Abstract
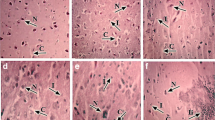
The heat shock response (HSR) is a cellular protective mechanism that is characterized by the induction of heat shock transcription factors (HSFs) and heat shock proteins (HSPs) in response to diverse cellular and environmental stressors, including cadmium (Cd). However, little is known about the relationship between the damaging effects of Cd and the HSR pathway in the chicken cerebrum following Cd exposure. To explore whether Cd exposure elicits cerebral damage and triggers the HSR pathway, chicks were exposed to Cd in the daily diet at different concentrations (35, 70, or 140 mg/kg feed) for 90 days, while a control group was fed the standard diet without Cd. Histopathological examination of cerebral tissue from Cd-exposed chickens showed neuronal damage, as evidenced by swelling and degeneration of neurons, loss of neurons, and capillary damage. Cd exposure significantly increased mRNA expression of HSF1, HSF2, and HSF3, and mRNA and protein expression of three major stress-inducible HSPs (HSP60, HSP70, and HSP90). Moreover, Cd exposure differentially modulated mRNA expression of small HSP (sHSPs), most notably reducing expression of HSP27 (HSPB1). Furthermore, Cd exposure increased TUNEL-positive neuronal apoptotic cells and up-regulated protein expression of caspase-1, caspase-8, caspase-3, and p53, leading to apoptosis. Taken together, these data demonstrate that activation of the HSR and apoptotic pathways by Cd exposure is involved in Cd-elicited cerebral damage in the chicken.
Graphical Abstract
Synopsis for the graphical abstract
Cadmium (Cd)-induced neuronal damage triggers the heat shock response (HSR) by activating heat shock transcription factors (HSFs) and subsequent induction of major heat shock proteins (notably, HSP60, HSP70, and HSP90). Moreover, Cd exposure activates caspase-1, caspase-8, caspase-3, and p53 protein, thereby resulting in neuronal apoptosis in the chicken brain.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdeen A, Abou-Zaid OA, Abdel-Maksoud HA, Aboubakr M, Abdelkader A, Abdelnaby A, Abo-Ahmed AI, El-Mleeh A, Mostafa O, Abdel-Daim M, Aleya L (2019) Cadmium overload modulates piroxicam-regulated oxidative damage and apoptotic pathways. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:25167–25177
Akerfelt M, Trouillet D, Mezger V, Sistonen L (2007) Heat shock factors at a crossroad between stress and development. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1113:15–27
Akerfelt M, Morimoto RI, Sistonen L (2010) Heat shock factors: integrators of cell stress, development and lifespan. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:545–555
Al Olayan EM, Aloufi AS, AlAmri OD, El-Habit OH, Abdel Moneim AE (2020) Protocatechuic acid mitigates cadmium-induced neurotoxicity in rats: role of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Sci Total Environ 723:137969
Albokhadaim IF, Althnaian TA, El-Bahr SM (2019) Gene expression of heat shoc kproteins/factors (HSP60, HSP70, HSP90, HSF-1, HSF-3) and antioxidant enzyme activities in heat stressed broilers treated with vitamin C. Pol J Vet Sci 22:565–572
Ali S, Awan Z, Mumtaz S, Shakir HA, Ahmad F, Ulhaq M, Tahir HM, Awan MS, Sharif S, Irfan M, Khan MA (2020) Cardiac toxicity of heavy metals (cadmium and mercury) and pharmacological intervention by vitamin C in rabbits. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:29266–29279
Alnahdi HS, Sharaf IA (2019) Possible prophylactic effect of omega-3 fatty acids on cadmium-induced neurotoxicity in rats’ brains. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:31254–31262
Al-Zghoul MB, Dalab AE, Yahya IE, Althnaian TA, Al-Ramadan SY, Ali AM, Albokhadaim IF, El-Bahr SM, Al Busadah KA, Hannon KM (2015) Thermal manipulation during broiler chicken embryogenesis: Effect on mRNA expressions of Hsp108, Hsp70, Hsp47 and Hsf-3 during subsequent post-hatch thermal challenge. Res Vet Sci 103:211–217
Balakrishnan KN, Ramiah SK, Zulkifli I (2023) Heat shock protein response to stress in poultry: a review. Animals (basel) 13:317
