Abstract
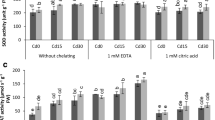
Manganese (Mn) is one of the essential mineral micronutrients most demanded by cacao. Cadmium (Cd) is highly toxic to plants and other living beings. There are indications that Mn can interact with Cd and mitigate its toxicity. The objective of this study was to evaluate the action of Mn on the toxic effect of Cd in young plants of the CCN 51 cacao genotype, subjected to different doses of Mn, Cd, and Mn+Cd in soil, through physiological, biochemical, molecular, and micromorphological and ultrastructural changes. High soil Mn doses favored the maintenance and performance of adequate photosynthetic processes in cacao. However, high doses of Cd and Mn+Cd in soil promoted damage to photosynthesis, alterations in oxidative metabolism, and the uptake, transport, and accumulation of Cd in roots and leaves. In addition, high Cd concentrations in roots and leaf tissues caused irreversible damage to the cell ultrastructure, compromising cell function and leading to programmed cell death. However, there was a mitigation of Cd toxicity when cacao was grown in soils with low Cd doses and in the presence of Mn. Thus, damage to the root and leaf tissues of cacao caused by Cd uptake from contaminated soils can be attenuated or mitigated by the presence of high Mn doses in soil.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Adjaloo MK, Oduro W, Banful BK (2012) Floral phenology of upper amazon cocoa trees: implications for reproduction and productivity of cocoa. ISRN Agronomy. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/461674
Almeida A-AF, Valle RR (2007) Ecophysiology of the cacao tree. Braz J Plant Physiol 19(4):425–448
Almeida A-AF, Valle RR (2010) Cacao: ecophysiology of growth and production. In: DaMatta FM (ed) Ecophysiology of tropical tree crops. Nova Science Publishers Inc., Hauppauge, pp 37–70
Almeida NM, Almeida A-AF, Mangabeira PAO, Ahnert D, Reis GSM, Castro AV (2015) Molecular, biochemical, morphological and ultrastructural responses of cacao seedlings to aluminum (Al3+) toxicity. Acta Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1732-4
Anjum NA et al (2015) Lipids and proteins: major targets of oxidative modifications in abiotic stressed plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:4099–4121
Apraez-Muñoz JJ, de Almeida AAF, Pirovani CP et al (2021) Mitigation of Pb toxicity by Mn in seedling of the cacao clonal CCN 51 genotype grown in soil: physiological, biochemical, nutritional and molecular responses. Ecotoxicology 30:240–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-021-02348-y
Araújo RP, Almeida A-AF, Pereira LS, Mangabeira PAO, Souza JO, Pirovani CP, Ahnert D, Baligar VC (2017) Photosynthetic, antioxidative, molecular and ultrastructural responses of young cacao plants to Cd toxicity in the soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.06.006
Arévalo-Gardini E, Arévalo-Hernández CO, Baligar VC, He ZL (2017) Heavy metal accumulation in leaves and beans of cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) in major cacao growing regions in Peru. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.122
Bai B, Nie Q, Zhang Y, Wang X, Hu W (2021) Cotransport of heavy metals and SiO2 particles at different temperatures by seepage. J Hydrol 597:125771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125771
Barceló J, Poschenrieder CH, Andreu L, Gunse B (1986) Cadmium-induced decrease of water stress resistance in bush bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv. Contender). I. Effects of Cd on water potential, relative water content and cell wall elasticity. J Plant Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(86)80239-5
