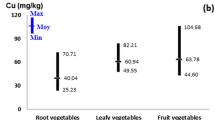
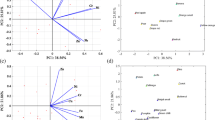
Abstract
Heavy metals (HMs) contamination in foodstuffs could pose serious health issues for public health and humans are continually exposed to HMs through the consumption of cereals, fruits, and vegetables. The present study was conducted to assess 11 HMs in foodstuffs to investigate pollution levels and health risks to children and adults. The mean contents of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Zn, Fe, Pb, Co, As, Mn and Ba in foodstuffs were 0.69, 2.73, 10.56, 6.60, 14.50, 9.63, 2.75, 0.50, 0.94, 15.39 and 0.43 mg/kg, respectively and the concentration of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni and Pb were higher than maximum permissible concentrations (MPCs) showing that these foods may be contaminated with metals and constitute a danger to consumers. Vegetables had relatively higher metal contents followed by cereals and fruits. The average value of the Nemerrow composite pollution index (NCPI) for cereals, fruits, and vegetables were 3.99, 6.53, and 11.34, respectively indicating cereal and fruits were moderately contaminated whereas vegetables were heavily contaminated by the studied metals. The total estimated daily and weekly intakes for all studied metals were higher than the maximum tolerable daily intake (MTDI) and provisional tolerance weekly intake (PTWI) recommended by FAO/WHO. The target hazard quotients and hazard index of all studied metals exceeded the standard limit for adults and children suggesting significant non-carcinogenic health hazards. The total cancer risk value of Cd, Cr, Ni, Pb, and As from food intake exceeded the threshold range (1.0E-04), suggesting potential carcinogenic risks. Based on practical and sensible evaluation techniques, the current work will assist policymakers in controlling metal contamination in foodstuffs.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abbasi H, Shah MH, Mohiuddin M et al (2020) Quantification of heavy metals and health risk assessment in processed fruits’ products. Arab J Chem 13:8965–8978
Ahmad W, Zubair M, Ahmed M et al (2023) Assessment of potentially toxic metal (loid) s contamination in soil near the industrial landfill and impact on human health: An evaluation of risk. Environ Geochem Health 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01499-7
Ahmad JU, Goni MA (2010) Heavy metal contamination in water, soil, and vegetables of the industrial areas in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ Monit Assess 166:347–357
Ahmed MK, Baki MA, Islam MS et al (2015a) Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in tropical fish and shellfish collected from the river Buriganga, Bangladesh. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:15880–15890
Ahmed MK, Shaheen N, Islam MS et al (2015b) Trace elements in two staple cereals (rice and wheat) and associated health risk implications in Bangladesh. Environ Monit Assess 187:326
Ahmed S, Mahdi MM, Nurnabi M et al (2022) Health risk assessment for heavy metal accumulation in leafy vegetables grown on tannery effluent contaminated soil. Toxicol Reports 9:346–355
Alamgir M, Mohsenipour M, Homsi R et al (2019) Parametric assessment of seasonal drought risk to crop production in Bangladesh. Sustainability 11:1442
Alfaro MR, Ugarte OM, Lima LHV et al (2022) Risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and edible parts of vegetables grown on sites contaminated by an abandoned steel plant in Havana. Environ Geochem Health 44:43–56
Altarawneh RM (2021) Levels of selected heavy metals (Pb, Ni, Cd, and Cr) in various widely consumed fruits and vegetables in Jordan. Int J Environ Anal Chem 101:1026–1033
Anawar HM, Garcia-Sanchez A, Hossain MN, Akter S (2012) Evaluation of health risk and arsenic levels in vegetables sold in markets of Dhaka (Bangladesh) and Salamanca (Spain) by hydride generation atomic absorption spectroscopy. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89:620–625
Bai B, Bai F, Sun C et al (2023) Adsorption mechanism of shell powders on heavy metal ions Pb2+/Cd2+ and the purification efficiency for contaminated soils. Front Earth Sci 10:1071228
Basaran B (2022) Comparison of heavy metal levels and health risk assessment of different bread types marketed in Turkey. J Food Compos Anal 108:104443
Blanco A, Högy P, Zikeli S et al (2022) Assessment of elevated CO2 concentrations and heat stress episodes in soybean cultivars growing in heavy metal polluted soils: Crop nutritional quality and food safety. Environ Pollut 303:119123