Batulan Z, Taylor DM, Aarons RJ, Minotti S, Doroudchi MM, Nalbantoglu J, Durham HD (2006) Induction of multiple heat shock proteins and neuroprotection in a primary culture model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol Dis 24:213–225
Behdarvandy M, Karimian M, Atlasi MA, Azami Tameh A (2020) Heat shock protein 27 as a neuroprotective biomarker and a suitable target for stem cell therapy and pharmacotherapy in ischemic stroke. Cell Biol Int 44:356–367
Ben P, Zhang Z, Xuan C, Sun S, Shen L, Gao Y, Cao X, Zhou Y, Lan L, Yin Z, Luo L (2015) Protective effect of L-theanine on cadmium-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by inhibiting the mitochondria-mediated pathway. Neurochem Res 40:1661–1670
Bi SS, Jin HT, Talukder M, Ge J, Zhang C, Lv MW, Yaqoob Ismail MA, Li JL (2021) The protective effect of nnano-selenium against cadmium-induced cerebellar injury via the heat shock protein pathway in chicken. Food Chem Toxicol : an International Journal Published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 154:112332
Branca JJV, Morucci G, Maresca M, Tenci B, Cascella R, Paternostro F, Ghelardini C, Gulisano M, Di Cesare ML, Pacini A (2018) Selenium and zinc: Two key players against cadmium-induced neuronal toxicity. Toxicol Vitro : an International Journal Published in Association with BIBRA 48:159–169
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55:611–622
Cao F, Zhou T, Simpson D, Zhou Y, Boyer J, Chen B, Jin T, Cordeiro-Stone M, Kaufmann W (2007) p53-Dependent but ATM-independent inhibition of DNA synthesis and G2 arrest in cadmium-treated human fibroblasts. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 218:174–185
Cao H, Gao F, Xia B, Zhang M, Liao Y, Yang Z, Hu G, Zhang C (2016) Alterations in trace element levels and mRNA expression of Hsps and inflammatory cytokines in livers of duck exposed to molybdenum or/and cadmium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 125:93–101
Cedraz H, Gromboni JGG, Garcia AAPJ, Farias Filho RV, Souza TM, Oliveira ER, Oliveira EB, Nascimento CSD, Meneghetti C, Wenceslau AA (2017) Heat stress induces expression of HSP genes in genetically divergent chickens. PLoS One 12:e0186083
Chen J, Pan T, Wan N, Sun Z, Zhang Z, Li S (2017) Cadmium-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in chicken neutrophils is alleviated by selenium. J Inorg Biochem 170:169–177
Chen S, Liu G, Long M, Zou H, Cui H (2018) Alpha lipoic acid attenuates cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in rat. J Inorg Biochem 184:19–26
Chunhabundit R (2016) Cadmium exposure and potential health risk from foods in contaminated area, Thailand. Toxicol Res 32:65–72
Cong Y, Chi Q, Teng X, Li S (2019) The protection of selenium against cadmium-induced mitochondrial damage via the cytochrome P450 in the livers of chicken. Biol Trace Elem Res 190:484–492
D’Souza SM, Brown IR (1998) Constitutive expression of heat shock proteins Hsp90, Hsc70, Hsp70 and Hsp60 in neural and non-neural tissues of the rat during postnatal development. Cell Stress Chaperones 3:188–199
D’Mello SR, Kuan CY, Flavell RA, Rakic P (2000) Caspase-3 is required for apoptosis-associated DNA fragmentation but not for cell death in neurons deprived of potassium. J Neurosci Res 59:24–31
Dukay B, Csoboz B, Toth ME (2019) Heat-Shock Proteins in Neuroinflammation. Front Pharmacol 10:920
Dutcher SA, Underwood BD, Walker PD, Diaz FG, Michael DB (1998) Patterns of heat-shock protein 70 biosynthesis following human traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 15:411–420
El-Kott AF, Abd-Lateif AM, Khalifa HS, Morsy K, Ibrahim EH, Bin-Jumah M, Abdel-Daim MM, Aleya L (2020) Kaempferol protects against cadmium chloride-induced hippocampal damage and memory deficits by activation of silent information regulator 1 and inhibition of poly (ADP-Ribose) polymerase-1. Sci Total Environ 728:138832
Fan TJ, Han LH, Cong RS, Liang J (2005) Caspase family proteases and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (shanghai) 37:719–727
