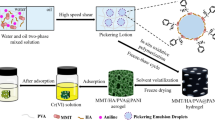
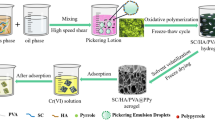
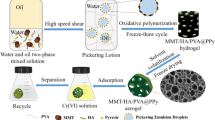
Abstract
Hexavalent chromium Cr(VI) is a typical harmful pollutant, which is carcinogenic or mutagenic to aquatic animals and humans. In this study, sepiolite/humic acid/polyvinyl alcohol@ polyaniline (SC/HA/PVA@PANI) composite porous hydrogel adsorbent was synthesized by Pickering emulsion template in situ chemical oxidative polymerization for adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. The in situ polymerization of aniline at the Pickering emulsion interface and the unique three-dimensional network structure of the hydrogel act as an effective “confinement” for the growth of the polymer. The porous structure of the material acts as a water channel, which effectively accelerates the binding of the adsorbate to the adsorption sites, and significantly improves the adsorption rate and adsorption capacity. The adsorption capacity of PANI for Cr(VI) confined in three-dimensional network of composite porous SC/HA/PVA@PANI hydrogel reached 1180.97 mg/g-PANI, which increased about 27-fold compared the adsorption capacity of pure PANI (43.48 mg/g). It is shown that the experimental design effectively avoids the agglomeration of PANI and improves its potential adsorption performance. In addition, the analysis of FESEM-EDX, FT-IR, and XPS spectra before and after adsorption confirmed that the main adsorption mechanisms of Cr(VI) on SC/HA/PVA@PANI included ion exchange, electrostatic attraction, and redox reaction. In conclusion, SC/HA/PVA@PANI has good stability and excellent adsorption performance, which is a new type of Cr(VI) ion adsorbent with great potential.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The dataset produced and processed during this research is available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Abilio TE, Soares BC, Jose JC, Milani PA, Labuto G, Carrilho E (2021) Hexavalent chromium removal from water: adsorption properties of in natura and magnetic nanomodified sugarcane bagasse. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(19):24816–24829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11726-8
Aigbe UO, Osibote OA (2020) A review of hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solutions by sorption technique using nanomaterials. J Environ Chem Eng 8(6):104503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104503
Anastopoulos I, Mittal A, Usman M, Mittal J, Yu GH, Núñez-Delgado A, Kornaros M (2018) A review on halloysite-based adsorbents to remove pollutants in water and wastewater. J Mol Liq 269:855–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.08.104
Azeez NA, Dash SS, Gummadi SN, Deepa VS (2021) Nano-remediation of toxic heavy metal contamination: hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)]. Chemosphere 266:129204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129204
Bhatti HN, Mahmood Z, Kausar A, Yakout SM, Shair OH, Iqbal M (2020) Biocomposites of polypyrrole, polyaniline and sodium alginate with cellulosic biomass: adsorption-desorption, kinetics and thermodynamic studies for the removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol. Int J Biol Macromol 153:146–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.306
Bo YQ, Yu AR, Liu HE, Chen S, Xu WL, Diao SA, Zhang CQ (2020) Preparation of elastic graphene aerogel and its adsorption of oil. J Porous Mater 28(1):39–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-020-00964-3
Chen J, Hong XQ, Xie QD, Li DK, Zhang QF (2014a) Highly efficient removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution using polyaniline/sepiolite nanofibers. Water Sci Technol 70(7):1236–1243. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2014.361
Chen J, Hong XQ, Zhao YT, Zhang QF (2014b) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using exfoliated polyaniline/montmorillonite composite. Water Sci Technol 70(4):678–684. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2014.277
Chen JD, Liang QW, Ploychompoo S, Luo HJ (2020) Functional rGO aerogel as a potential adsorbent for removing hazardous hexavalent chromium: adsorption performance and mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(10):10715–10728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07365-3
Chen ZS, Wei BB, Yang SY, Li Q, Liu L, Yu SJ, Wen T, Hu BW, Chen JR, Wang XK (2019) Synthesis of PANI/AlOOH composite for Cr(VI) adsorption and reduction from aqueous solutions. ChemistrySelect 4(8):2352–2362. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201803898