Bortey-Sam N, Nakayama SMM, Ikenaka Y et al (2015) Human health risks from metals and metalloid via consumption of food animals near gold mines in Tarkwa, Ghana: Estimation of the daily intakes and target hazard quotients (THQs). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 111:160–167
Brizio P, Benedetto A, Squadrone S et al (2016) Heavy metals and essential elements in Italian cereals. Food Addit Contam Part B 9:261–267
Cao S, Duan X, Zhao X et al (2016) Health risks of children’s cumulative and aggregative exposure to metals and metalloids in a typical urban environment in China. Chemosphere 147:404–411
Chen F, Khan ZI, Zafar A et al (2021) Evaluation of toxicity potential of cobalt in wheat irrigated with wastewater: health risk implications for public. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:21119–21131
Coetzee JJ, Bansal N, Chirwa EMN (2020) Chromium in environment, its toxic effect from chromite-mining and ferrochrome industries, and its possible bioremediation. Expo Heal 12:51–62
Dotaniya ML, Meena VD, Rajendiran S et al (2017) Geo-accumulation indices of heavy metals in soil and groundwater of Kanpur, India under long term irrigation of tannery effluent. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98:706–711
Edelstein M, Ben-Hur M (2018) Heavy metals and metalloids: Sources, risks and strategies to reduce their accumulation in horticultural crops. Sci Hortic (amsterdam) 234:431–444
Esposito M, De Roma A, Cavallo S et al (2019) Trace elements in vegetables and fruits cultivated in Southern Italy. J Food Compos Anal 84:103302
Gao L, Wang Z, Zhu A et al (2019) Quantitative source identification and risk assessment of trace elements in soils from Leizhou Peninsula, South China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess an Int J 25:1832–1852
Gao H, Hsu P-H, Li K, Zhang J (2020) The real effect of smoking bans: Evidence from corporate innovation. J Financ Quant Anal 55:387–427
Ge X, Khan ZI, Chen F et al (2022) A study on the contamination assessment, health risk and mobility of two heavy metals in the soil-plants-ruminants system of a typical agricultural region in the semi arid environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:14584–14594
Guadie A, Yesigat A, Gatew S et al (2021) Evaluating the health risks of heavy metals from vegetables grown on soil irrigated with untreated and treated wastewater in Arba Minch. Ethiopia Sci Total Environ 761:143302
Guo J, Zhang Y, Liu W et al (2022) Incorporating in vitro bioaccessibility into human health risk assessment of heavy metals and metalloid (As) in soil and pak choi (Brassica chinensis L.) from greenhouse vegetable production fields in a megacity in Northwest China. Food Chem 373:131488
Guo Z, Zhan R, Shi Y et al (2023) Innovative and green utilization of zinc-bearing dust by hydrogen reduction: Recovery of zinc and lead, and synergetic preparation of Fe/C micro-electrolysis materials. Chem Eng J 456:141157
Gupta N, Yadav KK, Kumar V et al (2019) Trace elements in soil-vegetables interface: translocation, bioaccumulation, toxicity and amelioration-a review. Sci Total Environ 651:2927–2942
Haque MM, Niloy NM, Khirul MA et al (2021) Appraisal of probabilistic human health risks of heavy metals in vegetables from industrial, non-industrial and arsenic contaminated areas of Bangladesh. Heliyon 7:e06309
Hasan MN, Hossain MS, Bari MA, Islam MR (2013) Agricultural land availability in Bangladesh. SRDI, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Landsat Satell Imag path 136;5:42
Herrero Fernandez Z, Estevez Álvarez JR, Montero Álvarez A et al (2021) Metal contaminants in rice from Cuba analyzed by ICP-MS, ICP-AES and CVAAS. Food Addit Contam Part B 14:59–65
Hoaghia M-A, Cadar O, Moisa C et al (2022) Heavy metals and health risk assessment in vegetables grown in the vicinity of a former non-metallic facility located in Romania. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:40079–40093
Hossain S, Anik AH, Khan R et al (2022) Public Health Vulnerability Due to the Exposure of Dissolved Metal (oid) s in Tap Water from a Mega City (Dhaka, Bangladesh): Source and Quality Appraisals. Expo Heal 14:713–732
Hossini H, Shafie B, Niri AD et al (2022) A comprehensive review on human health effects of chromium: insights on induced toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:70686–70705