Bartley BGD (2005) The genetic diversity of cacao and is utilization. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, UK
Baszynski T, Wajda L, Król M, Wolinska D, Krupa Z, Tukendorf A (1980) Photosynthetic activities of cadmium-treated tomato plants. Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1980.tb03269.x
Bates L, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Cakmak I, Horst WJ (1991) Effect of aluminum on lipid peroxidation, superoxide dismutase, catalase and peroxidase activities in root tips of soybean (Glycine max). Physiol Plant 83:463–468
CAOBISCO/ECA/FCC (2015) Cocoa Beans: chocolate and cocoa industry quality requirements. (End, M.J. and Dand, R., Editors). CAOBISCO/ECA/FCC
Capdevila M, Atrian S (2011) Metallothionein protein evolution: a miniassay. J Biol Inorg Chem 16:977–989
Castro AV, Almeida A-AF, Pirovani CP, Reis GSM, Almeida NM, Mangabeira PAO (2015) Morphological, biochemical, molecular and ultrastructural changes induced by Cd toxicity in seedlings of Theobroma cacao L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.02.003
Cataldo DA, Garland TR, Wildung RE (1983) Cadmium uptake kinetics in intact soybean plants. Plant Physiol 73:844–848
Cervantes-Martinez C, Brown JS, Scnell RJ, Phillipis-Mora W, Takrama JF, Motamayor JC (2006) Combining ability for disease resistance, yield, and horticultural traits of cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) Clones. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 131:231–241
Chaneva G, Parvanova P, Tzvetkova N, Uzunova A (2010) Photosynthetic response of maize plants against cadmium and paraquat impact. Water Air Soil Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0166-x
Chavez E, He ZL, Stofella PJ, Mylavarapu RS, Li YC, Baligar VC (2016) Chemical speciation of cadmium: an approach to evaluate plant-available cadmium in Ecuadorian soils under cacao production. Chemosphere 150:57–62
Chen C, Dickman MB (2005) Proline suppresses apoptosis in the fungal pathogen Colletotrichum trifolii. PNAS 102(9):3459–3464
Clemens S (2006) Toxic metal accumulation, responses to exposure and mechanisms of tolerance in plants. Biochimie 88:1707–1719
Clemens S, Ma JF (2016) Toxic heavy metal and metalloid accumulation in crop plants and foods. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67:489–512. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurevarplant-043015-112301
DalCorso G, Farinati S, Maistri S, Furini A (2008) How plants cope with cadmium: staking all on metabolism and gene expression. J Integr Plant Biol 50:1268–1280
Dalcorso G, Manara A, Furini A (2013) An overview of heavy metal challenge in plants: from roots to shoots. Metallomics 5:11–17
Demirevska-Kepova K et al (2004) Biochemical changes in barley plants after excessive supply of copper and manganese. Environ Exp Bot 52:253–266
Dezhban A, Shirvany A, Attarod P, Delshad M, Matinizadeh M, Khoshnevis M (2015) Cadmium and lead effects on chlorophyll fluorescence, chlorophyll pigments and proline of Robinia pseudoacacia. J For Res 26:323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676015-0045-9
Djebali W, Hédiji H, Abbes Z, Barhoumi Z, Yaakoubi H, Boulila Zoghlami L, Chaibi W (2010) Aspects on growth and anatomy of internodes and leaves of cadmium-treated Solanum lycopersicum L. plants. J Biol Res-Thessalon 13:75–84
Djebali W, Zarrouk M, Brouquisse R, El Kahoui S, Limam F, Ghorbel H, Chaibi W (2005) Ultrastructure and lipid alterations induced by cadmium in tomato (Lycopersicon Esculentum) chloroplast membranes. Plant Biol 7:358–368
Ducic T, Polle A (2005) Transport and detoxification of manganese and copper in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:103–112
