Abstract
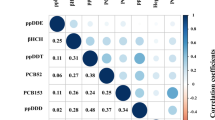
Dioxins and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls (DL-PCBs) are mainly released as by-products of human activities, often in the form of mixtures, and the potential harm on human health deserves attention. Therefore, our study aimed to analyze the combined effect of dioxins and DL-PCB exposures on hypertension (HTN) among US adults. Data of eligible participants were acquired from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Multiple logistic regression models with adjustment for covariates were applied to explore the associations between 13 persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and HTN. Stratified analyses and interaction analyses were then conducted by age and gender. Finally, the combined effects of dioxins and DL-PCBs on HTN were assessed by the weighted quantile sum (WQS) model and the Bayesian kernel machine regression (BKMR) model. A total of 976 adults were included in our study, of whom 397 had HTN. Spearman correlations indicated positive correlations among 13 POPs. And most of them (except PCB28, PCB66, and 1,2,3,4,7,8,9-hpcdf) had significant effects on HTN. The result of WQS revealed that mixed exposure to dioxins and DL-PCBs was significantly associated with increased risk of HTN (OR: 2.205; 95% CIs: 1.555, 3.127). The BKMR model also presented a positive trend of HTN risk with exposure to multiple dioxins and DL-PCBs. And 1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9-ocdd may be the main factor for this positive association. Considering the limitations of our cross-sectional study with the small sample, further prospective studies are necessary to validate our findings.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data was obtained from NHANES 2003–2004.
Abbreviations
- HTN:
-
Hypertension
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- POPs:
-
Persistent organic pollutants
- AhR:
-
Aromatic hydrocarbon receptor
- ARNT:
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator
- XRE:
-
Xenobiotic response element
- TCDD:
-
Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
- PCDDs:
-
Polychlorinated dibenzo-dioxins
- PCDFs:
-
Polychlorinated dibenzo-furans
- PCBs:
-
Polychlorinated biphenyls
- DL:
-
Dioxin-like
- MSW:
-
Municipal solid waste
- WQS:
-
Weighted quantile sum
- BKMR:
-
Bayesian kernel machine regression
- NHANES:
-
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- NCHS:
-
National Center for Health Statistics
- MEC:
-
Mobile examination center
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- LPM:
-
Laboratory/Medical Technologists Procedures Manual
- LOD:
-
Limit of detection
- hxcdd:
-
Hexachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
- hpcdd:
-
Heptachlororodibenzo-p-dioxin
- ocdd:
-
Octachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
- pncdf:
-
Pentachlorodibenzofuran
- hpcdf:
-
Heptachlorodibenzofuran
- pncb:
-
Pentachlorobiphenyl
- PIR:
-
Poverty-income ratio
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- ORs:
-
Odds ratios
- CIs:
-
Confidence intervals
- PIP:
-
Posterior inclusion probability
- TEQs:
-
Toxic equivalents
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- HUVEC:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- TEF:
-
Toxic equivalency factor
- CYP1A2:
-
Cytochrome P4501A2
- TEQs:
-
Total toxic equivalents
References
Andersson H, Garscha U, Brittebo E (2011) Effects of PCB126 and 17 beta-oestradiol on endothelium-derived vasoactive factors in human endothelial cells. Toxicology 285:46–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2011.04.003
Arredondo A, Recaman AL, Suarez-Herrera JC, Cuadra SM (2021) Recent trends for the management of hypertension in older adults in Latin America in the context of universal coverage: evidence from Mexico. Int J Health Plann Manage 36:579–586. https://doi.org/10.1002/hpm.3103
Bakker EA, Sui XM, Brellenthin AG, Lee DC (2018) Physical activity and fitness for the prevention of hypertension. Curr Opin Cardiol 33:394–401. https://doi.org/10.1097/hco.0000000000000526
Bobb JF, Henn BC, Valeri L, Coull BA (2018) Statistical software for analyzing the health effects of multiple concurrent exposures via Bayesian kernel machine regression. Environ Health 17.https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-018-0413-y
Butler L, Gennings C, Peli M, Borgese L, Placidi D, Zimmerman N, Hsu HL, Coull BA, Wright RO, Smith DR, Lucchini RG, Claus HB (2019) Assessing the contributions of metals in environmental media to exposure biomarkers in a region of ferroalloy industry. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 29:674–687. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41370-018-0081-6
Collins JJ, Bodner KM, Aylward LL, Bender TJ, Anteau S, Wilken M, Bodnar CM (2016) Mortality risk among workers with exposure to dioxins. Occupational Medicine-Oxford 66:706–712. https://doi.org/10.1093/occmed/kqw167