Chigondo M, Nyamunda B, Maposa M, Chigondo F (2022) Polypyrrole-based adsorbents for Cr(VI) ions remediation from aqueous solution: a review. Water Sci Technol 85(5):1600–1619. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2022.050
Ding J, Pu L, Wang Y, Wu B, Yu A, Zhang X, Pan B, Zhang Q, Gao G (2018) Adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) together with Cr(III) sequestration by polyaniline confined in pores of polystyrene beads. Environ Sci Technol 52(21):12602–12611. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b02566
Dognani G, Hadi P, Ma HY, Cabrera FC, Job AE, Agostini DLS, Hsiao BS (2019) Effective chromium removal from water by polyaniline-coated electrospun adsorbent membrane. Chem Eng J 372:341–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.154
Essekri A, Hsini A, Naciri Y, Laabd M, Ajmal Z, El Ouardi M, Ait Addi A, Albourine A (2021) Novel citric acid-functionalized brown algae with a high removal efficiency of crystal violet dye from colored wastewaters: insights into equilibrium, adsorption mechanism, and reusability. Int J Phytoremediation 23(4):336–346. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2020.1813686
Gao CJ, Dong ZL, Hao XC, Yao Y, Guo SY (2020) Preparation of reduced graphene oxide aerogel and its adsorption for Pb(II). ACS Omega 5(17):9903–9911. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00183
Geng JJ, Liang QW, Yu WY, Chen W, Lu GN, Luo HJ (2022) Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by polymer-mediated nitrogen-rich reduced graphene oxide. J Hazard Mater 436:129184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129184
Gulyuz U, Arslan M (2021) Simple preparation of a novel poly(vinyl alcohol)/gallic acid adsorbent for effective removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Water Air Soil Pollut 232(12):506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05460-1
Hato MJ, Maponya TC, Ramohlola KE, Modibane KD, Maity A, Monama GR, Makgopa K, Bello A (2019) Polymer-based magnetic nanocomposites for the removal of highly toxic hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions, advanced nanostructured materials for environmental remediation. Environ Chem Sustain World:189–227
Hosseini H, Mousavi SM (2021) Bacterial cellulose/polyaniline nanocomposite aerogels as novel bioadsorbents for removal of hexavalent chromium: Experimental and simulation study. J Clean Prod 278:123817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123817
Hosseini SA, Samani MR, Toghraie D (2021) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using ostrich feathers amended by polyaniline. J Mater Res Technol 15:488–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.08.041
Hsini A, Essekri A, Aarab N, Laabd M, Ait Addi A, Lakhmiri R, Albourine A (2020) Elaboration of novel polyaniline@ Almond shell biocomposite for effective removal of hexavalent chromium ions and Orange G dye from aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(13):15245–15258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08039-1
Hsini A, Naciri Y, Laabd M, Bouziani A, Navío JA, Puga F, Boukherroub R, Lakhmiri R, Albourine A (2021) Development of a novel PANI@WO3 hybrid composite and its application as a promising adsorbent for Cr(VI) ions removal. J Environ Chem Eng 9(5):105885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105885
Humpolicek P, Radaszkiewicz KA, Capakova Z, Pachernik J, Bober P, Kasparkova V, Rejmontova P, Lehocky M, Ponizil P, Stejskal J (2018) Polyaniline cryogels: biocompatibility of novel conducting macroporous material. Sci Rep 8(1):135. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18290-1
Hussein MA, Mohammed AA, Atiya MA (2019) Application of emulsion and Pickering emulsion liquid membrane technique for wastewater treatment: an overview. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(36):36184–36204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06652-3
Jiang YL, Liu ZF, Zeng GM, Liu YJ, Shao BB, Li ZG, Liu Y, Zhang W, He QY (2018) Polyaniline- based adsorbents for removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution: a mini review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(7):6158–6174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1188-3
Kaur K, Jindal R, Saini D (2019) Synthesis, optimization and characterization of PVA-co-poly (methacrylic acid) green adsorbents and applications in environmental remediation. Polym Bull 77(6):3079–3100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02900-1
Khan MI, Almesfer MK, Elkhaleefa A, Shigidi I, Shamim MZ, Ali IH, Rehan M (2021) Conductive polymers and their nanocomposites as adsorbents in environmental applications. Polymers (Basel) 13(21):3810. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213810
