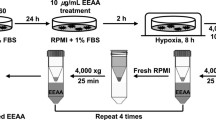
Abstract
Abnormal angiogenesis contributes to the pathogenesis of various diseases. The medicinal usage of Agrostemma githago L. seed (A. githago herein) has been stated in traditional medicine. This study aims to investigate the anti-angiogenic potential of aqueous extract of A. githago. In order to test the effect of A. githago extract, its impact on HUVECs, T98G, and HGF2PI2 cells was assessed by looking at cellular viability, changes in the distribution of cells in different phases of the cell cycle, induction of oxidative stress, and apoptosis. In addition, the release of VEGF, ANG2, and MMP2/9 factors, along with the expressions of the critical Notch signaling pathway players and VEGF receptors (VEGFR), was measured. Furthermore, a γ-secretase inhibitor (LY411575) was applied to determine whether Notch inhibition restores A. githago effects. As a further characterization, total phenolic and flavonoid contents of A. githago were estimated, and five triterpene saponin compounds were identified using LC–ESI–MS. In response to A. githago extract, a reduction in total cell viability, along with the induction of ROS and apoptosis, was detected. Exposure to the A. githago extract could modulate the release of VEGF and ANG2 from T98G and HUVECs, respectively. In addition, A. githago reduced the release of MMP2/9. Furthermore, Notch1, DLL4, and HEY2 transcripts and protein expressions were up-regulated, while VEGFR2 was down-regulated in treated HUVEC cells. Treatment with the A. githago extract resulted in a dose-dependent inhibition of AKT phosphorylation. Inhibition of Notch signaling retrieved the viability loss, reduced intracellular ROS, and alleviated the impaired tube formation in A. githago-treated HUVECs. Overall, these data underscore the anti-angiogenic potential of A. githago via inducing apoptosis, modifying the expression levels of VEGF/VEGFR2, and impacting the release of MMP2/9 and ANG2, effects that are most probably modulated through the Notch/VEGF signaling axis.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abdolmalekia Z, Araba HA, Amanpourb S, Muhammadnejad S (2016) Anti-angiogenic effects of ethanolic extract of Artemisia sieberi compared to its active substance, artemisinin. Rev Bras Farmacogn 26:326–333
Adeola HA, Bano A, Vats R, Vashishtha A, Verma D, Kaushik D, Mittal V, Rahman MH, Najda A, Albadrani GM, Sayed AA, Farouk SM, Hassanein EHM, Akhtar MF, Saleem A, Abdel-Daim MM, Bhardwaj R (2021) Bioactive compounds and their libraries: an insight into prospective phytotherapeutics approach for oral mucocutaneous cancers. Biomed Pharmacother 141:111809
Akwii RG, Sajib MS, Zahra FT, Mikelis CM (2019) Role of angiopoietin-2 in vascular physiology and pathophysiology. Cells 8:471
Antfolk D, Sjoqvist M, Cheng F, Isoniemi K, Duran CL, Rivero-Muller A, Antila C, Niemi R, Landor S, Bouten CVC, Bayless KJ, Eriksson JE, Sahlgren CM (2017) Selective regulation of Notch ligands during angiogenesis is mediated by vimentin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E4574–E4581
Avicenna BL (2014) The Canon of Medicine (al-Qānūn Fī'l-ṭibb)(the Law of Natural Healing). Systemic diseases, orthopedics and cosmetics. Great Books of the Islamic World
Baharara J, Amini E, Mousavi M (2015) The anti-proliferative and anti-angiogenic effect of the methanol extract from brittle star. Rep Biochem Mol Biol 3:68–75
Blanco R, Gerhardt H (2013) VEGF and Notch in tip and stalk cell selection. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 3:a006569
Bohlooli S, Bohlooli S, Aslanian R, Nouri F, Teimourzadeh A (2015) Aqueous extract of Agrostemma githago seed inhibits caspase-3 and induces cell-cycle arrest at G1 phase in AGS cell line. J Ethnopharmacol 175:295–300
Caporarello N, Lupo G, Olivieri M, Cristaldi M, Cambria MT, Salmeri M, Anfuso CD (2017) Classical VEGF, Notch and Ang signalling in cancer angiogenesis, alternative approaches and future directions (Review). Mol Med Rep 16:4393–4402
Chen W, Xia P, Wang H, Tu J, Liang X, Zhang X, Li L (2019) The endothelial tip-stalk cell selection and shuffling during angiogenesis. J Cell Commun Signal 13:291–301
Chiu LC, Ooi VE, Sun SS (2001) Induction of apoptosis by a ribosome-inactivating protein from Agrostemma githago is associated with down-regulation of anti-apoptotic bcl-2 protein expression. Int J Oncol 19:137–141