Emamverdian A, Ghorbani A, Pehlivan N, Alwahibi MS, Elshikh MS, Liu G, Li Y, Barker J, Zargar M, Chen M (2023a) Co-application of melatonin and zeolite boost bamboo tolerance under cadmium by enhancing antioxidant capacity, osmolyte accumulation, plant nutrient availability, and decreasing cadmium absorption. Sci Hortic 322:112433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2023.112433
Emamverdian A, Ghorbani A, Li Y, Pehlivan N, Barker J, Ding Y, Liu G, Zargar M (2023b) Responsible mechanisms for the restriction of heavy metal toxicity in plants via the co-Foliar Spraying of Nanoparticles. Agronomy 13(7):1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071748
Esposito S, Sorbo S, Conte B, Basile A (2012) Effects of heavy metals on ultrastructure and HSP70s induction in the aquatic moss Leptodictyum riparium Hedw. Int J Phytoremediation 14:443
EU (2021) No 1881/2006 as regards maximum levels of cadmium in foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Union L 138, 13 May 2014, p 75–79
Foyer C, Noctor G (2005) Oxidant and antioxidant signalling in plants: a re-evaluation of the concept of oxidative stress in a physiological context. Plant Cell and Environment 28:1056–1071
Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Iannone MF, Rosales EP, Zawoznik MS, Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2012) Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms Environ. Exp Bot 83:3346
Ge W et al (2012) Cadmium-mediated oxidative stress and ultrastructural changes in root cells of poplar cultivars. S Afr J Bot 83:98–108
Gill SS, Khana NA, Tujeta N (2012) Cadmium at high dose perturbs growth, photosynthesis and nitrogen metabolism while at low dose it up regulates sulfur assimilation and antioxidant machinery in garden cress (Lepidium sativum L.). Plant Sci 182:112–120
Gill SS, Tujeta N (2011) Cadmium stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Signal Behav 6(2):215–222. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.6.2.14880
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930
Gill SS et al (2015) Superoxide dismutase—mentor of abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:10375–10394
Gomes MP et al (2012) Cd-tolerance markers of Pfaffia glomerata (Spreng.) Pedersen plants: anatomical and physiological features. Braz J Plant Physiol 24(4):293–304
Gowayed SMH, Almaghrabi OA (2013) Effect of copper and cadmium on germination and anatomical structure of leaf and root seedling in maize (Zea mays L). Aust J Basic & Appl Sci 7:548–555
Grant CA, Buckley WT, Bailey LD, Selles F (1997) Cadmium accumulation in crops. Can J Plant Sci 78:1–17
Hakmaoui A, Ater M, Bóka K, Barón M (2007) Copper and Cadmium Tolerance, Uptake and Effect on Chloroplast Ultrastructure. Studies on Salix purpurea and Phragmites australis. Z Naturforsch C 62:417–426
Hattab S, Dridi B, Chouba L, Kheder MB, Bousetta H (2009) Photosynthesis and growth responses of pea Pisum sativum L. under heavy metals stress. J Environ Sci 21:1552–1556
He S, He Z, Yang X, Stoffella PJ, Baligar VC (2015) Soil biogeochemistry, plant physiology, and phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soils. Adv Agronomy 134:135–225
Hernández LE, Lozano-Rodriguez E, Gárate A, Carpena-Ruiz R (1998) Influence of cadmium on the uptake, tissue accumulation and subcellular distribution of manganese in pea seedlings. Plant Sci 132:139–151
Hossain MA, Hasanuzzaman M, Fujita M (2010) Up-regulation of antioxidant and glyoxalase systems by exogenous glycinebetaine and proline in mung bean confer tolerance to cadmium stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 16(3):259–272
ICCO (2023) ICCO Quarterly Bulletin of Cocoa Statistics, Vol. XLIX, No.2, Cocoa year 2022/23. Available in: https://www.icco.org/wp-content/uploads/Production_QBCS-XLIX-No.-2.pdf Accessed Juny 2023.
