Abstract
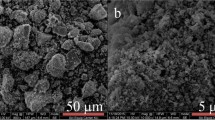
Sorption is prominent in low price, high efficiency, availability, and eco-friendliness. Organic porous materials have the characteristics of easy functionalization, diverse structure and stability, and show great potential in adsorption, energy storage, catalysis, and other fields. A mesoporous phenolic resin-type polymer (PRP) was successfully synthesized and modified by solid state reaction with maleic anhydride to prepare adsorbent (called as PRP-MAH) for sorption of Pb2+. The impact of reaction conditions (the pH value, reaction temperature, fresh concentration of solution, ionic strength and reaction time, etc.) was systematically studied. Characterization methods such as SEM, FTIR, and XPS indicated that the synthesized adsorbent PRP-MAH had regular morphology and good stability. The fitting of isothermal adsorption experiment data conforms to Langmuir sorption isotherm, and the sorption capacity reached 366.40 mg·g−1 at 308 K. The kinetic data were consistent with the quasi-second-order model, which indicated that the chemisorption might play the main role in the sorption process. Thermodynamic research manifested that the sorption of Pb2+ by PRP-MAH was carried out by a spontaneous process at the study temperature. The studies show that PRP-MAH can remove Pb2+ from water solution through ion exchange, electrostatic attraction, and surface complexation.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated during the study are available from the corresponding author by reasonable request.
References
Ahmad R, Haseeb S (2017) Adsorption of Pb (II) on Mentha piperita carbon (MTC) in single and quaternary systems. Arab J Chem 10:S412–S421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2012.09.013
Awual MR, Hasan MM, Islam A Rahman MM, Asiri AM, Khaleque MA, Sheikh MC (2019) Offering an innovative composited material for effective lead(II) monitoring and removal from polluted water. J Clean Prod 231:214–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.125
Bala K, Singh B (2017) Electrochemical synthesis of cadmium (II) carboxylates compounds at sacrificial cadmium anode. Asian J Chem 29(02):336–340. https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2017.20186
Chen C, Feng XT, Yao S (2021) Ionic liquid-multi walled carbon nanotubes composite tablet for continuous adsorption of tetracyclines and heavy metals. J Clean Prod 286:124937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124937
Chen MH, Yu MD, Kang RF, Sun HM, Zhang W, Wang SS, Wang N, Wang J (2022) Removal of Pb (II) and V (V) from aqueous solution by glutaraldehyde crosslinked chitosan and nanocomposites. Chemosphere 297:134084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134084
Chen XY, Hossain MF, Duan CY, Lu J, Tsang YF, Islam MS, Zhou YB (2022) Isotherm models for adsorption of heavy metals from water – a review. Chemosphere 307:135545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135545
Dong SY, Rene ER, Zhao LX, Lun XX, Ma WF (2022) Design and preparation of functional azo linked polymers for the adsorptive removal of bisphenol A from water: performance and analysis of the mechanism. Environ Res 206:112601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112601
Du Y, Wang J, Zou YD, Wen Y, Hou J, Xia LS, Peng A, Alsaedi A, Hayat T, Wang XK (2017) Synthesis of molybdenum disulfide/reduced graphene oxide composites for effective removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solutions. Sci Bull 62(13):913–922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2017.05.025
Fontanals N, Marcé RM, Borrull F, Cormack PAG (2015) Hypercrosslinked materials: preparation, characterisation and applications. Polym Chem-UK 6:7231–7244. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5py00771b
Fu KX, Zhang YQ, Liu HZ, Lv CY, Guo J, Luo JM, Yin K, Luo SL (2022) Construction of metal-organic framework/polymer beads for efficient lead ions removal from water: experiment studies and full-scale performance prediction. Chemosphere 303(2):135084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135084
Guo XZ, Han SS, Yang JM, Wang XM, Chen SS, Quan S (2020) Effect of synergistic interplay between surface charge, crystalline defects, and pore volume of MIL-100(Fe) on adsorption of aqueous organic dyes. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:2113–2122. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05715
