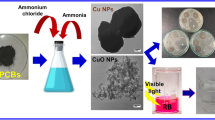
Abstract
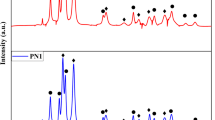
The demand for environmentally friendly and sustainable resource utilization techniques for recycling waste printed circuit boards is significant due to their status as valuable secondary resources, containing high-purity copper and precious metals. In this context, Cu(OH)2/CuO and CuO nanostructures were fabricated using alkaline precipitation and low-temperature aging methods using the strip solution originated from laboratory-scale spent mobile phone printed circuit board recovery process. XRD, FTIR, FESEM-EDX, and TEM were utilized to characterize the as-recovered nanoproducts. A hybrid structure of Cu(OH)2/CuO was formed at 70°, and monoclinic CuO phase was formed at 80 °C aging time. The results show that Cu(OH)2/CuO nanoflakes have an average crystallite size of 24.06 nm and a particle width of 22 ± 3 nm. Cu(OH)2/CuO nanoflakes formed at 70 °C aging temperature and 24-h residence time have finer crystallite and particle sizes than CuO-ridged nanospheres formed at 80 °C aging temperature. The optical band gap energy of Cu(OH)2/CuO and CuO nanostructures formed was found to be 2.28 eV and 2.22 eV, respectively. The hybrid Cu(OH)2/CuO nanostructure photocatalyzed the decomposed 97.28% rhodamine blue using a visible light source, whereas the CuO nanostructure degraded only 14.64% rhodamine blue dye under similar conditions. A surfactant-less hybrid structure is developed without the use of any chemical precursor. Thus, a high value-added product is produced using one waste material to remove another waste in wastewater treatment.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
References
Abdo DM, Abdelbasir SM, El-Sheltawy ST, Ibrahim IA (2021) Recovery of tin as tin oxide nanoparticles from waste printed circuit boards for photocatalytic dye degradation. Korean J Chem Eng 38:1934–1945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-021-0838-9
Adeyemi JO, Onwudiwe DC, Oyedeji AO (2022) Biogenic synthesis of CuO, ZnO, and CuO-ZnO nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Dovyalis caffra and their biological properties. Molecules 27:175–190. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103206
Aguirre JM, Gutiérrez A, Giraldo O (2011) Simple route for the synthesis of copper hydroxy salts. J Braz Chem Soc 22:546–551. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532011000300019
Akhavan O, Azimirad R, Safa S, Hasani E (2011) CuO/Cu(OH)2 hierarchical nanostructures as bactericidal photocatalysts. J Mater Chem 21:9634–9640. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0jm04364h
Akintelu SA, Folorunso AS, Folorunso FA, Oyebamiji AK (2020) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for biomedical application and environmental remediation. Heliyon 6:e04508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04508
Akram N, Guo J, Ma W et al (2020) Synergistic catalysis of Co(OH)2/CuO for the degradation of organic pollutant under visible light irradiation. Sci Rep 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59053-9
Alhebshi N, Huang H, Ghandour R et al (2020) Green synthesized CuxO@Cu nanocomposites on a Cu mesh with dual catalytic functions for dye degradation and hydrogen evaluation. J Alloys Compd 848:156284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156284
Al-Jawhari H, Al-Murashi R, Abu Saba L et al (2019) Effective degradation of MB under natural daylight using green synthesized Cu-Cu2O composite films. Mater Lett 254:233–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.07.070
AlSalhi MS, Sakthisabarimoorthi A, Devanesan S et al (2019) Study on photocatalytic and impedance spectroscopy investigations of composite CuO/ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30:13708–13718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01752-9
Amaresh A, Thammaiah R, Guptha CKN, Nagarathna A (2020) E-waste Disposal in India: Challenges and constraints, Environ Sci An Indian J 16(4):2–9
Anani OA, Adama KK, Ukhurebor KE, et al (2023) Application of nanofibrous protein for the purification of contaminated water as a next generational sorption technology: a review. Nanotechnology 34. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/acbd9f
Azimi S, Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh A (2015) Enhanced activity of clinoptilolite-supported hybridized PbS-CdS semiconductors for the photocatalytic degradation of a mixture of tetracycline and cephalexin aqueous solution. J Mol Catal a: Chem 408:152–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2015.07.017
Bagyalakshmi S, Sivakami A, Pal K et al (2022) Manufacturing of electrochemical sensors via carbon nanomaterials novel applications: a systematic review. J Nanopart Res 24:201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05576-3