Jalbani N, Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Arain MB (2009) Determination of toxic metals in different brand of chocolates and candies, marketed in Pakistan. Pak J Anal Environ Chem 10:48–52
Kabata-Pendias A (2011) Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Khan NA, Samiullah Singh S, Nazar R (2007) Activities of antioxidative enzymes, sulphur assimilation, photosynthetic activity and growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum) Cultivars Differing in Yield Potential Under Cadmium Stress. J Agron Crop Sci 193:435–444
Khedr AH, Abbas MA, Wahid AA, Quick WP, Abogadallah GM (2003) Proline induces the expression of salt-stress-responsive proteins and may improve the adaptation of Pancratium maritimum L. to salt-stress. J Exp Bot 54:2553–2562. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erg277
Khudsar T, Mahmooduzzafar Iqbal M (2001) Cadmium-induced changes in leaf epidermis, photosynthetic rate and pigment concentrations in Cajanus cajan. Biol Plant 44:59–64
Kirkham MB (2006) Cadmium in plants on polluted soils: effects of soil factors, hyperaccumulation, and amendments. Geoderma 137:19–32
Küpper H, Lombi E, Zhao FJ, Mcgrath SP (2000) Cellular compartmentation of cadmium and zinc in relation to other elements in the hyperaccumulator. Planta 212:75–84
Lee S-H et al (2007) Simultaneous overexpression of both CuZn superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase in transgenic tall fescue plants confers increased tolerance to a wide range of abiotic stresses. J Plant Physiol 164:1626–1638
Li Q et al (2010) Effects of manganese-excess on CO2 assimilation, ribulose-1,5bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, carbohydrates and photosynthetic electron transport of leaves, and antioxidant systems of leaves and roots in Citrus grandis seedlings. BMC Plant Biol 10:42
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1983) Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 603:591–592
Lindon FC, Teixeira MG (2000) Oxy- radicals production and control in the chloroplast of Mn-treated rice. Plant Sci 152:7–15
Liu DH, Kottke I (2004) Subcellular localization of Cd in the root cells of Allium cepa by electron energy loss spectroscopy and cytochemistry. J Biosci 29:329–335
Liu H, Zhang Y, Chai T, Tan J, Wang J, Feng S, Liu G (2013) Manganese mitigation of cadmium toxicity to seedling growth of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. is controlled by the manganese/cadmium molar ratio under hydroponic conditions. Plant Physiol Biochem 73:144–153
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Logan DC (2006) Plant mitochondrial dynamics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763:430–441
Metwally A, Safronova VI, Belimov AA, Dietz K-J (2005) Genotypic variation of the response to cadmium toxicity in Pisum sativum L. J Exp Bot 56:167–178
Millaleo R, Reyes-Díaz M, Alberdi M, Ivanov AG, Krol M, Hüner NPA (2013) Excess manganese differentially inhibits photosystem I versus II in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 64:343–354
Mir G et al (2004) Plant type 2 metallothionein (MT) from cork tissue responds to oxidative stress. J Exp Bot 408:2483–2493
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7(9):405–410
Möller IM, Jensen PE, Hansson A (2007) Oxidative modifications to cellular components in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58:459–481
Moradi L, Ehsanzadeh P (2015) Effects of Cd on photosynthesis and growth of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) genotypes. Photosynthetica. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-015-0150-1
Murakami R, Ifuku K, Takabayashi A, Shikanai T, Endo T, Sato F (2005) Functional dissection of two Arabidopsis PsbO proteins PsbO1 and PsbO2. FEBS the Journal 272:2165–2175
Nazar R, Iqbal N, Massod A, Khan MIR, Syeed S, Khan NA (2012) Cadmium toxicity in plants and role of mineral nutrients in its alleviation. Amer J Plant Sci 3:1476–1489