Howe A, Fung LH, Lalor G et al (2005) Elemental composition of Jamaican foods 1: A survey of five food crop categories. Environ Geochem Health 27:19–30
Hu B, Shao S, Fu Z et al (2019) Identifying heavy metal pollution hot spots in soil-rice systems: A case study in South of Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci Total Environ 658:614–625
Huang Z, Pan X-D, Wu P-G et al (2014) Heavy metals in vegetables and the health risk to population in Zhejiang, China. Food Control 36:248–252
Hwang IM, Ha J-H (2021) Human health risk assessment of toxic elements in South Korean cabbage, Kimchi, using Monte Carlo simulations. J Food Compos Anal 102:104046
Hwang IM, Lee HM, Lee H-W et al (2021) Determination of Toxic Elements and Arsenic Species in Salted Foods and Sea Salt by ICP–MS and HPLC–ICP–MS. ACS Omega 6:19427–19434
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M (2014a) Heavy metals in cereals and pulses: health implications in Bangladesh. J Agric Food Chem 62:10828–10835
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M et al (2014b) Arsenic and lead in foods: a potential threat to human health in Bangladesh. Food Addit Contam Part A 31:1982–1992
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M (2015a) Determination of heavy metals in fish and vegetables in Bangladesh and health implications. Hum Ecol Risk Assess an Int J 21:986–1006
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M, Masunaga S (2015b) Assessment of trace metals in foodstuffs grown around the vicinity of industries in Bangladesh. J Food Compos Anal 42:8–15
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M et al (2016) Health risk assessment due to heavy metal exposure from commonly consumed fish and vegetables. Environ Syst Decis 36:253–265
Islam MS, Proshad R, Asadul Haque M et al (2020) Assessment of heavy metals in foods around the industrial areas: Health hazard inference in Bangladesh. Geocarto Int 35:280–295
Islam MS, Islam ARMT, Phoungthong K et al (2022) Potentially toxic elements in vegetable and rice species in Bangladesh and their exposure assessment. J Food Compos Anal 106:104350
Islam MS, Hoque MF (2014) Concentrations of heavy metals in vegetables around the industrial area of Dhaka city, Bangladesh and health risk assessment. Int Food Res J 21: 2121–2126
Janani R, Gurunathan B, Sivakumar K et al (2022) Advancements in heavy metals removal from effluents employing nano-adsorbents: way towards cleaner production. Environ Res 203:111815
Jiang C, Zhao Q, Zheng L et al (2021) Distribution, source and health risk assessment based on the Monte Carlo method of heavy metals in shallow groundwater in an area affected by mining activities, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 224:112679
Joseph T, Dubey B, McBean EA (2015) Human health risk assessment from arsenic exposures in Bangladesh. Sci Total Environ 527:552–560
Karahan F (2023) Evaluation of trace element and heavy metal levels of some ethnobotanically important medicinal plants used as remedies in Southern Turkey in terms of human health risk. Biol Trace Elem Res 201:493–513
Kato M, Ohgami N, Ohnuma S et al (2020) Multidisciplinary approach to assess the toxicities of arsenic and barium in drinking water. Environ Health Prev Med 25:1–7
Kazapoe RW, Amuah EEY, Dankwa P et al (2021) Compositional and source patterns of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in soils in southwestern Ghana using robust compositional contamination index (RCCI) and k-means cluster analysis. Environ Challenges 5:100248
Khaneghah AM, Fakhri Y, Nematollahi A, Pirhadi M (2020) Potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in cereal-based foods: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Trends Food Sci Technol 96:30–44
Kharazi A, Leili M, Khazaei M et al (2021) Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil and food crops in Hamadan, Iran. J Food Compos Anal 100:103890
Kibria KQ, Islam M, Hoque S et al (2022) Variations in cadmium accumulation among amon rice cultivars in Bangladesh and associated human health risks. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:39888–39902
Kormoker T, Proshad R, Islam MS et al (2021) Concentrations, source apportionment and potential health risk of toxic metals in foodstuffs of Bangladesh. Toxin Rev 40:1447–1460
Kukusamude C, Sricharoen P, Limchoowong N, Kongsri S (2021) Heavy metals and probabilistic risk assessment via rice consumption in Thailand. Food Chem 334:127402
