Abstract
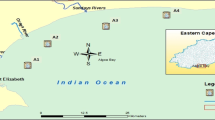
Surface soil and river sediment samples were collected from the downstream of Chuhe River basin, East China, to investigate the occurrence and accumulation characteristics of legacy and novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs). The respective concentrations of BDE-209 and nine NBFRs ranged from n.d. to 41.4 ng/g dry weight (dw) and from 0.35 to 362.78 ng/g dw in the collected surface soil samples and ranged from 0.29 to 19.73 ng/g dw and from 0.70 to 66.83 ng/g dw in the collected river sediment samples. Soil samples exhibited a higher potential to accumulate BTBPE while the relative abundance of PBT in the collected sediment samples was significantly higher than that in soils. Even so, BTBPE was the predominant NBFR in both soil and sediment samples. The concentrations and relative abundances of legacy and NBFRs exhibited large spatial variation. The calculated concentration ratios of the total of the nine NBFRs (∑9NBFRs) to BDE-209 (∑9NBFRs/BDE-209) in most of the analyzed samples far exceeded 1, implying a clear shift from legacy brominated flame retardants to NBFRs in the downstream of Chuhe River basin.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
An Q, Aamir M, Mao S, Liu Y, Wang Y, Zheng P, Liu W (2022) Current pollution status, spatial features, and health risks of legacy and emerging halogenated flame retardants in agricultural soils across China. Sci Total Environ 803:150043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150043
Aznar-Alemany O, Aminot Y, Vila-Cano J, Kock-Schulmeyer M, Readman JW, Marques A, Godinho L, Botteon E, Ferrari F, Boti V, Albanis T, Eljarrat E, Barcelo D (2018) Halogenated and organophosphorus flame retardants in European aquaculture samples. Sci Total Environ 612:492–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.199
Bergman A, Ryden A, Law RJ, de Boer J, Covaci A, Alaee M, Birnbaum L, Petreas M, Rose M, Sakai S, Van den Eede N, van der Veen I (2012) A novel abbreviation standard for organobromine, organochlorine and organophosphorus flame retardants and some characteristics of the chemicals. Environ Int 49:57–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2012.08.003
Brown DJ, Van Overmeire I, Goeyens L, Denison MS, De Vito MJ, Clark GC (2004) Analysis of Ah receptor pathway activation by brominated flame retardants. Chemosphere 55:1509–1518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.10.019
Cao Z, Xu F, Covaci A, Wu M, Wang H, Yu G, Wang B, Deng S, Huang J, Wang X (2014) Distribution patterns of brominated, chlorinated, and phosphorus flame retardants with particle size in indoor and outdoor dust and implications for human exposure. Environ Sci Technol 48:8839–8846. https://doi.org/10.1021/es501224b
Cao Y, Gao Y, Hu X, Zeng Y, Luo X, Li G, An T, Mai B (2022) Insight into phototransformation mechanism and toxicity evolution of novel and legacy brominated flame retardants in water: a comparative analysis. Water Res 211:118041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118041
Chen SJ, Gao XJ, Mai BX, Chen ZM, Luo XJ, Sheng GY, Fu JM, Zeng EY (2006) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surface sediments of the Yangtze River Delta: levels, distribution and potential hydrodynamic influence. Environ Pollut 144:951–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.01.044
Chen SJ, Feng AH, He MJ, Chen MY, Luo XJ, Mai BX (2013) Current levels and composition profiles of PBDEs and alternative flame retardants in surface sediments from the Pearl River Delta, southern China: comparison with historical data. Sci Total Environ 444:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.104
Covaci A, Harrad S, Abdallah MA, Ali N, Law RJ, Herzke D, de Wit CA (2011) Novel brominated flame retardants: a review of their analysis, environmental fate and behaviour. Environ Int 37:532–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2010.11.007
Dong L, Wang S, Qu J, You H, Liu D (2021) New understanding of novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs): neuro(endocrine) toxicity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:111570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111570
EFSA (2011) Scientific opinion on polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in food. EFSA J 9:2156
EFSA (2012) Scientific opinion on emerging and novel brominated flame retardants BFRs in food. EFSA J 10:2908. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2908
Eng ML, Karouna-Renier NK, Henry PFP, Letcher RJ, Schultz SL, Bean TG, Peters LE, Palace VP, Williams TD, Elliott JE, Fernie KJ (2019) In ovo exposure to brominated flame retardants Part II: assessment of effects of TBBPA-BDBPE and BTBPE on hatching success, morphometric and physiological endpoints in American kestrels. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 179:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.04.047