Feder ME, Hofmann GE (1999) Heat-shock proteins, molecular chaperones, and the stress response: evolutionary and ecological physiology. Annu Rev Physiol 61:243–282
Franklin TB, Krueger-Naug AM, Clarke DB, Arrigo AP, Currie RW (2005) The role of heat shock proteins Hsp70 and Hsp27 in cellular protection of the central nervous system. Int J Hyperthermia 21:379–392
Friedman MJ, Li S, Li XJ (2009) Activation of gene transcription by heat shock protein 27 may contribute to its neuronal protection. J Biol Chem 284:27944–27951
Fujimoto M, Nakai A (2010) The heat shock factor family and adaptation to proteotoxic stress. FEBS J 277:4112–4125
Gass P, Schroder H, Prior P, Kiessling M (1994) Constitutive expression of heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) in neurons of the rat brain. Neurosci Lett 182:188–192
Ge J, Huang Y, Lv M, Zhang C, Talukder M, Li J, Li J (2022) Cadmium induced Fak-mediated anoikis activation in kidney via nuclear receptors (AHR/CAR/PXR)-mediated xenobiotic detoxification pathway. J Inorg Biochem 227:111682
Genchi G, Sinicropi MS, Lauria G, Carocci A, Catalano A (2020) The effects of cadmium toxicity. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:3782
Giri SS, Sen SS, Jun JW, Sukumaran V, Park SC (2016) Immunotoxicological effects of cadmium on Labeo rohita, with emphasis on the expression of HSP genes. Fish Shellfish Immunol 54:164–171
Hall L, Martinus RD (2013) Hyperglycaemia and oxidative stress upregulate HSP60 & HSP70 expression in HeLa cells. Springerplus 2:431
Hao R, Song X, Li F, Tan X, Sun-Waterhouse D, Li D (2020) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester reversed cadmium-induced cell death in hippocampus and cortex and subsequent cognitive disorders in mice: Involvements of AMPK/SIRT1 pathway and amyloid-tau-neuroinflammation axis. Food Chem Toxicol 144:111636
Huang M, Su L, Yang L, Zhu L, Liu Z, Duan R (2017) Effect of exogenous TGF-beta1 on the cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibiting apoptosis of proximal tubular cells through PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact 269:25–32
Kang D, Shim K (2021) Early heat exposure effect on the heat shock proteins in broilers under acute heat stress. Poult Sci 100:100964
Kawazoe Y, Tanabe M, Sasai N, Nagata K, Nakai A (1999) HSF3 is a major heat shock responsive factor duringchicken embryonic development. Eur J Biochem 265:688–697
Khan A, Ikram M, Muhammad T, Park J, Kim MO (2019) Caffeine modulates cadmium-induced oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and cognitive impairments by regulating Nrf-2/HO-1 in vivo and in vitro. J Clin Med 8:680
Lee JY, Tokumoto M, Hattori Y, Fujiwara Y, Shimada A, Satoh M (2016) Different regulation of p53 expression by cadmium exposure in kidney, liver, intestine, vasculature, and brain astrocytes. Toxicol Res 32:73–80
Li JL, Jiang CY, Li S, Xu SW (2013) Cadmium induced hepatotoxicity in chickens (Gallus domesticus) and ameliorative effect by selenium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 96:103–109
Li T, Yu H, Song Y, Zhang R, Ge M (2019) Protective effects of Ganoderma triterpenoids on cadmium-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory injury in chicken livers. J Trace Elem Med Biol 52:118–125
Liang Y, Zeng T, Tian J, Yan J, Lan Z, Chen J, Xin X, Lei B, Cai Z (2021) Long-term environmental cadmium exposure induced serum metabolic changes related to renal and liver dysfunctions in a female cohort from Southwest China. Sci Total Environ 798:149379
Lin J, Zhao HS, Qin L, Li XN, Zhang C, Xia J, Li JL (2018) Atrazine triggers mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in quail (Coturnix C. coturnix) cerebrum via activating xenobiotic-sensing nuclear receptors and modulating cytochrome P450 systems. J Agric Food Chem 66:6402–6413
Liu L, Liu Y, Cheng X, Qiao X (2021) The alleviative effects of quercetin on cadmium-induced necroptosis via inhibition ROS/iNOS/NF-kappaB pathway in the chicken brain. Biol Trace Elem Res 199:1584–1594