Laboni FA, Ahmed M, Kaium A et al (2022) Heavy metals in widely consumed vegetables grown in industrial areas of bangladesh: a potential human health hazard. Biol Trace Elem Res 201:995–1005
Lebelo K, Malebo N, Mochane MJ, Masinde M (2021) Chemical contamination pathways and the food safety implications along the various stages of food production: a review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:5795
Li Q, Chen Y, Fu H et al (2012) Health risk of heavy metals in food crops grown on reclaimed tidal flat soil in the Pearl River Estuary, China. J Hazard Mater 227:148–154
Li L, Zhang Y, Ippolito JA et al (2020) Lead smelting effects heavy metal concentrations in soils, wheat, and potentially humans. Environ Pollut 257:113641
Li J, Zhao Y, Zhang A et al (2021) Effect of grazing exclusion on nitrous oxide emissions during freeze-thaw cycles in a typical steppe of Inner Mongolia. Agric Ecosyst Environ 307:107217
Li C, Smith P, Bai X et al (2023) Effects of carbonate minerals and exogenous acids on carbon flux from the chemical weathering of granite and basalt. Glob Planet Chang 221:104053
Liang X, Wang C, Song Z et al (2021) Soil metal (loid) s pollution around a lead/zinc smelter and source apportionment using isotope fingerprints and receptor models. Appl Geochem 135:105118
Lidiková J, Čeryová N, Šnirc M et al (2021) Heavy Metals Presence in the Soil and Their Content in Selected Varieties of Chili Peppers in Slovakia. Foods 10:1738
Liu X, Song Q, Tang Y et al (2013) Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil–vegetable system: a multi-medium analysis. Sci Total Environ 463:530–540
Liu Z, Zheng J, Liu W et al (2020) Identification of the key host phases of Cr in fresh chromite ore processing residue (COPR). Sci Total Environ 703:135075
Liu W, Yang X, Duan L et al (2021a) Variability in plant trace element uptake across different crops, soil contamination levels and soil properties in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of northwest China. Sci Rep 11:1–13
Liu X, Gu S, Yang S et al (2021b) Heavy metals in soil-vegetable system around E-waste site and the health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 779:146438
Lü Q, Xiao Q, Wang Y et al (2021) Risk assessment and hotspots identification of heavy metals in rice: A case study in Longyan of Fujian province, China. Chemosphere 270:128626
Lü Q, Xiao Q, Guo Y et al (2022) Pollution monitoring, risk assessment and target remediation of heavy metals in rice from a five-year investigation in Western Fujian region, China. J Hazard Mater 424:127551
Lu J, Lin Y, Wu J, Zhang C (2021) Continental-scale spatial distribution, sources, and health risks of heavy metals in seafood: challenge for the water-food-energy nexus sustainability in coastal regions? Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:63815–63828
Mahajan M, Gupta PK, Singh A et al (2022) A comprehensive study on aquatic chemistry, health risk and remediation techniques of cadmium in groundwater. Sci Total Environ 818:151784
Mallongi A, Astuti RDP, Amiruddin R et al (2022) Identification source and human health risk assessment of potentially toxic metal in soil samples around karst watershed of Pangkajene, Indonesia. Environ Nanotechnol, Monit Manag 17:100634
Mandal R, Kaur S (2019) Impact of environmental pollution on trace elements in vegetables and associated potential risk to human health in industrial town Mandi-gobindgarh (India). Chemosphere 219:574–587
Marrugo-Negrete J, Pinedo-Hernández J, Díez S (2017) Assessment of heavy metal pollution, spatial distribution and origin in agricultural soils along the Sinú River Basin, Colombia. Environ Res 154:380–388
Martins-Noguerol R, Matías L, Pérez-Ramos IM et al (2022) Differences in nutrient composition of sea fennel (Crithmum maritimum) grown in different habitats and optimally controlled growing conditions. J Food Compos Anal 106:104266
Meng M, Yang L, Wei B et al (2021) Plastic shed production systems: The migration of heavy metals from soil to vegetables and human health risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 215:112106
Millour S, Noel L, Kadar A et al (2011) Simultaneous analysis of 21 elements in foodstuffs by ICP-MS after closed-vessel microwave digestion: Method validation. J Food Compos Anal 24:111–120
Muhammad S, Ullah R, Jadoon IAK (2019) Heavy metals contamination in soil and food and their evaluation for risk assessment in the Zhob and Loralai valleys, Baluchistan province, Pakistan. Microchem J 149:103971