Nedjimi B, Daoud Y (2009) Cadmium accumulation in Atriplex halimus subsp. schweinfurthii and its influence on growth, proline, root hydraulic conductivity and nutriente uptake. Flora 204:316–324
Neumann D, Zur Nieden U, Schwieger W, Leopold I, Lichtenberger O (1997) Heavy metal tolerance of Minuartia verna. J Plant Physiol 151:101–108
Oliva M, Rubio K, Epquin M, Marlo G, Leiva S (2020) Cadmium uptake in native cacao trees in agricultural lands of Bagua, Peru. Agronomy 10:1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101551
Oliveira BRM, de Almeida AF, Pirovani CP, Barroso JP, Neto CHC, Santos NA, Ahnert D, Baligar VC, Mangabeira PAO (2020) Mitigation of Cd toxicity by Mn in young plants of cacao, evaluated by the proteomic profiles of leaves and roots. Ecotoxicology 29:340–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02178-4
Olmos E, Kiddle G, Pellny TK, Kumar S, Foyer CH (2006) Modulation of plant morphology, root architecture, and cell structure by low vitamin C in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 57:1645–1655
Parmar P, Kumari N, Sharma V (2013) Structural and functional al terations in photosynthetic apparatus of plants under cadmium stress. Bot Stud 54:45
Pawlowicz I, Kosmala A, Rapacz M (2012) Expression pattern of the psbO gene and its involvement in acclimation of the photosynthetic apparatus during abiotic stresses in Festuca arundinacea and F pratensis. Acta Physiol Plant 34:1915–1924
Peng K, Luo C, You W, Lian C, Li X, Shen Z (2008) Manganese uptake and interactions with cadmium in the hyperaccumulator - Phytolacca Americana L. J Hazard Mater 154:674–681
Pérez Chaca MV, Vigliocco A, Reinoso H, Molina A, Abdala G, Zirulnik F, Pedranzani H (2014) Effects of cadmium stress on growth, anatomy and hormone contents in Glycine max (L.) Merr. Acta Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738014-1656-z
Pinto AP, Motab AM, Varennes A, Pinto FC (2004) Influence of organic matter on the uptake of cadmium, zinc, copper and iron by sorghum plants. Sci Total Environ 326:239–247
Polle A (2001) Dissecting the superoxide dismutase-ascorbate peroxidaseglutathione pathway in chloroplast by metabolic modeling. Computer simulations as a step towards flux analysis. Plant Physiol 126:445–462
Reis GSM, Almeida A-AF, Almeida NM, Castro AV, Mangabeira PAO, Pirovani CP (2015) Molecular, biochemical and ultrastructural changes induced by pb toxicity in seedlings of Theobroma cacao L. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0129696
Rodríguez-Serrano M, Romero-Puertas M, Pazmiño DM, Testillano PS, Risuen MC, Rio LA, Sandalio LM (2009) Cellular response of pea plants to cadmium toxicity: cross talk between reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide, and calcium. Plant Physiol 150:229–243
Sandalio LM, Dalurzo HC, Gómez M, Romero-Puertas MC, Del Rio LA (2001) Cadmium-induced changes in the growth and oxidative metabolism of pea plants. J Exp Bot 52:2115–2126
Sanità di Toppi L, Gabbrielli R (1999) Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ Exp Bot 41:105–130
Santos IC et al (2014) Molecular, physiological and biochemical responses of Theobroma cacao l. genotypes to soil water deficit. PLoS One 9(12):e115746
Santos MLS, Almeida AAF, Silva MN, Oliveira BRM, Silva JVS, Souza Junior JO, Ahnert D, Baligar VC (2020) Mitigation of cadmium toxicity by zinc in juvenile cacao: physiological, biochemical, molecular and micromorphological responses. Environ Exp Bot 179:104201
Sarwar N, Saifullah Malhi SS, Zia MH, Naeem A, Bibi S, Farid G (2010) Role of mineral nutrition in minimizing cadmium accumulation by plants. J Sci Food Agric 90:925–937
Sharma SS, Dietz K-J (2008) The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci 14(1):1360–1385
Shi GR, Cai QS (2008) Photosynthetic and anatomic responses of peanut leaves to cadmium stress. Photosynthetica 46:627–630
Shi Q, Wang J, Zou J, Jiang Z, Wang J, Wu H, Jiang W, Liu D (2016) Cd subcellular localization in root tips of Hordeum vulgare. Pol J Environ Stud 25(2):903–908