Loones MT, Chang Y, Morange M (2000) The distribution of heat shock proteins in the nervous system of the unstressed mouse embryo suggests a role in neuronal and non-neuronal differentiation. Cell Stress Chaperones 5:291–305
Mitra T, Mahanty A, Ganguly S, Purohit GK, Mohanty S, Parida PK, Behera PR, Raman RK, Mohanty BP (2018) Expression patterns of heat shock protein genes in Rita rita from natural riverine habitat as biomarker response against environmental pollution. Chemosphere 211:535–546
Musial K, Zwolinska D (2012) Hsp27 as a marker of cell damage in children on chronic dialysis. Cell Stress Chaperones 17:675–682
Nakai A, Morimoto RI (1993) Characterization of a novel chicken heat shock transcription factor, heat shock factor 3, suggests a new regulatory pathway. Mol Cell Biol 13:1983–1997
Nakai A, Kawazoe Y, Tanabe M, Nagata K, Morimoto RI (1995) The DNA-binding properties of two heat shock factors, HSF1 and HSF3, are induced in the avian erythroblast cell line HD6. Mol Cell Biol 15:5268–5278
Nazimabashir MV, Miltonprabu S (2015) Cadmium induced cardiac oxidative stress in rats and its attenuation by GSP through the activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact 242:179–193
Pirkkala L, Nykanen P, Sistonen L (2001) Roles of the heat shock transcription factors in regulation of the heat shock response and beyond. FASEB J 15:1118–1131
Quraishe S, Asuni A, Boelens WC, O’Connor V, Wyttenbach A (2008) Expression of the small heat shock protein family in the mouse CNS: differential anatomical and biochemical compartmentalization. Neuroscience 153:483–491
Rajdev S, Sharp FR (2000) Stress proteins as molecular markers of neurotoxicity. Toxicol Pathol 28:105–112
Rogalska J, Pilat-Marcinkiewicz B, Brzoska MM (2011) Protective effect of zinc against cadmium hepatotoxicity depends on this bioelement intake and level of cadmium exposure: a study in a rat model. Chem Biol Interact 193:191–203
Saedi S, Jafarzadeh Shirazi MR, Niazi A, Tahmasebi A, Ebrahimie E (2021) Prepubertal exposure to high dose of cadmium induces hypothalamic injury through transcriptome profiling alteration and neuronal degeneration in female rats. Chem Biol Interact 337:109379
Sanjeev S, Bidanchi RM, Murthy MK, Gurusubramanian G, Roy VK (2019) Influence of ferulic acid consumption in ameliorating the cadmium-induced liver and renal oxidative damage in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:20631–20653
Shabtay A, Arad Z (2006) Reciprocal activation of HSF1 and HSF3 in brain and blood tissues: is redundancy developmentally related? Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 291:R566–R572
Shinkai Y, Masuda A, Akiyama M, Xian M, Kumagai Y (2017) Cadmium-mediated activation of the HSP90/HSF1 pathway regulated by reactive persulfides/polysulfides. Toxicol Sci 156:412–421
Shinkawa T, Tan K, Fujimoto M, Hayashida N, Yamamoto K, Takaki E, Takii R, Prakasam R, Inouye S, Mezger V, Nakai A (2011) Heat shock factor 2 is required for maintaining proteostasis against febrile-range thermal stress and polyglutamine aggregation. Mol Biol Cell 22:3571–3583
Song Y, Zhang R, Wang H, Yan Y, Ming G (2018) Protective effect of Agaricus blazei polysaccharide against cadmium-induced damage on the testis of chicken. Biol Trace Elem Res 184:491–500
Taghavizadeh Yazdi ME, Amiri MS, Nourbakhsh F, Rahnama M, Forouzanfar F, Mousavi SH (2021) Bio-indicators in cadmium toxicity: Role of HSP27 and HSP70. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:26359–26379
Talukder M, Bi SS, Jin HT, Ge J, Zhang C, Lv MW, Li JL (2021) Cadmium induced cerebral toxicity via modulating MTF1-MTs regulatory axis. Environ Pollut 285:117083
Tamas MJ, Fauvet B, Christen P, Goloubinoff P (2018) Misfolding and aggregation of nascent proteins: a novel mode of toxic cadmium action in vivo. Curr Genet 64:177–181
Tan S, Chi Q, Liu T, Sun Z, Min Y, Zhang Z, Li S (2017) Alleviation mechanisms of selenium on cadmium-spiked neutrophil injury to chicken. Biol Trace Elem Res 178:301–309