Clochard J, Jerz G, Schmieder P, Mitdank H, Troger M, Sama S, Weng A (2020) A new acetylated triterpene saponin from Agrostemma githago L. modulates gene delivery efficiently and shows a high cellular tolerance. Int J Pharm 589:119822
Dai ZJ, Lu WF, Gao J, Kang HF, Ma YG, Zhang SQ, Diao Y, Lin S, Wang XJ, Wu WY (2013) Anti-angiogenic effect of the total flavonoids in Scutellariabarbata D Don. BMC Complement Altern Med 13:150
Deryugina EI, Quigley JP (2015) Tumor angiogenesis: MMP-mediated induction of intravasation- and metastasis-sustaining neovasculature. Matrix Biol 44–46:94–112
Dong Y, Zhang T, Li J, Deng H, Song Y, Zhai D, Peng Y, Lu X, Liu M, Zhao Y, Yi Z (2014) Oridonin inhibits tumor growth and metastasis through anti-angiogenesis by blocking the Notch signaling. PLoS ONE 9:e113830
Fan TP, Yeh JC, Leung KW, Yue PY, Wong RN (2006) Angiogenesis: from plants to blood vessels. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27:297–309
Foster S, Duke JA, Society NA, Peterson RT, Federation NW, Institute RTP (1990) A field guide to medicinal plants: Eastern and Central North America. Houghton Mifflin
Foubert K, Breynaert A, Theunis M, Van Den Bossche R, De Meyer GR, Van Daele A, Faizal A, Goossens A, Geelen D, Conway EM, Vlietinck A, Pieters L, Apers S (2012) Evaluation of the anti-angiogenic activity of saponins from Maesa lanceolata by different assays. Nat Prod Commun 7:1149–1154
Funahashi Y, Shawber CJ, Sharma A, Kanamaru E, Choi YK, Kitajewski J (2011) Notch modulates VEGF action in endothelial cells by inducing Matrix Metalloprotease activity. Vasc Cell 3:2
Garcia A, Kandel JJ (2012) Notch: a key regulator of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Histol Histopathol 27:151–156
Hassan LE, Ahamed MB, Majid AS, Baharetha HM, Muslim NS, Nassar ZD, Majid AM (2014) Correlation of antiangiogenic, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of some Sudanese medicinal plants with phenolic and flavonoid contents. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:406
Hiratsuka S, Nakamura K, Iwai SH, Murakami M, Itoh T, Kijima H, Shipley JM, Senior RM, Shibuya M (2002) MMP9 induction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 is involved in lung-specific metastasis. Cancer Cell 2:289–300
Jakobsson L, Bentley K, Gerhardt H (2009) VEGFRs and Notch: a dynamic collaboration in vascular patterning. Biochem Soc Trans 37:1233–1236
Jantova S, Topolska D, Janoskova M, Panik M, Milata V (2016) Study of the cytotoxic/toxic potential of the novel anticancer selenodiazoloquinolone on fibroblast cells and 3D skin model. Interdiscip Toxicol 9:106–112
Kim YW, Byzova TV (2014) Oxidative stress in angiogenesis and vascular disease. Blood 123:625–631
Kofler NM, Shawber CJ, Kangsamaksin T, Reed HO, Galatioto J, Kitajewski J (2011) Notch signaling in developmental and tumor angiogenesis. Genes Cancer 2:1106–1116
Koon YL, Zhang S, Rahmat MB, Koh CG, Chiam KH (2018) Enhanced delta-Notch lateral inhibition model incorporating intracellular Notch heterogeneity and tension-dependent rate of delta-Notch binding that reproduces sprouting angiogenesis patterns. Sci Rep 8:9519
Liang N, Li Y, Chung HY (2017) Two natural eudesmane-type sesquiterpenes from Laggera alata inhibit angiogenesis and suppress breast cancer cell migration through VEGF- and angiopoietin 2-mediated signaling pathways. Int J Oncol 51:213–222
Liu CT, Bi KW, Huang CC, Wu HT, Ho HY, JH SP, Huang ST, (2017) Davallia bilabiata exhibits anti-angiogenic effect with modified MMP-2/TIMP-2 secretion and inhibited VEGF ligand/receptors expression in vascular endothelial cells. J Ethnopharmacol 196:213–224
Liu Z, Fan F, Wang A, Zheng S, Lu Y (2014) Dll4-Notch signaling in regulation of tumor angiogenesis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140:525–536
Loutrari H, Hatziapostolou M, Skouridou V, Papadimitriou E, Roussos C, Kolisis FN, Papapetropoulos A (2004) Perillyl alcohol is an angiogenesis inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 311:568–575
Lu K, Bhat M, Basu S (2016) Plants and their active compounds: natural molecules to target angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 19:287–295
Lugano R, Ramachandran M, Dimberg A (2020) Tumor angiogenesis: causes, consequences, challenges and opportunities. Cell Mol Life Sci 77:1745–1770
M HR, Ghosh D, Banerjee R, