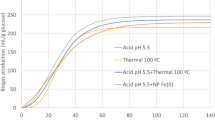
Abstract
Low biological hydrogen (bioH2) production due to non-optimal metabolic pathways occurs frequently. In this work, magnetic nitrogen-doped activated carbon (MNAC) was prepared and added into the inoculated sludge with glucose as substrate to enhance hydrogen (H2) yield by mesophilic dark fermentation (DF). The highest H2 yield appeared in 400 mg/L AC (252.8 mL/g glucose) and 600 mg/L MNAC group (304.8 mL/g glucose), which were 26.02% and 51.94% higher than that of 0 mg/L MNAC group (200.6 mL/g glucose). The addition of MNAC allowed for efficient enrichment of Firmicutes and Clostridium-sensu-stricto-1, accelerating the metabolic pathway shifted towards butyrate type. The Fe ions released by MNAC facilitated electron transfer and favored the reduction of ferredoxin (Fd), thereby obtaining more bioH2. Finally, the generation of [Fe-Fe] hydrogenase and cellular components of H2-producing microbes (HPM) during homeostasis was discussed to understand on the use of MNAC in DF system.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Akobi C, Hafez H, Nakhla G (2017) Impact of furfural on biological hydrogen production kinetics from synthetic lignocellulosic hydrolysate using mesophilic and thermophilic mixed cultures. Int J Hydrogen Energy 42:12159–12172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.03.173
Aly SS, Imai T, Hassouna MS, Kim Nguyen D, Higuchi T, Kanno A, Yamamoto K, Akada R, Sekine M (2018) Identification of factors that accelerate hydrogen production by Clostridium butyricum RAK25832 using casamino acids as a nitrogen source. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43:5300–5313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.08.171
Barca C, Soric A, Ranava D, Giudici-Orticoni MT, Ferrasse JH (2015) Anaerobic biofilm reactors for dark fermentative hydrogen production from wastewater: a review. Bioresour Technol 185:386–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.02.063
Cai Z, Deng X, Wang Q, Lai J, Xie H, Chen Y, Huang B, Lin G (2020) Core-shell granular activated carbon and its adsorption of trypan blue. J Clean Prod 242:118496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118496
Carere CR, Sparling R, Cicek N, Levin DB (2008) Third generation biofuels via direct cellulose fermentation. Int J Mol Sci 9:1342–1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms9071342
Chen W, Chen Y, Yang H, Li K, Chen X, Chen H (2018) Investigation on biomass nitrogen-enriched pyrolysis: influence of temperature. Bioresour Technol 249:247–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.022
Chen WF, Zhang J, Zhang X, Wang W, Li Y (2016) Investigation of heavy metal (Cu, Pb, Cd, and Cr) stabilization in river sediment by nano-zero-valent iron/activated carbon composite. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:1460–1470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5387-5
Chen Y, Zhang X, Chen W, Yang H, Chen H (2017) The structure evolution of biochar from biomass pyrolysis and its correlation with gas pollutant adsorption performance. Bioresour Technol 246:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.138
Cheng J, Hua J, Kang T, Meng B, Yue L, Dong H, Li H, Zhou J (2020) Nanoscale zero-valent iron improved lactic acid degradation to produce methane through anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 317:124013–124013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124013
Cheng J, Li H, Zhang J, Ding L, Ye Q, Lin R (2019) Enhanced dark hydrogen fermentation of Enterobacter aerogenes/HoxEFUYH with carbon cloth. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44:3560–3568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.12.080
Elbeshbishy E, Dhar BR, Nakhla G, Lee HS (2017) A critical review on inhibition of dark biohydrogen fermentation. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 79:656–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.075
Fan C, Zhang J, Zang L (2019) Improving biohydrogen evolution from glucose with magnetic activated carbon. Water Air Soil Pol 230(5):110–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4155-4
Feng Z, Chen H, Li H, Yuan R, Wang F, Chen Z, Zhou B (2020) Preparation, characterization, and application of magnetic activated carbon for treatment of biologically treated papermaking wastewater. Sci Total Environ 713:136423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136423
Fröhlich AC, Foletto EL, Dotto GL (2019) Preparation and characterization of NiFe2O4/activated carbon composite as potential magnetic adsorbent for removal of ibuprofen and ketoprofen pharmaceuticals from aqueous solutions. J Clean Prod 229:828–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.037
García-Becerra M, Macías-Muro M, Arellano-García L, Aguilar-Juárez O (2019) Bio-hydrogen production from tequila vinasses: effect of detoxification with activated charcoal on dark fermentation performance. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44:31860–31872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.10.059
Hallenbeck PC (2009) Fermentative hydrogen production: principles, progress, and prognosis. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:7379–7389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.12.080