Tanabe M, Nakai A, Kawazoe Y, Nagata K (1997) Different thresholds in the responses of two heat shock transcription factors, HSF1 and HSF3. J Biol Chem 272:15389–15395
Tanabe M, Kawazoe Y, Takeda S, Morimoto RI, Nagata K, Nakai A (1998) Disruption of the HSF3 gene results in the severe reduction of heat shock gene expression and loss of thermotolerance. EMBO J 17:1750–1758
Tang KK, Liu XY, Wang ZY, Qu KC, Fan RF (2019) Trehalose alleviates cadmium-induced brain damage by ameliorating oxidative stress, autophagy inhibition, and apoptosis. Metallomics 11:2043–2051
Tonkin RS, Bowles C, Perera CJ, Keating BA, Makker PGS, Duffy SS, Lees JG, Tran C, Don AS, Fath T, Liu L, O’Carroll SJ, Nicholson LFB, Green CR, Gorrie C, Moalem-Taylor G (2018) Attenuation of mechanical pain hypersensitivity by treatment with Peptide5, a connexin-43 mimetic peptide, involves inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome in nerve-injured mice. Exp Neurol 300:1–12
Toth ME, Gonda S, Vigh L, Santha M (2010) Neuroprotective effect of small heat shock protein, Hsp27, after acute and chronic alcohol administration. Cell Stress Chaperones 15:807–817
Turner A (2019) Cadmium pigments in consumer products and their health risks. Sci Total Environ 657:1409–1418
Unsal C, Kanter M, Aktas C, Erboga M (2015) Role of quercetin in cadmium-induced oxidative stress, neuronal damage, and apoptosis in rats. Toxicol Ind Health 31:1106–1115
van der Weerd L, Tariq Akbar M, Aron Badin R, Valentim LM, Thomas DL, Wells DJ, Latchman DS, Gadian DG, Lythgoe MF, de Belleroche JS (2010) Overexpression of heat shock protein 27 reduces cortical damage after cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:849–856
Verma P, Pfister JA, Mallick S, D’Mello SR (2014) HSF1 protects neurons through a novel trimerization- and HSP-independent mechanism. J Neurosci 34:1599–1612
Wang B, Du Y (2013) Cadmium and its neurotoxic effects. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:898034
Wang YJ, Yan J, Zou XL, Guo KJ, Zhao Y, Meng CY, Yin F, Guo L (2017) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells repair cadmium-induced rat testis injury by inhibiting mitochondrial apoptosis. Chem Biol Interact 271:39–47
Wang H, Abel GM, Storm DR, Xia Z (2019) Cadmium exposure impairs adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Toxicol Sci 171:501–514
Wang Y, Liu J, Chen R, Qi M, Tao D, Xu S (2020) The antagonistic effects of selenium yeast (SeY) on cadmium-induced inflammatory factors and the heat shock protein expression levels in chicken livers. Biol Trace Elem Res 198:260–268
Wang J, Zhu H, Lin S, Wang K, Wang H, Liu Z (2021) Protective effect of naringenin against cadmium-induced testicular toxicity in male SD rats. J Inorg Biochem 214:111310
Wang X, Hu R, Wang C, Wei Z, Pi S, Li Y, Li G, Yang F, Zhang C (2022) Nrf2 axis and endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated autophagy activation is involved in molybdenum and cadmium co-induced hepatotoxicity in ducks. J Inorg Biochem 229:111730
Wei Z, Nie G, Yang F, Pi S, Wang C, Cao H, Guo X, Liu P, Li G, Hu G, Zhang C (2020) Inhibition of ROS/NLRP3/Caspase-1 mediated pyroptosis attenuates cadmium-induced apoptosis in duck renal tubular epithelial cells. Environ Pollut 273:115919
Wen S, Wang L, Zhang W, Xu M, Song R, Zou H, Gu J, Bian J, Yuan Y, Liu Z (2021a) Induction of mitochondrial apoptosis pathway mediated through caspase-8 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase by cadmium-activated Fas in rat cortical neurons. Metallomics 13:mfab042
Wen S, Wang L, Zou H, Gu J, Song R, Bian J, Yuan Y, Liu Z (2021b) Puerarin attenuates cadmium-induced neuronal injury via stimulating cadmium excretion, inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis. Biomolecules 11:978
Xiao X, Zuo X, Davis AA, McMillan DR, Curry BB, Richardson JA, Benjamin IJ (1999) HSF1 is required for extra-embryonic development, postnatal growth and protection during inflammatory responses in mice. EMBO J 18:5943–5952