Ezechias M, Covino S, Cajthaml T (2014) Ecotoxicity and biodegradability of new brominated flame retardants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 110:153–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.08.030
Feng H, Cheng Y, Ruan Y, Tsui MMP, Wang Q, Jin J, Wu R, Zhang H, Lam PKS (2021) Occurrence and spatial distribution of legacy and novel brominated flame retardants in seawater and sediment of the South China sea. Environ Pollut 271:116324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116324
Gao S, Hong J, Yu Z, Wang J, Yang G, Sheng G, Fu J (2011) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surface soils from e-waste recycling areas and industrial areas in South China: concentration levels, congener profile, and inventory. Environ Toxicol Chem 30:2688–2696. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.668
Guo J, Venier M, Salamova A, Hites RA (2017) Bioaccumulation of dechloranes, organophosphate esters, and other flame retardants in Great Lakes fish. Sci Total Environ 583:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.063
Hao Y, Xiong S, Wang P, Yang R, Pei Z, Li Y, Zhang Q, Jiang G (2022) Novel brominated and organophosphate flame retardants in the atmosphere of Fildes Peninsula, West Antarctica: continuous observations from 2011 to 2020. J Hazard Mater 440:129776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129776
Hoang AQ, Takahashi S, Da Le N, Duong TT, Huong Pham TM, Mai Pham TN, Huong Nguyen TA, Tran TM, Tu MB, Le Quynh TP (2021) Comprehensive determination of polychlorinated biphenyls and brominated flame retardants in surface sediment samples from Hanoi urban area, Vietnam: contamination status, accumulation profiles, and potential ecological risks. Environ Res 197:111158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111158
Hou R, Lin L, Li H, Liu S, Xu X, Xu Y, Jin X, Yuan Y, Wang Z (2021) Occurrence, bioaccumulation, fate, and risk assessment of novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs) in aquatic environments-a critical review. Water Res 198:117168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117168
Hou R, Huang Q, Pan Y, Lin L, Liu S, Li H, Xu X (2022) Novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs) in a tropical marine food web from the South China Sea: the influence of hydrophobicity and biotransformation on structure-related trophodynamics. Environ Sci Technol 56:3147–3158. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c08104
Hu Y, Pei N, Sun Y, Xu X, Zhang Z, Li H, Wang W, Zuo L, Xiong Y, Zeng Y, He K, Mai B (2019) Halogenated flame retardants in mangrove sediments from the Pearl River Estuary, South China: comparison with historical data and correlation with microbial community. Chemosphere 227:315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.075
Jiang Y, Wang X, Zhu K, Wu M, Sheng G, Fu J (2012) Occurrence, compositional patterns, and possible sources of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in agricultural soil of Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 89:936–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.06.047
Klopcic I, Skledar DG, Masic LP, Dolenc MS (2016) Comparison of in vitro hormone activities of novel flame retardants TBB, TBPH and their metabolites TBBA and TBMEPH using reporter gene assays. Chemosphere 160:244–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.06.091
Lee HK, Lee S, Lim JE, Moon HB (2020) Legacy and novel flame retardants in water and sediment from highly industrialized bays of Korea: occurrence, source tracking, decadal time trend, and ecological risks. Mar Pollut Bull 160:111639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111639
Lewis PJ, Lashko A, Chiaradia A, Allinson G, Shimeta J, Emmerson L (2022) New and legacy persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in breeding seabirds from the East Antarctic. Environ Pollut 309:119734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119734
Li WL, Ma WL, Zhang ZF, Liu LY, Song WW, Jia HL, Ding YS, Nakata H, Minh NH, Sinha RK, Moon HB, Kannan K, Sverko E, Li YF (2017) Occurrence and source effect of novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs) in soils from five Asian countries and their relationship with PBDEs. Environ Sci Technol 51:11126–11135. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b03207
Ling S, Zhou S, Tan J, Lu C, Fu M, Peng C, Zhang W, Hu S, Lin K, Zhou B (2022) Brominated flame retardants (BFRs) in sediment from a typical e-waste dismantling region in Southern China: occurrence, spatial distribution, composition profiles, and ecological risks. Sci Total Environ 824:153813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153813
Ling S, Lu C, Peng C, Zhang W, Lin K, Zhou B (2021) Characteristics of legacy and novel brominated flame retardants in water and sediment surrounding two e-waste dismantling regions in Taizhou, eastern China. Sci Total Environ 794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148744.