Hallenbeck PC, Abo-Hashesh M, Ghosh D (2012) Strategies for improving biological hydrogen production. Bioresour Technol 110:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.103
Hallenbeck PC, Ghosh D (2009) Advances in fermentative biohydrogen production: the way forward? Trends Biotechnol 27:287–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2009.02.004
Han H, Cui M, Wei L, Yang H, Shen J (2011) Enhancement effect of hematite nanoparticles on fermentative hydrogen production. Bioresour Technol 102:7903–7909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.05.089
Jamali NS, Md Jahim J, Wan Isahak WNR (2016) Biofilm formation on granular activated carbon in xylose and glucose mixture for thermophilic biohydrogen production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 41:21617–21627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.05.092
Karadag D, Puhakka JA (2010) Enhancement of anaerobic hydrogen production by iron and nickel. Int J Hydrogen Energy 35:8554–8560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.04.174
Ke N, Lu X, Zhang X, Kuang B, Zhang Y (2023) Urban land use carbon emission intensity in China under the “double carbon” targets: spatiotemporal patterns and evolution trend. Environ Sci Pollut R 30:18213–18226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23294-0
Keskin T, Arslan K, Nalakth Abubackar H, Vural C, Eroglu D, Karaalp D, Yanik J, Ozdemir G, Azbar N (2018) Determining the effect of trace elements on biohydrogen production from fruit and vegetable wastes. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43:10666–10677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.01.028
Khan MA, Ngo HH, Guo W, Liu Y, Zhang X, Guo J, Chang SW, Nguyen DD, Wang J (2018) Biohydrogen production from anaerobic digestion and its potential as renewable energy. Renew Energy 129:754–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.04.029
Kim DH, Yoon JJ, Kim SH, Park JH (2022) Acceleration of lactate-utilizing pathway for enhancing biohydrogen production by magnetite supplementation in Clostridium butyricum. Bioresour Technol 359:127448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127448
Leng L, Xu S, Liu R, Yu T, Zhuo X, Leng S, Xiong Q, Huang H (2020) Nitrogen containing functional groups of biochar: an overview. Bioresour Technol 298:122286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122286
Lenssen N, Flavin C (1996) Sustainable energy for tomorrow's world—the case for an optimistic view of the future. Energy Policy 24(9):769–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-4215(96)00060-2
Li M, Bi Z, Xie L, Sun G, Liu Z, Kong Q, Wei X, Chen C (2019) From starch to carbon materials: insight into the cross-linking reaction and its influence on the carbonization process. Acs Sustain Chem Eng 7:14796–14804. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02821
Li R, Huang J, Li J, Cao L, Zhong X, Yu A, Lu G (2020a) Nitrogen-doped porous hard carbons derived from shaddock peel for high-capacity lithium-ion battery anodes. J Electroanal Chem 862:114044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114044
Li W, He L, Cheng C, Cao G, Ren N (2020b) Effects of biochar on ethanol-type and butyrate-type fermentative hydrogen productions. Bioresour Technol 306:123088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123088
Lin R, Cheng J, Ding L, Song W, Liu M, Zhou J, Cen K (2016) Enhanced dark hydrogen fermentation by addition of ferric oxide nanoparticles using Enterobacter aerogenes. Bioresour Technol 207:213–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.02.009
Liu Y, Li X, Kang X, Yuan Y, Du M (2014) Short chain fatty acids accumulation and microbial community succession during ultrasonic-pretreated sludge anaerobic fermentation process: effect of alkaline adjustment. Int Biodeter Biodegr 94:128–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.07.004
Liu Z, Lv F, Zheng H, Zhang C, Wei F, Xing X (2012) Enhanced hydrogen production in a UASB reactor by retaining microbial consortium onto carbon nanotubes (CNTs). Int J Hydrogen Energy 37:10619–10626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.04.057
Lu J, Chen C, Huang C, Leu S, Lee D (2020) Glucose fermentation with biochar amended consortium: sequential fermentations. Bioresour Technol 303:122933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122933
McInerney MJ, Rohlin L, Mouttaki H, Kim U, Krupp RS, Rios-Hernandez L, Sieber J, Struchtemeyer CG, Bhattacharyya A, Campbell JW, Gunsalus RP (2007) The genome of Syntrophus aciditrophicus: life at the thermodynamic limit of microbial growth. P Natl Acad Sci USA 104:7600–7605. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0610456104
Miao Z, Huang Y, Xin J, Su X, Sang Y, Liu H, Wang J (2019) High-performance symmetric supercapacitor constructed using carbon cloth boosted by engineering oxygen-containing functional groups. ACS Appl Mater Inter 11:18044–18050. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b04426
Moestedt J, Nordell E, Shakeri Yekta S, Lundgren J, Martí M, Sundberg C, Ejlertsson J, Svensson BH, Björn A (2016) Effects of trace element addition on process stability during anaerobic co-digestion of OFMSW and slaughterhouse waste. Waste Manag 47:11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.03.007