Dickerson R, Howie L, Davis D, Safe S (1990) The structure-dependent effects of heptachlorodibenzofuran isomers in male C57BL/6 mice: immunotoxicity and monooxygenase enzyme induction. Fundam Appl Toxicol: Official J Soc Toxicol 15:298–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/0272-0590(90)90056-p
Donat-Vargas C, Akesson A, Tornevi A, Wennberg M, Sommar J, Kiviranta H, Rantakokko P, Bergdahl IA (2018) Persistent organochlorine pollutants in plasma, blood pressure, and hypertension in a longitudinal study. Hypertension 71:1258–1268. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.117.10691
Du Y, Jin Y, Lu S, Peng Z, Li X, Yan J (2013) Study of PCDD/Fs distribution in fly ash, ash deposits, and bottom ash from a medical waste incinerator in China. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 63:230–236. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2012.746753
Endemann DH, Schiffrin EL (2004) Endothelial dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:1983–1992. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.Asn.0000132474.50966.Da
Everett CJ, Mainous AG 3rd, Frithsen IL, Player MS, Matheson EM (2008) Association of polychlorinated biphenyls with hypertension in the 1999–2002 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Environ Res 108:94–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2008.05.006
Fernandez-Salguero PM, Hilbert DM, Rudikoff S, Ward JM, Gonzalez FJ (1996) Aryl-hydrocarbon receptor-deficient mice are resistant to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 140:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1006/taap.1996.0210
Fommei E, Turci R, Ripoli A, Balzan S, Bianchi F, Morelli L, Coi A (2017) Evidence for persistent organochlorine pollutants in the human adrenal cortex. J Appl Toxicol 37:1091–1097. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3460
Fukutomi M, Kario K (2010) Aging and hypertension. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 8:1531–1539. https://doi.org/10.1586/erc.10.78
Goncharov A, Pavuk M, Foushee HR, Carpenter DO, Anniston C (2011) Blood pressure in relation to concentrations of PCB congeners and chlorinated pesticides. Environm Health Perspect 119:319–325. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1002830
Guerrot D, Humalda JK (2020) Blood pressure targets in chronic kidney disease: an update on the evidence. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 29:327–332. https://doi.org/10.1097/mnh.0000000000000601
Guo X, Ke Y, Wu B, Song Q, Sun C, Li Y, Wang H, Su W, Liang Q, Lowe S, Bentley R, Song EJ, King B, Zhou Q, Xie R, Deng F (2022a) Exploratory analysis of the association between organophosphate ester mixtures with high blood pressure of children and adolescents aged 8–17 years: cross-sectional findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23740-z
Guo X, Li N, Wang H, Su W, Song Q, Liang Q, Liang M, Sun C, Li Y, Lowe S, Bentley R, Song EJ, Zhou Q, Ding X, Sun Y (2022b) Combined exposure to multiple metals on cardiovascular disease in NHANES under five statistical models. Environ Res 215:114435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114435
Guo X, Li N, Wang H, Su W, Song Q, Liang Q, Sun C, Liang M, Ding X, Lowe S, Sun Y (2022c) Exploratory analysis of the association between pyrethroid exposure and rheumatoid arthritis among US adults: 2007–2014 data analysis from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23145-y
Guo X, Wang H, Song Q, Li N, Liang Q, Su W, Liang M, Ding X, Sun C, Lowe S, Sun Y (2022d) Association between exposure to organophosphorus pesticides and the risk of diabetes among US adults: cross-sectional findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Chemosphere 301:134471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134471
Guo X, Wu B, Xia W, Gao J, Xie P, Feng L, Sun C, Liang M, Ding X, Zhao D, Ma S, Liu H, Lowe S, Bentley R, Huang C, Qu G, Sun Y (2022e) Association of organophosphate ester exposure with cardiovascular disease among US adults: cross-sectional findings from the 2011–2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Chemosphere 308:136428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136428
Ha MH, Lee DH, Son HK, Park SK, Jacobs DR (2009) Association between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and prevalence of newly diagnosed hypertension: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2002. J Hum Hypertens 23:274–286. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2008.124
Haase H, Fahlenkamp A, Schettgen T, Esser A, Gube M, Ziegler P, Kraus T, Rink L (2016) Immunotoxicity monitoring in a population exposed to polychlorinated biphenyls. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13030295
Hajjar I, Kotchen TA (2003) Trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in the United States, 1988–2000. JAMA 290:199–206. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.290.2.199
Hansson GK (2005) Mechanisms of disease - inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 352:1685–1695. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra043430