Siripornadulsil S, Traina S, Verma DPS, Sayre RT (2002) Molecular mechanisms of proline-mediated tolerance to toxic heavy metals in transgenic microalgae. Plant Cell 14:2837–2847
Souza Júnior JO et al (2011) Substrato e adubação fosfatada para a produção de mudas clonais de cacau. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 35:151–159
Souza Júnior JO et al (2012) Diagnose foliar na cultura do cacau. In: Prado RM (ed) Nutrição de Plantas: Diagnose Foliar em Frutíferas. Jaboticabal: FCAV/FAPESP, p 443–476
Souza VL, de Almeida AA, de Souza JS, Mangabeira PA, de Jesus RM, Pirovani CP, Ahnert D, Baligar VC, Loguercio LL (2014) Altered physiology, cell structure, and gene expression of Theobroma cacao seedlings subjected to Cu toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:1217–1230
Sunitha MS, Prashant S, Anil Kumar S, Rao S, Narasu ML, Kishor PBK (2012) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of heavy metal tolerance in plants: a brief overview of transgenic plants over-expressing phytochelatin synthase and metallothionein genes. Plant Cell Biotechnol Mol Biol 13:99–104
Torres CA, Andrews PK, Davies NM (2006) Physiological and biochemical responses of fruit exocarp of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) mutants to natural photo-oxidative conditions. J Exp Bot 57(9):1933–1947
Verbruggen N, Hermans C, Schat H (2009) Mechanisms to cope with arsenic or cadmium excess in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:364–372
White PJ, Greenwood DJ (2013) Properties and management of cationic elements for crop growth. In: Gregory PJ, Nortcliff S (eds) Soil Conditions and Plant Growth. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford, pp 160–194
Wickramasuriya AM, Dunwell JM (2017) Cacao biotechnology: current status and future prospects. Plant Biotechnol J. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12848
Wu F, Zhang G, Yu J (2003) Interaction of cadmium and four microelements for uptake and translocation in different barley genotypes. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 34:2003–2020
Zornoza P, Vazquez S, Esteban E, Fernández-Pascual M, Ca R (2002) Cadmium-stress in nodulated white lupin: strategies to avoid toxicity. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:1003–1009
Zornoza P, Sánchez-Pardo B, Carpena RO (2010) Interaction and accumulation of manganese and cadmium in the manganese accumulator Lupinus albus. J Plant Physiol 167:1027–1032
Code availability
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was funded by a grant from USDA-ARS (NACA 58-8042-8-014F), within an international cooperative agreement with Universidade Estadual de Santa Cruz (UESC) and FUNPAB, Bahia, Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Joedson P. Barroso, Alex-Alan F. Almeida, Junea L. Nascimento, Bruna R. M. Oliveira, Ivanildes C. Santos, José O. Souza Júnior, Pedro A. O. Mangabeira, Dário Ahnert, and Virupax Baligar. Methodology: Joedson P. Barroso, Junea L. Nascimento, and Pedro A. O. Mangabeira. Formal analysis and investigation: Joedson P. Barroso and Junea L. Nascimento. Writing and preparation of the original draft: Joedson P. Barroso and Bruna R. M. Oliveira. Writing, reviewing, and editing: Joedson P. Barroso, Alex-Alan F. Almeida, and Bruna R. M. Oliveira. Resources: Joedson P. Barroso, Alex-Alan F. Almeida, Dário Ahnert, and Virupax Baligar. Supervision: Alex-Alan F. Almeida. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1986 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Barroso, J.P., de Almeida, AA.F., do Nascimento, J.L. et al. The damage caused by Cd toxicity to photosynthesis, cellular ultrastructure, antioxidant metabolism, and gene expression in young cacao plants are mitigated by high Mn doses in soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 115646–115665 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30561-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30561-1