Khan MI, Almesfer MK, Elkhaleefa AM, Aamary A, Ali IH, Shamim MZ, Shoukry H, Rehan M (2022) Efficient adsorption of hexavalent chromium ions onto novel ferrochrome slag/polyaniline nanocomposite: ANN modeling, isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:86665–86679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21778-7
Lai YX, Wang F, Zhang YM, Ou P, Wu PP, Fang QL, Chen Z, Li SA (2019) UiO-66 derived N-doped carbon nanoparticles coated by PANI for simultaneous adsorption and reduction of hexavalent chromium from waste water. Chem Eng J 378:122069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122069
Lei C, Wang CW, Chen WQ, He MH, Huang BB (2020) Polyaniline@ magnetic chitosan nanomaterials for highly efficient simultaneous adsorption and in-situ chemical reduction of hexavalent chromium: Removal efficacy and mechanisms. Sci Total Environ 733:139316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139316
Li TT, Li RX, Ma Z, Yang AT, Jiao CL, Wang J (2021) Preparation of cellulose/sodium alginate/sepiolite porous microspheres and their adsorption properties for methylene blue. J Phys Conf Ser 1790(1):012088. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1790/1/012088
Liu SJ, Gao J, Zhang L, Yang YK, Liu XL (2021a) Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid-thiourea-modified magnetic chitosan for adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions. Carbohydr Polym 274:118555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118555
Liu XQ, Liu Y, Zhang TA (2021b) Preparation of magnetic zeolite/chitosan composite using silane as modifier for adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. J Vinyl Addit Technol 27(3):640–654. https://doi.org/10.1002/vnl.21839
Long FL, Niu CG, Tang N, Guo H, Li ZW, Yang YY, Lin LS (2021) Highly efficient removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by calcined Mg/Al-layered double hydroxides/ polyaniline composites. Chem Eng J 404:127084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127084
Lyu W, Wu JM, Zhang WL, Liu YP, Yu MT, Zhao YF, Feng J, Yan W (2019) Easy separated 3D hierarchical coral-like magnetic polyaniline adsorbent with enhanced performance in adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) and immobilization of Cr(III). Chem Eng J 363:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.109
Mondal NK, Chakraborty S (2020) Adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution on graphene oxide (GO) prepared from graphite: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Appl Water Sci 10(2):61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-1142-2
Moradi E, Ebrahimzadeh H, Mehrani Z, Asgharinezhad AA (2019) The efficient removal of methylene blue from water samples using three-dimensional poly (vinyl alcohol)/starch nanofiber membrane as a green nanosorbent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(34):35071–35081. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06400-7
Muhammad A, Shah AHA, Bilal S (2020) Effective adsorption of hexavalent chromium and divalent nickel ions from water through polyaniline, iron oxide, and their composites. Appl Sci 10(8):2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10082882
Nasar A, Mashkoor F (2019) Application of polyaniline-based adsorbents for dye removal from water and wastewater-a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(6):5333–5356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3990-y
Rabipour M, Sekhavat Pour Z, Sahraei R, Ghaemy M, Erfani Jazi M, Mlsna TE (2019) pH-sensitive nanocomposite hydrogels based on poly(vinyl alcohol) macromonomer and graphene oxide for removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions. J Polym Environ 28(2):584–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01625-6
Riahi Samani M, Ebrahimbabaie P, Vafaei Molamahmood H (2016) Hexavalent chromium removal by using synthesis of polyaniline and polyvinyl alcohol. Water Sci Technol 74(10):2305–2313. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.412
Rout DR, Jena HM (2023) Synthesis of graphene oxide-modified porous chitosan cross-linked polyaniline composite for static and dynamic removal of Cr(VI). Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(9):22992–23011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23774-3
Singh S, Perween S, Ranjan A (2021) Dramatic enhancement in adsorption of congo red dye in polymer-nanoparticle composite of polyaniline-zinc titanate. J Environ Chem Eng 9(3):105149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105149