Baldé CP, D’Angelo E, Luda V et al (2022) Global transboundary e-waste flows monitor 2022. United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR), Bonn, Germany, p 66
Chan YB, Selvanathan V, Tey LH, et al (2022) Effect of calcination temperature on structural, morphological and optical properties of copper oxide nanostructures derived from Garcinia mangostana L. leaf extract. Nanomaterials 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203589
Chandra MR, Rao TS, Pammi SVN, Sreedhar B (2015) An enhanced visible light active rutile titania-copper/polythiophene nanohybrid material for the degradation of rhodamine B dye. Mater Sci Semicond Process 30:672–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2014.09.009
Chen D, Ray AK (1998) Photodegradation kinetics of 4-nitrophenol in TiO2 suspension. Water Res 32:3223–3234. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00118-3
Cucchiella F, D’Adamo I, Lenny Koh SC, Rosa P (2015) Recycling of WEEEs: an economic assessment of present and future e-waste streams. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 51:263–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.06.010
Deka P, Hazarika A, Deka RC, Bharali P (2016) Influence of CuO morphology on the enhanced catalytic degradation of methylene blue and methyl orange. RSC Adv 6:95292–95305. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra20173c
Dodoo-Arhin D, Mbu EE, Ntwampe SK, et al (2021) Synthesis of nanostructured cupric oxide for visible light assisted degradation of organic wastewater pollutants. Cogent Eng 8. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2021.1920563
Dong S, Feng J, Fan M et al (2015) Recent developments in heterogeneous photocatalytic water treatment using visible light-responsive photocatalysts: a review. RSC Adv 5:14610–14630. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra13734e
Edington JW (1975) Electron diffraction in the electron microscope. In: Edington JW (ed) Electron Diffraction in the Electron Microscope, Macmillan Education, London, p 1–77
Elkodous MA, El-Sayyad GS, Mohamed AEE et al (2019) Layer-by-layer preparation and characterization of recyclable nanocomposite (CoxNi1−xFe2O4; X = 0.9/SiO2/TiO2). J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30:8312–8328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01149-8
Elshabrawy SO, Elhussieny A, Taha MM et al (2023) Wastewater treatment via sugarcane bagasse pulp. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-04831-x
Elwakeel KZ, Guibal E (2015) Arsenic(V) sorption using chitosan/Cu(OH)2 and chitosan/CuO composite sorbents. Carbohyd Polym 134:190–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.07.012
Gautam P, Behera CK, Sinha I et al (2022) High added-value materials recovery using electronic scrap-transforming waste to valuable products. J Clean Prod 330:129836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129836
Gautam P, De AK, Sinha I, Kumar C (2023) Genesis of copper oxide nanoparticles from waste printed circuit boards and evaluation of their photocatalytic activity. Environ Res 229:115951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115951
Grigore ME, Biscu ER, Holban AM et al (2016) Methods of synthesis, properties and biomedical applications of CuO nanoparticles. Pharmaceuticals 9:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9040075
Hadi P, Xu M, Lin CSK et al (2015) Waste printed circuit board recycling techniques and product utilization. J Hazard Mater 283:234–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.09.032
Haseena S, Shanavas S, Duraimurugan J, et al (2019) Investigation on photocatalytic and antibacterial ability of green treated copper oxide nanoparticles using Artabotrys hexapetalus and Bambusa vulgaris plant extract. Mater Res Express 6.https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab59a9
He Z, Yang S, Ju Y, Sun C (2009) Microwave photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B using TiO2 supported on activated carbon: mechanism implication. J Environ Sci 21:268–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62262-7
He Y, Bin JD, Jiang DY et al (2018) Evaluation of MnO2-templated iron oxide-coated diatomites for their catalytic performance in heterogeneous photo Fenton-like system. J Hazard Mater 344:230–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.10.018
Henrist C, Traina K, Hubert C et al (2003) Study of the morphology of copper hydroxynitrate nanoplatelets obtained by controlled double jet precipitation and urea hydrolysis. J Cryst Growth 254:176–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0248(03)01145-X
Hossain R, Hassan K, Sahajwalla V (2022a) Utilising problematic waste to detect toxic gas release in the environment: fabricating a NiO doped CuO nanoflake based ammonia sensor from e-waste. Nanoscale Adv 4:4066–4079. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1na00743b