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Hu LM, Wang P, Shen TY, Wang Q, Wang XJ, Xu P, Zheng QZ, Zhang GS (2020) The application of microwaves in sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes for environmental remediation: a review. Sci Total Environ 722:137831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137831
Huang JH, Wang XG, Huang KL (2009) Adsorption of p-nitroaniline by phenolic hydroxyl groups modified hyper-cross-linked polymeric adsorbent and XAD-4: a comparative study. Chem Eng J 155:722–727
Huang XQ, Hong X, Lin H, Cao XM, Dang Q, Tang SB, Chen DL, Zhang Y (2022) Hypercrosslinked triazine-phloroglucinol hierarchical porous polymers for the effective removal of organic micropollutants. Chem Eng J 435:134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.134990
Kang DW, Lim KS, Lee KJ, Lee JH, Lee WR, Song JH, Yeom KH, Kim JY, Hong CS (2016) Cost-effective, high-performance porous-organic-polymer conductors functionalized with sulfonic acid groups by direct postsynthetic substitution. Angew Chem Int Edit 128:16357–16360. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201609049
Kang MJ, Kim JE, Dong WK, Lee HY, Moon D, Hong CH (2019) A diamine-grafted metal–organic framework with outstanding CO2 capture properties and a facile coating approach for imparting exceptional moisture stability. J Mater Chem A 7:8177–8183. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta07965j
Kang DW, Lee KA, Kang MJ, Kim JM, Moon MK, Choe JH, Kim H, Kim DW, Kim JY, Hong CS (2020) Cost-effective porous-organic-polymer-based electrolyte membranes with superprotonic conductivity and low activation energy. J Mater Chem A 8(3):1147–1153. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta06807d
Katsoulidis AP, Kanatzidis MG (2011) Phloroglucinol based microporous polymeric organic frameworks with OH functional groups and high CO2 capture capacity. Chem Mater 23(7):1818–1824. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm103206x
Langmuir I (1917) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I.—Solids. J Franklin 183(1):102–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-0032(17)90938-x
Langmuir I (1917) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part II. — Liquids. J Franklin 184(5):721. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-0032(17)90088-2
Li J, Wang XX, Zhao GX, Chen CL, Chai ZF, Alsaedi A, Hayat T, Wang XK (2018) Metal–organic framework-based materials: superior adsorbents for the capture of toxic and radioactive metal ions. Chem Soc Rev 47:2322. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cs00543a
Li B, Guo JZ, Liu JL, Fang L, Lv JQ, Lv K (2020) Removal of aqueous-phase lead ions by dithiocarbamate-modified hydrochar. Sci Total Environ 714:136897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136897
Liu XL, Zhang Y, Ju H, Yang F, Luo X, Zhang L (2021) Uptake of methylene blue on divinylbenzene cross-linked chitosan/maleic anhydride polymer by adsorption process. Colloid Surface A 629:127424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127424
Liu J, Zhou J, Wu ZH, Tian X, An XY, Zhang Y, Zhang GS, Deng FX, Meng XL, Qu JH (2022) Concurrent elimination and stepwise recovery of Pb(II) and bisphenol A from water using beta-cyclodextrin modified magnetic cellulose: adsorption performance and mechanism investigation. J Hazard Mater 432:128758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128758
Lu WG, Bosch M, Yuan DQ, Zhou HC (2014) Cost-effective synthesis of amine-tethered porous materials for carbon capture. Chemsuschem 8(3):433–438. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201402622
Melhi S (2021) Novel carbazole-based porous organic frameworks (CzBPOF) for efficient removal of toxic Pb(II) from water: synthesis, characterization, and adsorption studies. Environ Technol Inno 25:102172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.102172
Pan BC, Xiong Y, Su Q, Li AM, Chen JL, Zhang QX (2003) Role of amination of a polymeric adsorbent on phenol adsorption from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 51(9):953–962. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00038-9