Sun XT, Yang LR, Li Q, Liu ZN, Dong TT, Liu HZ (2015) Polyethylenimine-functionalized poly(vinyl alcohol) magnetic microspheres as a novel adsorbent for rapid removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 262:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.09.045
Teo SH, Chee CY, Fahmi MZ, Wibawa Sakti SC, Lee HV (2022) Review of functional aspects of nanocellulose-based pickering emulsifier for non-toxic application and its colloid stabilization mechanism. Molecules 27(21):7071. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217170
Ukhurebor KE, Aigbe UO, Onyancha RB, Nwankwo W, Osibote OA, Paumo HK, Ama OM, Adetunji CO, Siloko IU (2021) Effect of hexavalent chromium on the environment and removal techniques: a review. J Environ Manag 280:111809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111809
Wang T, Zhang LY, Li CF, Yang WC, Song TT, Tang CJ, Meng Y, Dai S, Wang HY, Chai LY, Luo J (2015) Synthesis of core-shell magnetic Fe3O4@poly(m-phenylenediamine) particles for chromium reduction and adsorption. Environ Sci Technol 49(9):5654–5662. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5061275
Wei Y, Wang HH, Zhang XQ, Liu CF (2021) Ammonia-assisted hydrothermal carbon material with schiff base structures synthesized from factory waste hemicelluloses for Cr(VI) adsorption. J Environ Chem Eng 9(5):106187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106187
Xie H, Zhang SL, Liu JY, Hu JQ, Tang AD (2021) A novel calcium oxalate/sepiolite composite for highly selective adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions. Minerals 11(6):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060552
Xu J, He JF, Zhu LT, Guo SL, Chen H (2022) A novel utilization of raw sepiolite: preparation of magnetic adsorbent directly based on sol-gel for adsorption of Pb(II). Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(51):77448–77461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21182-1
Yuan SB, Ning KG, He YJ (2020) Removal of copper ions using poly (acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) hydrogel microspheres with controllable size prepared by W/O Pickering emulsions. Colloid Polym Sci 298(11):1465–1472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04715-3
Zhang XL, Gao JT, Zhao SJ, Lei Y, Yuan Y, He CY, Gao CG, Deng LC (2019) Hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solution by adsorption on modified zeolites coated with Mg-layered double hydroxides. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(32):32928–32941. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06410-5
Zhao H, Yang YQ, Chen Y, Li J, Wang L, Li CS (2022) A review of multiple Pickering emulsions: solid stabilization, preparation, particle effect, and application. Chem Eng Sci 248:117085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2021.117085
Funding
This work was supported by the preparation of lignite humic acid-based magnetic composite microspheres and their adsorption properties for heavy metal ions, National Natural Science Foundation of China (21576001), and the National College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (202110360041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design.
Xuejiao Zhang: process the data and write the manuscript
Yulin Li, Wenjie Zou, Li Ding: work together to complete material preparation, data collection and analysis
Jun Chen: directed, revised, and supplemented the manuscript
All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript, and all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• A novel porous hydrogel adsorbent SC/HA/PVA@PANI was prepared for Cr(VI) removal.
• The in situ polymerization of aniline on the Pickering emulsion interface and the “confinement” effect of the hydrogel’s unique three-dimensional network structure on the polymer can effectively avoid the agglomeration of polyaniline and exert its potential adsorption efficiency.
• The porous structure of the material acts as a water channel, which effectively accelerates the combination of the adsorbate and adsorption site to improve the adsorption rate and capacity.
• The adsorption mechanism of Cr(VI) mainly includes electrostatic action, chemical reduction, and ion exchange.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Li, Y., Zou, W. et al. Sorption enhancement of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by polyaniline confined in three-dimensional network of composite porous hydrogel. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 92404–92416 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28948-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28948-1