Mohammadi M, Mohammadi P, Karami N, Barzegar A, Mohamad Annuar MS (2019) Efficient hydrogen gas production from molasses in hybrid anaerobic-activated sludge-rotating biological contactor. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44:2592–2602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.12.033
Mohan S, Mohanakrishna G, Reddy SS, Raju BD, Rao KSR, Sarma PN (2008) Self-immobilization of acidogenic mixed consortia on mesoporous material (SBA-15) and activated carbon to enhance fermentative hydrogen production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 33:6133–6142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.07.096
Mohanraj S, Kodhaiyolii S, Rengasamy M, Pugalenthi V (2014) Phytosynthesized iron oxide nanoparticles and ferrous iron on fermentative hydrogen production using Enterobacter cloacae: evaluation and comparison of the effects. Int J Hydrogen Energy 39:11920–11929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.06.027
Okonkwo O, Escudie R, Bernet N, Mangayil R, Lakaniemi A, Trably E (2019) Bioaugmentation enhances dark fermentative hydrogen production in cultures exposed to short-term temperature fluctuations. Appl Microbiol Biot 104:439–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10203-8
Paiano P, Menini M, Zeppilli M, Majone M, Villano M (2019) Electro-fermentation and redox mediators enhance glucose conversion into butyric acid with mixed microbial cultures. Bioelectrochemistry 130:107333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2019.107333
Rambabu K, Bharath G, Thanigaivelan A, Das DB, Show PL, Banat F (2021) Augmented biohydrogen production from rice mill wastewater through nano-metal oxides assisted dark fermentation. Bioresour Technol 319:124243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124243
Ratti RP, Delforno TP, Sakamoto IK, Varesche MBA (2015) Thermophilic hydrogen production from sugarcane bagasse pretreated by steam explosion and alkaline delignification. Int J Hydrogen Energy 40:6296–6306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.03.067
Sharififard H, Pepe F, Soleimani M, Aprea P, Caputo D (2016) Iron-activated carbon nanocomposite: synthesis, characterization and application for lead removal from aqueous solution. RSC Advances 6:42845–42853. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra27923b
Shen Y, Linville JL, Ignacio-de Leon PAA, Schoene RP, Urgun-Demirtas M (2016) Towards a sustainable paradigm of waste-to-energy process: enhanced anaerobic digestion of sludge with woody biochar. J Clean Prod 135:1054–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.144
Show KY, Lee DJ, Tay JH, Lin CY, Chang JS (2012) Biohydrogen production: current perspectives and the way forward. Int J Hydrogen Energy 37:15616–15631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.04.109
Sunyoto NMS, Zhu M, Zhang Z, Zhang D (2016) Effect of biochar addition on hydrogen and methane production in two-phase anaerobic digestion of aqueous carbohydrates food waste. Bioresour Technol 219:29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.089
Wainaina S, Awasthi MK, Sarsaiya S, Chen H, Singh E, Kumar A, Ravindran B, Awasthi SK, Liu T, Duan Y, Kumar S, Zhang Z, Taherzadeh MJ (2020) Resource recovery and circular economy from organic solid waste using aerobic and anaerobic digestion technologies. Bioresour Technol 301:122778–122778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122778
Wang F, Han H, Liu L, Zhao J (2023) Assessing the contribution of optimizing energy mix to China’s carbon peaking. Environ Sci Pollut R 30:18296–18311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23451-5
Wang J, Wan W (2008) The effect of substrate concentration on biohydrogen production by using kinetic models. Sci China Ser B-Chem 51:1110–1117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-008-0104-6
Wang J, Wan W (2009) Factors influencing fermentative hydrogen production: a review. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:799–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.11.015
Wang X, Jin B (2009) Process optimization of biological hydrogen production from molasses by a newly isolated Clostridium butyricum W5. J Biosci Bioeng 107:138–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2008.10.012
Wei W, Zhang Y, Huang Q, Ni B (2019) Polyethylene terephthalate microplastics affect hydrogen production from alkaline anaerobic fermentation of waste activated sludge through altering viability and activity of anaerobic microorganisms. Water Res 163:114881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.114881
Wu W, Zhang W, Long Y, Qin J, Ma J (2020) Different transfer hydrogenation pathways of halogenated nitrobenzenes catalyzed by Fe-, Co- or Ni-based species confined in nitrogen doped carbon. Mol Catal 497:111226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2020.111226
Xia A, Jacob A, Herrmann C, Tabassum MR, Murphy JD (2015) Production of hydrogen, ethanol and volatile fatty acids from the seaweed carbohydrate mannitol. Bioresour Technol 193:488–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.06.130