Nakagawa K, Imura T, Berndtsson R (2022) Distribution of heavy metals and related health risks through soil ingestion in rural areas of western Japan. Chemosphere 290:133316
Naseri M, Vazirzadeh A, Kazemi R, Zaheri F (2015) Concentration of some heavy metals in rice types available in Shiraz market and human health risk assessment. Food Chem 175:243–248
Nkansah MA, Agorsor P-I, Opoku F (2021) Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment of mechanically milled delicacy called fufu. Int J Food Contam 8:1–7
Oladoye PO, Olowe OM, Asemoloye MD (2022) Phytoremediation technology and food security impacts of heavy metal contaminated soils: A review of literature. Chemosphere 288:132555
Osman HEM, Abdel-Hamed EMW, Al-Juhani WSM et al (2021) Bioaccumulation and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in food crops irrigated with freshwater and treated wastewater: A case study in Southern Cairo, Egypt. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:50217–50229
Parvin R, Sultana A, Zahid MA (2014) Detection of heavy metals in vegetables cultivated in different locations in Chittagong, Bangladesh. IOSR J Env Sci Toxicol Food Tech 8:58–63
Pirsaheb M, Hadei M, Sharafi K (2021) Human health risk assessment by Monte Carlo simulation method for heavy metals of commonly consumed cereals in Iran-Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis. J Food Compos Anal 96:103697
Proshad R, Kormoker T, Islam MS, Chandra K (2020) Potential health risk of heavy metals via consumption of rice and vegetables grown in the industrial areas of Bangladesh. Hum Ecol Risk Assess an Int J 26:921–943
Proshad R, Kormoker T, Al MA et al (2022) Receptor model-based source apportionment and ecological risk of metals in sediments of an urban river in Bangladesh. J Hazard Mater 423:127030
Proshad R, Kormoker T, Islam MS, Chandra K (2019) Potential health risk of heavy metals via consumption of rice and vegetables grown in the industrial areas of Bangladesh. Hum Ecol Risk Assess An Int J 26:921–943
Proshad R, Kormoker T, Sayed A et al (2021) Potential toxic metals (PTMs) contamination in agricultural soils and foodstuffs with associated source identification and model uncertainty. Sci Total Environ 789:147962
Qin J, Niu A, Liu Y, Lin C (2021) Arsenic in leafy vegetable plants grown on mine water-contaminated soils: Uptake, human health risk and remedial effects of biochar. J Hazard Mater 402:123488
Rahman M, Islam MA (2019) Concentrations and health risk assessment of trace elements in cereals, fruits, and vegetables of Bangladesh. Biol Trace Elem Res 191:243–253
Rahman Z, Singh VP (2019) The relative impact of toxic heavy metals (THMs)(arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr)(VI), mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb)) on the total environment: an overview. Environ Monit Assess 191:1–21
Rahman MM, Asaduzzaman M, Naidu R (2013) Consumption of arsenic and other elements from vegetables and drinking water from an arsenic-contaminated area of Bangladesh. J Hazard Mater 262:1056–1063
Rai PK, Lee SS, Zhang M et al (2019) Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ Int 125:365–385
Rajendran S, Priya TAK, Khoo KS et al (2022) A critical review on various remediation approaches for heavy metal contaminants removal from contaminated soils. Chemosphere 287:132369
Raknuzzaman M, Ahmed MK, Islam MS et al (2016) Trace metal contamination in commercial fish and crustaceans collected from coastal area of Bangladesh and health risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:17298–17310
Ran H, Guo Z, Yi L et al (2021) Pollution characteristics and source identification of soil metal (loid) s at an abandoned arsenic-containing mine, China. J Hazard Mater 413:125382
Real M, Hossen I, Azam HM, Majed N (2017) Consumption of heavy metal contaminated foods and associated risks in Bangladesh. Environ Monit Assess 189:1–14
Reshmy R, Philip E, Madhavan A et al (2022) Nanocellulose as green material for remediation of hazardous heavy metal contaminants. J Hazard Mater 424:127516
Román-Ochoa Y, Delgado GTC, Tejada TR et al (2021) Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in grains and grain-based processed food in Arequipa region of Peru. Chemosphere 274:129792
Saha N, Zaman MR (2013) Evaluation of possible health risks of heavy metals by consumption of foodstuffs available in the central market of Rajshahi City, Bangladesh. Environ Monit Assess 185:3867–3878