Xie J, Tang L, Lu L, Zhang L, Xi L, Liu HC, Odle J, Luo X (2014) Differential expression of heat shock transcription factors and heat shock proteins after acute and chronic heat stress in laying chickens (Gallus gallus). PLoS One 9:e102204
Yang XF, Fan GY, Liu DY, Zhang HT, Xu ZY, Ge YM, Wang ZL (2015) Effect of cadmium exposure on the histopathology of cerebral cortex in juvenile mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 165:167–172
Yang M, Chen W, Zhang Y, Yang R, Wang Y, Yuan H (2018) EphrinB/EphB signaling contributes to spinal nociceptive processing via calpain-1 and caspase-3. Mol Med Rep 18:268–278
Yu Y, Hu LL, Liu L, Yu LL, Li JP, Rao JA, Zhu LJ, Bao HH, Cheng XS (2021) Hsp22 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Bioengineered 12:12544–12554
Yuan Y, Jiang C, Hu F, Wang Q, Zhang K, Wang Y, Gu J, Liu X, Bian J, Liu Z (2015) The role of mitogen-activated protein kinase in cadmium-induced primary rat cerebral cortical neurons apoptosis via a mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. J Trace Elem Med Biol 29:275–283
Yuan Y, Zhang Y, Zhao S, Chen J, Yang J, Wang T, Zou H, Wang Y, Gu J, Liu X, Bian J, Liu Z (2018) Cadmium-induced apoptosis in neuronal cells is mediated by Fas/FasL-mediated mitochondrial apoptotic signaling pathway. Sci Rep 8:8837
Yuan Y, Yang J, Chen J, Zhao S, Wang T, Zou H, Wang Y, Gu J, Liu X, Bian J, Liu Z (2019) Alpha-lipoic acid protects against cadmium-induced neuronal injury by inhibiting the endoplasmic reticulum stress eIF2alpha-ATF4 pathway in rat cortical neurons in vitro and in vivo. Toxicology 414:1–13
Zhang R, Zhu Y, Dong X, Liu B, Zhang N, Wang X, Liu L, Xu C, Huang S, Chen L (2017) Celastrol Attenuates Cadmium-Induced Neuronal Apoptosis via Inhibiting Ca(2+) -CaMKII-Dependent Akt/mTOR Pathway. J Cell Physiol 232:2145–2157
Zhang R, Liu Y, Xing L, Zhao N, Zheng Q, Li J, Bao J (2018) The protective role of selenium against cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity in laying hens: Expression of Hsps and inflammation-related genes and modulation of elements homeostasis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 159:205–212
Zhang T, Gao X, Luo X, Li L, Ma M, Zhu Y, Zhao L, Li R (2019) The effects of long-term exposure to low doses of cadmium on the health of the next generation of mice. Chem Biol Interact 312:108792
Zhao P, Guo Y, Zhang W, Chai H, Xing H, Xing M (2017) Neurotoxicity induced by arsenic in Gallus Gallus: Regulation of oxidative stress and heat shock protein response. Chemosphere 166:238–245
Zhao Y, Fan JH, Luo Y, Talukder M, Li XN, Zuo YZ, Li JL (2019) Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP)-induced hepatotoxicity in quail (Coturnix japonica) via suppression of the heat shock response. Chemosphere 228:685–693
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32172932), the Key Program of the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (No. ZD2021C003), the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (No. CARS-35), Distinguished Professor of the Longjiang Scholars Support Project (No. T201908), and the Heilongjiang Touyan Innovation Team Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Milton Talukder: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Shao-Shuai Bi: methodology, formal analysis, writing—review and editing. Mei-Wei Lv: investigation, formal analysis. Jing Ge: formal analysis, writing—review and editing. Cong Zhang: writing—review and editing. Jin-Long Li: conceptualization, funding acquisition, supervision, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Animal experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals and were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Northeast Agricultural University, China (approval number: NEAUEC20190314).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Talukder, M., Bi, SS., Lv, MW. et al. Involvement of the heat shock response (HSR) regulatory pathway in cadmium-elicited cerebral damage. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 106648–106659 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29880-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29880-0