Hossain R, Nekouei RK, Al MA, Sahajwalla V (2022b) Value-added fabrication of NiO-doped CuO nanoflakes from waste flexible printed circuit board for advanced photocatalytic application. Sci Rep 12:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-16614-4
Hu L, Wang Z, Hu Y, et al (2020) The preparation of Janus Cu(OH)2@Cu2O/Cu mesh and application in purification of oily wastewater. Mater Res Bull 126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2020.110815
Jadhav U, Hocheng H (2015) Hydrometallurgical recovery of metals from large printed circuit board pieces. Sci Rep 5:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14574
Khaki MRD, Shafeeyan MS, Raman AAA, Daud WMAW (2017) Application of doped photocatalysts for organic pollutant degradation - a review. J Environ Manag 198:78–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.04.099
Kumar A, Holuszko ME, Janke T (2018) Characterization of the non-metal fraction of the processed waste printed circuit boards. Waste Manag 75:94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.02.010
Kumari S, Baby BK (2016) Tech waste: environmental impact and management. Int J Comput Appl Technol Res 5:66–70. https://doi.org/10.7753/IJCATR0502.1005
Leong CY, Teh HL, Chen MC, Lee SL (2022) Effect of synthesis methods on properties of copper oxide doped titanium dioxide photocatalyst in dye photodegradation of rhodamine B. Sci Technol Indonesia 7:91–97. https://doi.org/10.26554/sti.2022.7.1.91-97
Li N, Bai R (2005) A novel amine-shielded surface cross-linking of chitosan hydrogel beads for enhanced metal adsorption performance. Ind Eng Chem Res 44:6692–6700. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie050145k
Li H, Eksteen J, Oraby E (2018) Hydrometallurgical recovery of metals from waste printed circuit boards (WPCBs): current status and perspectives – a review. Resour Conserv Recycl 139:122–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.08.007
Liu J, Huang X, Li Y et al (2006) Self-assembled CuO monocrystalline nanoarchitectures with controlled dimensionality and morphology. Cryst Growth Des 6:1690–1696. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg060198k
Mahmoud AED, Al-Qahtani KM, Alflaij SO et al (2021) Green copper oxide nanoparticles for lead, nickel, and cadmium removal from contaminated water. Sci Rep 11:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-91093-7
Mamba G, Pulgarin C, Kiwi J et al (2017) Synchronic coupling of Cu2O(p)/CuO(n) semiconductors leading to Norfloxacin degradation under visible light: kinetics, mechanism and film surface properties. J Catal 353:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2017.06.036
Marathey P, Khanna S, Pati R et al (2019) Low temperature-controlled synthesis of hierarchical Cu2O/Cu(OH)2/CuO nanostructures for energy applications. J Mater Res 34:3173–3185. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.231
Martins TAG, Falconi IBA, Pavoski G et al (2021) Green synthesis, characterization, and application of copper nanoparticles obtained from printed circuit boards to degrade mining surfactant by Fenton process. J Environ Chem Eng 9:106576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106576
Mathew AA, Parthasarathy P, Vivekanandan S (2021) Development of copper nanoparticles from e-waste for biomedical applications. Lecture notes in electrical engineering. Springer Science and Business Media, Deutschland GmbH, pp 703–715
Mbenga Y, Mthiyane MN, Botha TL et al (2022) Nanoarchitectonics of ZnO nanoparticles mediated by extract of Tulbaghia violacea and their cytotoxicity evaluation. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 32:3249–3259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02248-6
Meyer BK, Polity A, Reppin D et al (2012) Binary copper oxide semiconductors: from materials towards devices. Phys Status Solidi (B) Basic Res 249:1487–1509. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.201248128
Murugadoss G, Rajesh Kumar M, Kuppusami P (2021) Synthesis of Cu2O-Cu(OH)2 nanocomposite from CuSCN precursor by a facile chemical precipitation method. Mater Lett 284:128866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128866
Nascimento MA, Castro Cruz J, Dos Reis MF et al (2018) Synthesis of polymetallic nanoparticles from printed circuit board waste and application in textile dye remediation. J Environ Chem Eng 6:5580–5586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.08.056
Natarajan TS, Thomas M, Natarajan K et al (2011) Study on UV-LED/TiO2 process for degradation of rhodamine B dye. Chem Eng J 169:126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.02.066
Nayak P, Kumar S, Sinha I, Singh KK (2019) ZnO/CuO nanocomposites from recycled printed circuit board: preparation and photocatalytic properties. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:16279–16288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04986-6