Helyar SG, Patel B, Headington K, El Assal M, Chatterjee PK, Pacher P, Mabley JG (2009) PCB-induced endothelial cell dysfunction: Role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Biochem Pharmacol 78:959–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.019
Huang T, Liu LF, Zhou LL, Yang K (2018) Operating optimization for the heavy metal removal from the municipal solid waste incineration fly ashes in the three-dimensional Chock tar electrokinetics. Chemosphere 204:294–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.065
Huang T, Zhang SW, Liu LF (2019) Immobilization of trace heavy metals in the electrokinetics-processed municipal solid waste incineration fly ashes and its characterizations and mechanisms. J Environ Manage 232:207–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.11.051
Huang T, Zhou LL, Chen L, Liu WH, Zhang SW, Liu LF (2020) Mechanism exploration on the aluminum supplementation coupling the electrokinetics-activating geopolymerization that reinforces the solidification of the municipal solid waste incineration fly ashes. Waste Manage 103:361–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.12.048
Iadecola C, Yaffe K, Biller J, Bratzke LC, Faraci FM, Gorelick PB, Gulati M, Kamel H, Knopman DS, Launer LJ, Saczynski JS, Seshadri S, Al Hazzouri AZ, Amer Heart Assoc C, Council Clinical C, Council Cardiovasc Dis Y, Council Cardiovasc Stroke N, Council Quality Care Outcomes R, Stroke C (2016) Impact of hypertension on cognitive function: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 68:E67-E94.https://doi.org/10.1161/hyp.0000000000000053
Jayedi A, Zargar MS (2019) Dietary calcium intake and hypertension risk: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Eur J Clin Nutr 73:969–978. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-018-0275-y
Jung S, Kim MK, Shin J, Lee N, Woo HW, Choi BY, Shin MH, Shin DH, Lee YH (2020) Positive association of alcohol consumption with incidence of hypertension in adults aged 40 years and over: use of repeated alcohol consumption measurements. Clin Nutr 39:3125–3131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2020.01.020
Kerley-Hamilton JS, Trask HW, Ridley CJ, Dufour E, Lesseur C, Ringelberg CS, Moodie KL, Shipman SL, Korc M, Gui J, Shworak NW, Tomlinson CR (2012) Inherent and benzo[a]pyrene-induced differential aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling greatly affects life span, atherosclerosis, cardiac gene expression, and body and heart growth in mice. Toxicol Sci 126:391–404. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfs002
Koliaki C, Katsilambros N (2013) Dietary sodium, potassium, and alcohol: key players in the pathophysiology, prevention, and treatment of human hypertension. Nutr Rev 71:402–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/nure.12036
Kopf PG, Scott JA, Agbor LN, Boberg JR, Elased KM, Huwe JK, Walker MK (2010) Cytochrome P4501A1 is required for vascular dysfunction and hypertension induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Sci 117:537–546. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfq218
Lacroix A, Fournier M, Lebeuf M, Nagler JJ, Cyr DG (2001) Phagocytic response of macrophages from the pronephros of American plaice (Hipoglossoides platessoides) exposed to contaminated sediments from Baie des Anglais, Quebec. Chemosphere 45:599–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0045-6535(00)00604-4
Lee DH, Lee IK, Porta M, Steffes M, Jacobs DR (2007) Relationship between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome among non-diabetic adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2002. Diabetologia 50:1841–1851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-007-0755-4
Lee DH, Lee IK, Song K, Steffes M, Toscano W, Baker BA, Jacobs DR (2006) A strong dose-response relation between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and diabetes - results from the National Health and Examination Survey 1999–2002. Diabetes Care 29:1638–1644. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc06-0543
Letcher RJ, Lemmen JG, van der Burg B, Brouwer A, Bergman A, Giesy JP, van den Berg M (2002) In vitro antiestrogenic effects of aryl methyl sulfone metabolites of polychlorinated biphenyls and 2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,1-dichloroethene on 17beta-estradiol-induced gene expression in several bioassay systems. Toxicol Sci: Official J Soc Toxicol 69:362–372. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/69.2.362
Liao YL, Siegel PZ, White S, Dulin R, Taylor A (2016) Improving actions to control high blood pressure in Hispanic communities - racial and ethnic approaches to community health across the US project, 2009–2012. Prev Med 83:11–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2015.11.027