Qu JH, Liu Y, Cheng L, Jiang Z, Zhang GS, Deng FX, Wang L, Han W, Zhang Y (2020) Green synthesis of hydrophilic activated carbon supported sulfide nZVI for enhanced Pb (II) scavenging from water: characterization, kinetics, isotherms and mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 403:123607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123607
Qu JH, Wei SQ, Liu Y, Zhang XM, Zhao J, Tao Y, Zhang GS, Zhang B, Wang L, Zhang Y (2022) Effective lead passivation in soil by bone char/CMC-stabilized FeS composite loading with phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. J Hazard Mater 423:127043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127043
Qu GF, Zhou JH, Liang SY, Li YL, Ning P, Pan KH, Ji W, Tang HM (2022) Thiol-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for effective removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions. Mater Chem Phys 278:125688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125688
Rajahmundry GK, Garlapati C, Kumar PS, Alwi RS, Vo DN (2021) Statistical analysis of adsorption isotherm models and its appropriate selection. Chemosphere 276:130176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130176
Saruchi KV, Kaith BS, Jindal R (2016) Synthesis of hybrid ion exchanger for rhodamine B dye removal: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Ind Eng Chem Res 55:10492–10499. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b01690
Shen Y, Guo JZ, Bai LQ, Chen XQ, Li B (2021) High effective adsorption of Pb(II) from solution by biochar derived from torrefaction of ammonium persulphate pretreated bamboo. Bioresource Technol 323:124616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124616
Wang XM, Deng RJ, Jin XY, Huang JH (2012) Gallic acid modified hyper-cross-linked resin and its adsorption equilibria and kinetics toward salicylic acid from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 191:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.03.003
Xu P, Wang P, Wang Q, Wei R, Li Y, Xin YJ, Zheng T, Hu LM, Wang XJ, Zhang GS (2021) Facile synthesis of Ag2O/ZnO/rGO heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity under simulated solar light: kinetics and mechanism. J Hazard Mater 403:124011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124011
Xu WF, Liu X, Tang KW (2022) Adsorption of hydroquinone and Pb(II) from water by beta-cyclodextrin/polyethyleneimine bi-functional polymer. Carbohyd Polym 294:119806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119806
Zhang LQ, He X, Xu XW, Liu C, Duan YL, Hou LQ, Zhou QD, Ma C, Yang XP, Liu R, Yang F, Cui LS, Xu CM, Li YF (2017) Highly active TiO2/g-C3N4/G photocatalyst with extended spectral response towards selective reduction of nitrobenzene. Appl Catal B-Environ 203:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.10.003
Zhang LL, Yang HM, Zhang HX (2022) Hyper-crosslinked dicationic ionic liquid porous polymers for nitrophenol adsorption. Micropor Mesopor Mat 342:112118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2022.112118
Zhao YL, Kang SC, Qin L, Wang W, Zhang TT, Song SX, Komarneni S (2020) Self-assembled gels of Fe-chitosan/montmorillonite nanosheets: dye degradation by the synergistic effect of adsorption and photo-Fenton reaction. Chem Eng J 379:122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122322
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32271528, U1932126), and Zhejiang Province “Vanguard” and “Leading goose” Research and Development Project (Grant No. 2022C02036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kun Yu: material preparation, experimental section, analysis, and writing—original draft. Jiaqi Guo: conceptualization, methodology, and writing—original draft. Kun Yu and Jianqi Guo have the same contribution to this paper. Bing Li: writing, modifying, and funding acquisition. Jianzhong Guo: conception, experimental design, and writing—review and editing. All authors checked and agreed the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This work is original and has not been published elsewhere in any form or language. The manuscript has been submitted to this journal solely for consideration.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, K., Guo, J., Li, B. et al. Highly efficient removal of Pb2+ from wastewater by a maleic anhydride modified organic porous adsorbent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 68467–68476 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27272-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27272-y