Saher NU, Kanwal N (2019) Assessment of some heavy metal accumulation and nutritional quality of shellfish with reference to human health and cancer risk assessment: a seafood safety approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:5189–5201
Said I, Hursthouse A, Salman SAE-R (2021) Identification of pollution sources in roadside soils of Cairo-Alexandria Highway, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 14:1–11
Sanaei F, Amin MM, Alavijeh ZP et al (2021) Health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements intake via food crops consumption: Monte Carlo simulation-based probabilistic and heavy metal pollution index. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:1479–1490
Setia R, Dhaliwal SS, Singh R et al (2021) Phytoavailability and human risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and food crops around Sutlej river, India. Chemosphere 263:128321
Shaheen N, Irfan NM, Khan IN et al (2016) Presence of heavy metals in fruits and vegetables: health risk implications in Bangladesh. Chemosphere 152:431–438
Shahriar S, Rahman MM, Naidu R (2020) Geographical variation of cadmium in commercial rice brands in Bangladesh: Human health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 716:137049
Shahriar S, Haque MM, Naidu R, Rahman MM (2021) Concentrations of toxic elements and health risk assessment in arum grown in arsenic-contaminated areas of Bangladesh. Food Control 129:108240
Shammi SA, Salam A, Khan M, Hossain A (2021) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in the agricultural soils, plants, and in the atmospheric particulate matter of a suburban industrial region in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ Monit Assess 193:1–12
Shawon MA-A, Ahmed S, Karim MR (2021) Impact of Irrigation with Polluted River Water on the Accumulation of Toxic Metals in Soil and Crops in the Region of Dhaka, Bangladesh and Potential Effects on Health. Environ Process 8:219–237
Shi C, He H, Xia Z et al (2022) Heavy metals and Pb isotopes in a marine sediment core record environmental changes and anthropogenic activities in the Pearl River Delta over a century. Sci Total Environ 814:151934
Signes-Pastor AJ, Gutiérrez-González E, García-Villarino M et al (2021) Toenails as a biomarker of exposure to arsenic: A review. Environ Res 195:110286
Štofejová L, Fazekaš J, Fazekašová D (2021) Analysis of heavy metal content in soil and plants in the dumping ground of Magnesite Mining Factory Jelšava-Lubeník (Slovakia). Sustainability 13:4508
Sultana MS, Rana S, Yamazaki S et al (2017) Health risk assessment for carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic heavy metal exposures from vegetables and fruits of Bangladesh. Cogent Environ Sci 3:1291107
Tadić Đ, Hernandez MJB, Cerqueira F et al (2021) Occurrence and human health risk assessment of antibiotics and their metabolites in vegetables grown in field-scale agricultural systems. J Hazard Mater 401:123424
Tang M, Lu G, Fan B et al (2021) Bioaccumulation and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil-crop systems in Liujiang karst area, Southwestern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:9657–9669
Tariq FS (2021) Heavy metals concentration in vegetables irrigated with municipal wastewater and their human daily intake in Erbil city. Environ Nanotechnol, Monit Manag 16:100475
Tasrina RC, Rowshon A, Mustafizur AMR et al (2015) Heavy metals contamination in vegetables and its growing soil. J Env Anal Chem 2:2380–2391
Taylor MP, Isley CF, Fry KL et al (2021) A citizen science approach to identifying trace metal contamination risks in urban gardens. Environ Int 155:106582
Telloli C, Tagliavini S, Passarini F et al (2023) ICP-MS triple quadrupole as analytical technique to define trace and ultra-trace fingerprint of extra virgin olive oil. Food Chem 402:134247
Uddin ASM, Khan N, Islam ARM et al (2022) Changes in urbanization and urban heat island effect in Dhaka city. Theor Appl Climatol 147:891–907
Ullah AKM, Afrin S, Hosen MM et al (2021) Concentration, source identification, and potential human health risk assessment of heavy metals in chicken meat and egg in Bangladesh. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:22031–22042
Varol M, Gündüz K, Sünbül MR, Aytop H (2022) Arsenic and trace metal concentrations in different vegetable types and assessment of health risks from their consumption. Environ Res 206:112252
Wang F, Peng L, Zhou X et al (2021a) Typical sources of Cd to paddy fields in different contaminated areas and their impacts on Cd accumulation in topsoil and rice in Changzhutan, China. Environ Res 193:110523