Nekouei RK, Pahlevani F, Mayyas M et al (2019) Direct transformation of waste printed circuit boards into high surface area t-SnO2 for photocatalytic dye degradation. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103133. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2019.103133
Pal K, Chakroborty S, Panda P et al (2022) Environmental assessment of wastewater management via hybrid nanocomposite matrix implications—an organized review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:76626–76643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23122-5
Parekh ZR, Chaki SH, Hirpara AB et al (2021) CuO nanoparticles – synthesis by wet precipitation technique and its characterization. Phys B: Condens Matter 610:412950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2021.412950
Phutanon N, Pisitsak P, Manuspiya H, Ummartyotin S (2018) Synthesis of three-dimensional hierarchical CuO flower-like architecture and its photocatalytic activity for rhodamine b degradation. J Sci: Adv Mater Dev 3:310–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2018.05.001
Rajkumar S, Elanthamilan E, Balaji TE et al (2020) Recovery of copper oxide nanoparticles from waste SIM cards for supercapacitor electrode material. J Alloys Compd 849:156582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156582
Rajkumar S, Elanthamilan E, Wang SF et al (2022) One-pot green recovery of copper oxide nanoparticles from discarded printed circuit boards for electrode material in supercapacitor application. Resour Conserv Recycl 180:106180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106180
Ramesh M (2021) CuO as efficient photo catalyst for photocatalytic decoloration of wastewater containing azo dyes. Water Pract Technol 16:1078–1090. https://doi.org/10.2166/wpt.2021.067
Rao MD, Singh KK, Morrison CA, Love JB (2020) Challenges and opportunities in the recovery of gold from electronic waste. RSC Adv 10:4300–4309. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra07607g
Rao MD, Singh KK, Morrison CA, Love JB (2021) Recycling copper and gold from e-waste by a two-stage leaching and solvent extraction process. Sep Purif Technol 263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118400
Raul PK, Senapati S, Sahoo AK et al (2014) CuO nanorods: a potential and efficient adsorbent in water purification. RSC Adv 4:40580–40587. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra04619f
Ravi B, Duraisamy P, Marimuthu T (2023) A novel integrated circular economy approach in green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles from waste printed circuit boards and utilization of its residue for preparation of carbon engulfed nano polymer membrane. J Clean Prod 383:135457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135457
Rehman S, Mumtaz A, Hasanain SK (2011) Size effects on the magnetic and optical properties of CuO nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 13:2497–2507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-0143-8
Sagadevan S, Pal K, Chowdhury ZZ (2017) Fabrication of CuO nanoparticles for structural, optical and dielectric analysis using chemical precipitation method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28:12591–12597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7083-3
Sanjini NS, Winston B, Velmathi S (2017) Effect of precursors on the synthesis of CuO nanoparticles under microwave for photocatalytic activity towards methylene blue and rhodamine B dyes. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 17:495–501. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2017.11785
Saratale RG, Ghodake GS, Shinde SK et al (2018) Photocatalytic activity of CuO/Cu(OH)2 nanostructures in the degradation of Reactive Green 19A and textile effluent, phytotoxicity studies and their biogenic properties (antibacterial and anticancer). J Environ Manag 223:1086–1097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.04.072
Shah K, Gupta K, Sengupta B (2018) Reclamation of copper from spent ammoniacal printed circuit board (PCB) etch solutions. J Environ Chem Eng 6:2874–2880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.04.044
Sharma A, Pal K, Saini N, et al (2023) Remediation of contaminants from wastewater using algal nanoparticles via green chemistry approach: an organized review. Nanotechnology 34. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/acd45a
Singh PK, Kumar P, Hussain M et al (2016) Synthesis and characterization of CuO nanoparticles using strong base electrolyte through electrochemical discharge process. Bull Mater Sci 39:469–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-016-1159-1
