission of transportation industry in “the belt and road initiative” countries based on panel data. Energies 12(12):2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12122405
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WZ: supervision, writing—review and editing; XH: methodology, empirical analysis, writing—original draft, software; QD and DZ: resources, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The authors declare that all ethical guidelines for authors have been followed by all authors. Ethical approval is not required.
Consent to participate
All authors have given their consent to participate in submitting this manuscript to this journal.
Consent for publication
Written consent was sought from each author to publish the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: V.V.S.S. Sarma
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Region | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Beijing | 0.3361 | 0.2865 | 0.2965 | 0.3025 | 0.2988 | 0.3301 | 0.3213 | 0.3399 | 0.3145 | 0.2899 |
Tianjin | 0.6643 | 0.5478 | 0.6229 | 0.4914 | 0.5372 | 0.6286 | 0.5558 | 0.5921 | 0.5826 | 0.5777 |
Hebei | 1.1589 | 1.2489 | 1.2147 | 1.3015 | 1.2833 | 1.1903 | 1.2732 | 1.2286 | 1.2009 | 1.2790 |
Shanghai | 0.3946 | 0.3717 | 0.3813 | 0.4417 | 1.0377 | 1.0510 | 1.0732 | 1.0980 | 1.1076 | 1.1467 |
Jiangsu | 0.7957 | 1.0127 | 0.7865 | 0.7718 | 0.6093 | 0.6287 | 0.5674 | 0.6160 | 0.5846 | 0.7245 |
Zhejiang | 0.4367 | 0.4126 | 0.4259 | 0.4270 | 0.4343 | 0.4814 | 0.4319 | 0.4469 | 0.4635 | 0.3956 |
Fujian | 0.4344 | 0.4052 | 0.3861 | 0.3782 | 0.3855 | 0.4221 | 0.3845 | 0.3868 | 0.4056 | 0.4108 |
Shandong | 0.4744 | 0.4607 | 0.4749 | 0.5177 | 0.5252 | 0.5974 | 0.6217 | 0.6226 | 0.6378 | 0.6088 |
Guangdong | 0.3739 | 0.3730 | 0.3839 | 0.4040 | 0.4110 | 0.4423 | 0.4183 | 0.4359 | 0.4496 | 0.4095 |
Hainan | 0.2642 | 0.2926 | 0.2740 | 0.2773 | 0.2780 | 0.2872 | 0.2707 | 0.2761 | 0.3197 | 0.3166 |
East | 0.5333 | 0.5412 | 0.5247 | 0.5313 | 0.5800 | 0.6059 | 0.5918 | 0.6043 | 0.6066 | 0.6159 |
Shanxi | 0.2702 | 0.2847 | 0.2553 | 0.2569 | 0.2840 | 0.3143 | 0.3309 | 0.4172 | 0.4358 | 0.4596 |
Anhui | 1.0928 | 1.0640 | 1.0934 | 1.0900 | 1.0700 | 1.0411 | 1.0149 | 1.0285 | 1.0271 | 1.0270 |
Jiangxi | 0.3872 | 0.4875 | 0.4479 | 0.4504 | 0.4445 | 0.5013 | 0.4973 | 0.5977 | 0.6329 | 0.5976 |
Henan | 0.5081 | 0.6241 | 0.6879 | 1.0024 | 1.0123 | 1.0464 | 1.0429 | 1.0172 | 1.0114 | 0.8047 |
Hubei | 0.3617 | 0.3766 | 0.4164 | 0.4330 | 0.4341 | 0.4370 | 0.4165 | 0.4436 | 0.4179 | 0.3577 |
Hunan | 0.3730 | 0.4216 | 0.4118 | 0.4173 | 0.4170 | 0.4502 | 0.4223 | 0.4330 | 0.4028 | 0.3653 |
Central | 0.4988 | 0.5431 | 0.5521 | 0.6083 | 0.6103 | 0.6317 | 0.6208 | 0.6562 | 0.6546 | 0.6020 |
Inner Mongolia | 0.2974 | 0.3044 | 0.3269 | 0.3415 | 0.3505 | 0.4245 | 0.4131 | 0.4551 | 0.4788 | 0.4466 |
Guangxi | 0.2459 | 0.2390 | 0.2839 | 0.2698 | 0.2891 | 0.3164 | 0.2882 | 0.2992 | 0.3003 | 0.2969 |
Chongqing | 0.3661 | 0.3294 | 0.2901 | 0.2961 | 0.2825 | 0.3061 | 0.2694 | 0.3118 | 0.3264 | 0.2976 |
Sichuan | 0.1850 | 0.1796 | 0.1897 | 0.2098 | 0.2217 | 0.2452 | 0.2180 | 0.2543 | 0.2609 | 0.2199 |
Guizhou | 0.2412 | 0.2383 | 0.2483 | 0.2562 | 0.2495 | 0.2689 | 0.2658 | 0.2838 | 0.2875 | 0.2731 |
Yunnan | 0.1876 | 0.2151 | 0.2421 | 0.2480 | 0.2627 | 0.2946 | 0.2838 | 0.3115 | 0.3072 | 0.2764 |
Shaanxi | 0.2684 | 0.3005 | 0.3169 | 0.3266 | 0.3370 | 0.3797 | 0.3437 | 0.3549 | 0.3662 | 0.3625 |
Gansu | 0.4081 | 0.3995 | 0.3499 | 0.2993 | 0.2755 | 0.2688 | 0.2487 | 0.2611 | 0.2784 | 0.2443 |
Qinghai | 0.2350 | 0.2293 | 0.2077 | 0.2072 | 0.1898 | 0.1936 | 0.1629 | 0.1584 | 0.1496 | 0.1366 |
Ningxia | 0.5438 | 0.5840 | 0.5176 | 0.4566 | 0.4336 | 0.4259 | 0.3380 | 0.3249 | 0.3322 | 0.3408 |
Xinjiang | 0.1794 | 0.2275 | 0.2075 | 0.2449 | 0.2389 | 0.2522 | 0.2349 | 0.3058 | 0.3034 | 0.2366 |
West | 0.2871 | 0.2951 | 0.2892 | 0.2869 | 0.2846 | 0.3069 | 0.2788 | 0.3019 | 0.3083 | 0.2847 |
Liaoning | 0.2483 | 0.2489 | 0.2463 | 0.2474 | 0.2772 | 0.3500 | 0.3370 | 0.3812 | 0.3843 | 0.4155 |
Jilin | 0.3511 | 0.3510 | 0.3614 | 0.3419 | 0.3225 | 0.3543 | 0.3118 | 0.3250 | 0.3002 | 0.2919 |
Heilongjiang | 0.1740 | 0.1846 | 0.1795 | 0.1987 | 0.1905 | 0.2032 | 0.1887 | 0.2072 | 0.1920 | 0.1952 |
Northeast | 0.2578 | 0.2615 | 0.2624 | 0.2627 | 0.2634 | 0.3025 | 0.2792 | 0.3045 | 0.2922 | 0.3009 |
National | 0.4086 | 0.4234 | 0.4176 | 0.4302 | 0.4461 | 0.4711 | 0.4516 | 0.4738 | 0.4754 | 0.4602 |
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Han, X., Ding, Q. et al. Analysis of spatial spillover effects and influencing factors of transportation carbon emission efficiency from a provincial perspective in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 12174–12193 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-31840-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-31840-1