Liu D, Perkins JT, Petriello MC, Hennig B (2015) Exposure to coplanar PCBs induces endothelial cell inflammation through epigenetic regulation of NF-kappa B subunit p65. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 289:457–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2015.10.015
Long Y, Huang C, Wu J, Cheng JN, Liang GN, Jiang CX, Wan Q (2017) 2,3’,4,4’,5-Pentachlorobiphenyl impairs insulin-induced NO production partly through excessive ROS production in endothelial cells. Toxicol Mech Methods 27:592–597. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2017.1337259
Marinkovic N, Pasalic D, Ferencak G, Grskovic B, Rukavina AS (2010) Dioxins and human toxicity. Arhiv Za Higijenu Rada I Toksikologiju-Arch Ind Hygiene Toxicol 61:445–453. https://doi.org/10.2478/10004-1254-61-2010-2024
Matta K, Lefebvre T, Vigneau E, Cariou V, Marchand P, Guitton Y, Royer AL, Ploteau S, Le Bizec B, Antignac JP, Cano-Sancho G (2022) Associations between persistent organic pollutants and endometriosis: a multiblock approach integrating metabolic and cytokine profiling. Environ Int 158.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.106926
McMaster WG, Kirabo A, Madhur MS, Harrison DG (2015) Inflammation, immunity, and hypertensive end-organ damage. Circ Res 116:1022–1033. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.116.303697
Miller CS, Glick M, Rhodus NL (2018) 2017 Hypertension guidelines New opportunities and challenges. J Am Dent Assoc 149:229–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adaj.2018.01.047
Mirzaei M, Mirzaei M, Mirzaei M, Bagheri B (2020) Changes in the prevalence of measures associated with hypertension among Iranian adults according to classification by ACC/AHA guideline 2017. Bmc Cardiovasc Disor 20.https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-020-01657-0
Nakamoto M, Arisawa K, Uemura H, Katsuura S, Takami H, Sawachika F, Yamaguchi M, Juta T, Sakai T, Toda E, Mori K, Hasegawa M, Tanto M, Shima M, Sumiyoshi Y, Morinaga K, Kodama K, Suzuki T, Nagai M, Satoh H (2013) Association between blood levels of PCDDs/PCDFs/dioxin-like PCBs and history of allergic and other diseases in the Japanese population. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 86:849–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-012-0819-8
National Research Council (US) Committee on the Health Risks of Phthalates (2008) Phthalates and cumulative risk assessment: the tasks ahead. National Academies Press, Washington DC. https://doi.org/10.17226/12528
Noth RH, Mazzaferri EL (1985) Age and the endocrine system. Clin Geriatr Med 1:223–250
Omboni S (2020) Smoking and hypertension: what is behind the mask? J Hypertens 38:1029–1030. https://doi.org/10.1097/hjh.0000000000002423
Ostchega Y, Hughes JP, Wright JD, McDowell MA, Louis T (2008) Are demographic characteristics, health care access and utilization, and comorbid conditions associated with hypertension among US adults? Am J Hypertens 21:159–165. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajh.2007.32
Park SH, Lim JE, Park H, Jee SH (2016) Body burden of persistent organic pollutants on hypertension: a meta-analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:14284–14293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6568-6
Pesatori AC, Zocchetti C, Guercilena S, Consonni D, Turrini D, Bertazzi PA (1998) Dioxin exposure and non-malignant health effects: a mortality study. Occup Environ Med 55:126–131. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.55.2.126
Rahman F, Wulandari A, Sofyan TM, Iqram AM, Marlina FP, Rahmitasari N, Yulisa R, Rahma DD, Anindya A, Camelia S (2018) Evaluation of the association between hypertension and the factors: gender, age, education level and work status in Pantai Linuh, Indonesia. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 49:1072–1077
Raymond MR, Christensen KY, Thompson BA, Anderson HA (2016) Associations between fish consumption and contaminant biomarkers with cardiovascular conditions among older male anglers in Wisconsin. J Occup Environ Med 58:676–682. https://doi.org/10.1097/jom.0000000000000757
Roka R, Michimi A, Macy G (2015) Associations between hypertension and body mass index and waist circumference in U.S. adults: a comparative analysis by gender. High Blood Pressure Cardiovasc Prev: Official J Italian Soc Hypertension 22:265–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-015-0106-3
Rosario RF, Wesson DE (2006) Primary hypertension and nephropathy. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 15:130–134. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mnh.0000214771.88737.ee
Safe S, Wang F, Porter W, Duan R, McDougal A (1998) Ah receptor agonists as endocrine disruptors: antiestrogenic activity and mechanisms. Toxicol Lett 102–103:343–347
Schildroth S, Friedman A, Bauer JA, Claus Henn B (2022) Associations of a metal mixture with iron status in U.S. adolescents: evidence from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. New directions for child and adolescent development. https://doi.org/10.1002/cad.20457.