Xu R, Yang Z, Zheng Y, Zhang H, Liu J, Xiong W, Zhang Y, Ahmad K (2017) Depth-resolved microbial community analyses in the anaerobic co-digester of dewatered sewage sludge with food waste. Bioresour Technol 244:824–835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.056
Yang G, Wang J (2019) Changes in microbial community structure during dark fermentative hydrogen production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44:25542–25550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.08.039
Ye S, Zeng G, Tan X, Wu H, Liang J, Song B, Tang N, Zhang P, Yang Y, Chen Q, Li X (2020) Nitrogen-doped biochar fiber with graphitization from Boehmeria nivea for promoted peroxymonosulfate activation and non-radical degradation pathways with enhancing electron transfer. Appl Catal B-Environ 269:118850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118850
Yu L, Falco C, Weber J, White RJ, Howe JY, Titirici M (2012) Carbohydrate-derived hydrothermal carbons: a thorough characterization study. Langmuir 28:12373–12383. https://doi.org/10.1021/la3024277
Yuan S, Tan Z, Huang Q (2018) Migration and transformation mechanism of nitrogen in the biomass–biochar–plant transport process. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 85:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.01.008
Zhang C, Kang X, Liang N, Abdullah A (2017a) Improvement of biohydrogen production from dark fermentation by cocultures and activated carbon immobilization. Energy Fuel 31:12217–12222. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b02035
Zhang J, Fan C, Zang L (2017b) Improvement of hydrogen production from glucose by ferrous iron and biochar. Bioresour Technol 245:98–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.198
Zhang J, Fan C, Zhang H, Wang Z, Zhang J, Song M (2018a) Ferric oxide/carbon nanoparticles enhanced bio-hydrogen production from glucose. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43:8729–8738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.03.143
Zhang J, Fan C, Zhao W, Zang L (2019) Improving bio-H2 production by manganese doped magnetic carbon. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44:26920–26932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.08.148
Zhang J, Zhao W, Yang J, Li Z, Zhang J, Zang L (2021) Comparison of mesophilic and thermophilic dark fermentation with nickel ferrite nanoparticles supplementation for biohydrogen production. Bioresour Technol 329:124853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124853
Zhang J, Zhao W, Zhang H, Wang Z, Fan C, Zang L (2018b) Recent achievements in enhancing anaerobic digestion with carbon-based functional materials. Bioresour Technol 266:555–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.076
Zhang R, El-Mashad HM, Hartman K, Wang F, Liu G, Choate C, Gamble P (2007) Characterization of food waste as feedstock for anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 98:929–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.02.039
Zhao L, Zhang J, Zhao W, Zang L (2019) Improved fermentative hydrogen production with the addition of calcium-lignosulfonate-derived biochar. Energy Fuel 33:7406–7414. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.9b01380
Zhao W, Zhang J, Zhang H, Yang M, Zang L (2020) Comparison of mesophilic and thermophilic biohydrogen production amended by nickel-doped magnetic carbon. J Clean Prod 270:122730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122730
Zheng H, Guo W, Yang S, Feng X, Du J, Zhou X, Chang J, Ren N (2014) Thermophilic hydrogen production from sludge pretreated by thermophilic bacteria: Analysis of the advantages of microbial community and metabolism. Bioresour Technol 172:433–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.020
Zhong D, Li J, Ma W, Xin H (2020) Magnetite nanoparticles enhanced glucose anaerobic fermentation for bio-hydrogen production using an expanded granular sludge bed (EGSB) reactor. Int J Hydrogen Energy 45:10664–10672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.01.095
Zhuang H, Xie Q, Shan S, Fang C, Ping L, Zhang C, Wang Z (2020) Performance, mechanism and stability of nitrogen-doped sewage sludge based activated carbon supported magnetite in anaerobic degradation of coal gasification wastewater. Sci Total Environ 737:140285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140285
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (ZR2016EEM33), and the Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Biobased Material and Green Papermaking, China (ZZ20210125).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jishi Zhang, Kexin Tian, Mengchen Yang, and Lihua Zang contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Kexin Tian and Mengchen Yang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Kexin Tian, Chen Zhou, Xiaoying Zhang, and Xiao Yan, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, ., Zhang, J., Zhou, C. et al. Magnetic nitrogen-doped activated carbon improved biohydrogen production. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 87215–87227 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28584-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28584-9