Wang J, Wang L, Wang Y et al (2021b) Emerging risks of toxic metal (loid) s in soil-vegetables influenced by steel-making activities and isotopic source apportionment. Environ Int 146:106207
Wei J, Cen K (2020a) Contamination and health risk assessment of heavy metals in cereals, legumes, and their products: A case study based on the dietary structure of the residents of Beijing, China. J Clean Prod 260:121001
Wei J, Cen K (2020b) Assessment of human health risk based on characteristics of potential toxic elements (PTEs) contents in foods sold in Beijing, China. Sci Total Environ 703:134747
Xiang M, Li Y, Yang J et al (2021) Heavy metal contamination risk assessment and correlation analysis of heavy metal contents in soil and crops. Environ Pollut 278:116911
Xu R, Wang Y, Sun Y et al (2023) External sodium acetate improved Cr (VI) stabilization in a Cr-spiked soil during chemical-microbial reduction processes: Insights into Cr (VI) reduction performance, microbial community and metabolic functions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 251:114566
Yadav D, Rangabhashiyam S, Verma P et al (2021) Environmental and health impacts of contaminants of emerging concerns: Recent treatment challenges and approaches. Chemosphere 272:129492
Yang L, Ren Q, Zheng K et al (2022) Migration of heavy metals in the soil-grape system and potential health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 806:150646
Yaqub G, Khan A, Zishan Ahmad M, Irshad U (2021) Determination of concentration of heavy metals in fruits, vegetables, groundwater, and soil samples of the cement industry and nearby communities and assessment of associated health risks. J Food Qual 2021: 3354867
Zakir HM, Quadir QF, Mollah MZI (2021) Human health risk assessment of heavy metals through the consumption of common foodstuffs collected from two divisional cities of Bangladesh. Expo Heal 13:253–268
Zeng Q, Yi H, Huang L et al (2018) Reduced testosterone and Ddx3y expression caused by long-term exposure to arsenic and its effect on spermatogenesis in mice. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 63:84–91
Zhang Y, Chu C, Li T et al (2017) A water quality management strategy for regionally protected water through health risk assessment and spatial distribution of heavy metal pollution in 3 marine reserves. Sci Total Environ 599:721–731
Zhang J, Li H, Zhou Y et al (2018) Bioavailability and soil-to-crop transfer of heavy metals in farmland soils: A case study in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ Pollut 235:710–719
Zhang T, Zhang Y, Li W et al (2021) Occurrence and dietary exposure of heavy metals in marketed vegetables and fruits of Shandong Province, China. Food Sci Nutr 9:5166–5173
Zhang L, Liu X, Zhang M et al (2023) The effect of pH/PAC on the coagulation of anionic surfactant wastewater generated in the cosmetic production. J Environ Chem Eng 11:109312
Zheng S, Wang Q, Yuan Y, Sun W (2020) Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil and food crops in the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration of China. Food Chem 316:126213
Zhou W, Zhang J, Zou M et al (2019) Feasibility of using rice leaves hyperspectral data to estimate CaCl2-extractable concentrations of heavy metals in agricultural soil. Sci Rep 9:1–9
Zhou M, Tang T, Qin D et al (2023) Hematite nanoparticle decorated MIL-100 for the highly selective and sensitive electrochemical detection of trace-level paraquat in milk and honey. Sensors Actuators B Chem 376:132931
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all of the reviewers for their valuable suggestions and help to improve the manuscript quality.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through large group Research Project under grant number RGP2/103/44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ram Proshad: Sample collection and processing, Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing- Original draft. Abubakr M. Idris: Writing- Reviewing and Editing. All authors reviewed and approved this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Proshad, R., Idris, A.M. Evaluation of heavy metals contamination in cereals, vegetables and fruits with probabilistic health hazard in a highly polluted megacity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 79525–79550 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27977-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27977-0