Singh D, Jain D, Rajpurohit D et al (2023) Bacteria assisted green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and their potential applications as antimicrobial agents and plant growth stimulants. Front Chem 11(1154128):1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2023.1154128
Subash B, Krishnakumar B, Swaminathan M, Shanthi M (2014) ZnS-Ag-ZnO as an excellent UV-light-active photocatalyst for the degradation of AV 7, AB 1, RR 120, and RY 84 dyes: synthesis, characterization, and catalytic applications. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:12953–12963. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie5018145
Sun S (2015) Recent advances in hybrid Cu2O-based heterogeneous nanostructures. Nanoscale 7:10850–10882. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr02178b
Swarnambiga AK, Vidya Kalaivani M, Sathyawathi S, Ramyaa Lakshmi TS (2019) Reprocess of copper from worn printed circuit boards. OnLine J Biol Sci 19:57–68. https://doi.org/10.3844/ojbsci.2019.57.68
Truong TT, Pham TT, Truong TTT, Pham TD (2022) Synthesis, characterization of novel ZnO/CuO nanoparticles, and the applications in photocatalytic performance for rhodamine B dye degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:22576–22588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17106-0
Waheed A, Mansha M, Kazi IW, Ullah N (2019) Synthesis of a novel 3,5-diacrylamidobenzoic acid based hyper-cross-linked resin for the efficient adsorption of Congo red and rhodamine B. J Hazard Mater 369:528–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.058
Wang X, Gaustad G (2012) Prioritizing material recovery for end-of-life printed circuit boards. Waste Manag 32:1903–1913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.05.005
Wang TX, Xu SH, Yang FX (2012) Green synthesis of CuO nanoflakes from CuCO3·Cu(OH)2 powder and H2O2 aqueous solution. Powder Technol 228:128–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2012.05.007
Wang Y, Jiang T, Meng D et al (2015) Controllable fabrication of nanostructured copper compound on a Cu substrate by a one-step route. RSC Adv 5:16277–16283. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra14523b
Wu Y, Zhang J, Xiao L, Chen F (2010) Properties of carbon and iron modified TiO2 photocatalyst synthesized at low temperature and photodegradation of acid orange 7 under visible light. Appl Surf Sci 256:4260–4268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.02.012
Yaseen M, Humayun M, Khan A et al (2022) Photo-assisted removal of rhodamine B and Nile blue dyes from water using CuO–SiO2 composite. Molecules 27:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165343
Yazici EY, Deveci H (2013) Extraction of metals from waste printed circuit boards (WPCBs) in H2SO4-CuSO4-NaCl solutions. Hydrometallurgy 139:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2013.06.018
Yi EKM, Chandren S (2022) Synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles from waste Sim cards as photocatalyst in the photodegradation of phenol. Proc Sci Math 14:8–17
Yu Y, Zhang J (2009) Solution-phase synthesis of rose-like CuO. Mater Lett 63:1840–1843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.05.061
Zeng QX, Xu GC, Zhang L et al (2018) Porous CuO nanofibers derived from a Cu-based coordination polymer as a photocatalyst for the degradation of rhodamine B. New J Chem 42:7016–7024. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nj00608c
Zhu P, Xia B, Li H et al (2021) Visible-light-driven photoreduction of Cr(VI) by waste-based Cu2O photocatalyst from waste printed circuit boards. Environ Eng Sci 38:565–574. https://doi.org/10.1089/EES.2020.0237
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the CIF, Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) (Banaras Hindu University (BHU)) Varanasi, for providing the sophisticated characterization facilities such as XRD, FTIR, FESEM, and HR-SEM. Dr. Indrajit Sinha, Department of Chemistry, IIT (BHU) Varanasi, is acknowledged for the UV-DRS and UV-visible spectrometer facility in his lab. The authors are grateful to the Head, Department of Metallurgical Engineering, IIT (BHU) Varanasi, Varanasi, India, for being unconditionally supportive during this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and formal analysis were performed by Pushpa Gautam and Arup Kumar De. The first draft of the manuscript was conceptualized and written by Pushpa Gautam and Mudila Dhanunjaya Rao. Kamalesh Kumar Singh administered the project. Indrajit Sinha, Chhail Kumar Behera, and Kamalesh Kumar Singh supervised and provided the resources. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gautam, P., De, A.K., Rao, M.D. et al. Waste remediation: Low-temperature synthesis of hybrid Cu(OH)2/CuO and CuO nanostructures from spent printed circuit boards and their dye degradation studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29005-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29005-7