Selvaraj S, Gaonkar O, Kumar B, Cincinelli A, Chakraborty P (2021) Legacy persistent organochlorine pollutants and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surface soil from the industrial corridor of South India: occurrence, sources and risk assessment. Environ Geochem Health 43:2105–2120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00786-x
Shargorodsky J, Garcia-Esquinas E, Navas-Acien A, Lin SY (2015) Allergic sensitization, rhinitis, and tobacco smoke exposure in U.S. children and adolescents (vol 5, pg 471, 2015). Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 5:768–768. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.21617
Song JJ, Ma Z, Wang J, Chen LX, Zhong JC (2020) Gender differences in hypertension. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 13:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-019-09888-z
Sowers JR (1998) Diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease in women. Arch Intern Med 158:617–621. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.158.6.617
Staff M, Sheppeard V, Abeywardana S, Forssman B, Rutherford A, Mueller JF, Paepke O (2012) Blood dioxin biomonitoring to assess local residents’ exposure from a large urban remediation project. Chemosphere 88:316–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.003
Sutter CH, Rahman M, Sutter TR (2006) Uncertainties related to the assignment of a toxic equivalency factor for 1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9-octachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 44:219–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2005.12.005
Valera B, Jorgensen ME, Jeppesen C, Bjerregaard P (2013) Exposure to persistent organic pollutants and risk of hypertension among Inuit from Greenland. Environ Res 122:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2012.12.006
Van den Berg M, Birnbaum L, Bosveld AT, Brunstrom B, Cook P, Feeley M, Giesy JP, Hanberg A, Hasegawa R, Kennedy SW, Kubiak T, Larsen JC, van Leeuwen FX, Liem AK, Nolt C, Peterson RE, Poellinger L, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tillitt D, Tysklind M, Younes M, Waern F, Zacharewski T (1998) Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for humans and wildlife. Environ Health Perspect 106:775–792. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.98106775
Xu YK, Wu Q (2021) Prevalence trend and disparities in rheumatoid arthritis among US adults, 2005-2018. J Clin Med 10.https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153289
Zhao XY, Guo SG, Zhang R, Liu L, Guo L, Liu GS, Jiang LQ, Li Q, Pan BL, Nie JS, Yang J (2022) The interaction effects of secondhand smoke exposure and overweight on the prevalence of hypertension in Chinese coke oven workers and NHANES participants (2013-2016). Chemosphere 303.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135120
Acknowledgements
All authors in this study thank NHANES for providing the publicly available data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Birong Wu and Xianwei Guo: conceptualization, methodology, software, data curation, formal analysis, visualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Linya Feng and Juan Gao: methodology, validation, formal analysis, software, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Weihang Xia and Peng Xie: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, visualization, writing—review and editing. Shaodi Ma, Haixia Liu, Dongdong Zhao, and Guangbo Qu: methodology, formal analysis, writing—review and editing. Chenyu Sun: conceptualization, writing—review and editing. Scott Lowe and Rachel Bentley: writing—review and editing. Yehuan Sun: conceptualization, supervision, funding acquisition, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The study protocol was approved by the NCHS Institutional Review Board.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in the NHANES.
Consent for publication
The participants have consented to the submission of this article to the journal and publication of it.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, B., Guo, X., Feng, L. et al. Combined exposure to multiple dioxins and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls on hypertension among US adults in NHANES: a cross-sectional study under three statistical models. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 28730–28744 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24271-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24271-3