Liu D, Ma J, Qiu X, Zhao Y, Lin Y, Yang Q, Gao Z, Zhu T (2014) Gridded field observations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soils of North China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 66:482–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-013-9971-8
Mai B, Chen S, Luo X, Chen L, Yang Q, Sheng G, Peng P, Fu J, Zeng EY (2005) Distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments of the Pearl River Delta and adjacent South China Sea. Environ Sci Technol 39:3521–3527. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048083x
Mo L, Zheng J, Wang T, Shi YG, Chen BJ, Liu B, Ma YH, Li M, Zhuo L, Chen SJ (2019) Legacy and emerging contaminants in coastal surface sediments around Hainan Island in South China. Chemosphere 215:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.022
Moller A, Xie Z, Cai M, Sturm R, Ebinghaus R (2012) Brominated flame retardants and dechlorane plus in the marine atmosphere from Southeast Asia toward Antarctica. Environ Sci Technol 46:3141–3148. https://doi.org/10.1021/es300138q
OJEU (2011) Directive 2011/65/EU of the European parliament and of the council of 8 June 2011 on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2011:174:0088:0110:en:PDF. Accessed 14 Aug 2023
Schuhmacher M, Mari M, Nadal M, Domingo JL (2019) Concentrations of dioxins and furans in breast milk of women living near a hazardous waste incinerator in Catalonia, Spain. Environ Int 125:334–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.074
Shi T, Chen SJ, Luo XJ, Zhang XL, Tang CM, Luo Y, Ma YJ, Wu JP, Peng XZ, Mai BX (2009) Occurrence of brominated flame retardants other than polybrominated diphenyl ethers in environmental and biota samples from southern China. Chemosphere 74:910–916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.10.047
Stockholm Convention (2019) All POPs listed in the Stockholm Convention. http://chm.pops.int/TheConvention/ThePOPs/AllPOPs/tabid/2509/Default.aspx. Accessed 14 Aug 2023
Sun Y, Zhu B, Ling S, Yan B, Wang X, Jia S, Martyniuk CJ, Zhang W, Yang L, Zhou B (2022) Decabromodiphenyl ethane mainly affected the muscle contraction and reproductive endocrine system in female adult zebrafish. Environ Sci Technol 56:470–479. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c06679
Tian M, Chen S-J, Wang J, Zheng X-B, Luo X-J, Mai B-X (2011) Brominated flame retardants in the atmosphere of e-waste and rural sites in southern China: seasonal variation, temperature dependence, and gas-particle partitioning. Environ Sci Technol 45:8819–8825. https://doi.org/10.1021/es202284p
Van den Eede N, Dirtu AC, Ali N, Neels H, Covaci A (2012) Multi-residue method for the determination of brominated and organophosphate flame retardants in indoor dust. Talanta 89:292–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2011.12.031
Wang X, Ling S, Guan K, Luo X, Chen L, Han J, Zhang W, Mai B, Zhou B (2019) Bioconcentration, biotransformation, and thyroid endocrine disruption of decabromodiphenyl ethane (Dbdpe), a novel brominated flame retardant, in zebrafish larvae. Environ Sci Technol 53:8437–8446. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b02831
Xiong P, Yan X, Zhu Q, Qu G, Shi J, Liao C, Jiang G (2019) A review of environmental occurrence, fate, and toxicity of novel brominated flame retardants. Environ Sci Technol 53:13551–13569. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b03159
Xiong S, Hao Y, Li Y, Yang R, Pei Z, Zhang Q, Jiang G (2021) Accumulation and influencing factors of novel brominated flame retardants in soil and vegetation from Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica. Sci Total Environ 756:144088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144088
Yin H, Tang Z, Meng T, Zhang M (2020) Concentration profile, spatial distributions and temporal trends of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments across China: implications for risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 206:111205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111205
Zhao XF, Zhang HJ, Ni YW, Lu XB, Zhang XP, Su F, Fan JF, Guan DM, Chen JP (2011) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments of the Daliao River Estuary, China: levels, distribution and their influencing factors. Chemosphere 82:1262–1267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.12.032
Zhao S, Tian L, Zou Z, Liu X, Zhong G, Mo Y, Wang Y, Tian Y, Li J, Guo H, Zhang G (2021) Probing legacy and alternative flame retardants in the air of Chinese cities. Environ Sci Technol 55:9450–9459. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c07367
Zheng G, Wan Y, Shi S, Zhao H, Gao S, Zhang S, An L, Zhang Z (2018) Trophodynamics of emerging brominated flame retardants in the aquatic food web of Lake Taihu: relationship with organism metabolism across trophic levels. Environ Sci Technol 52:4632–4640. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b06588
Zhu B, Lai NL, Wai TC, Chan LL, Lam JC, Lam PK (2014) Changes of accumulation profiles from PBDEs to brominated and chlorinated alternatives in marine mammals from the South China Sea. Environ Int 66:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.01.023
Zhu H, Sun H, Yao Y, Gan Z, Wang Y, Kannan K (2018) Legacy and alternative brominated flame retardants in outdoor dust and pine needles in mainland China: spatial trends, dust-plant partitioning and human exposure. Environ Pollut 243:758–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.097
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Innovation Fund of Nanjing Institute of Environmental Science, Ministry of Ecology and Environment, China (Grant No. ZX2023QT003) and Ecological Environment Research Project of Jiangsu Province, China (Grant No. 2022014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Weilong Xing: resources, investigation. Liangchen Zhong: methodology, investigation. Wen Gu: resources, investigation. Mengyuan Liang: investigation. Lei Wang: supervision, funding acquisition. Zhen Wang: supervision. Lili Shi: supervision. Shuai Sun: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, writing review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Hongwen Sun
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11356_2023_29300_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Details of the chemicals, instrumental analysis, method detection limits, and results of mass concentrations of BFRs in the soil and sediment samples from the downstream of Chuhe River basin, East China. 1 (DOCX 96 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, W., Zhong, L., Gu, W. et al. Occurrence and accumulation characteristics of legacy and novel brominated flame retardants in surface soil and river sediments from the downstream of Chuhe River basin, East China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 97416–97425 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29300-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29300-3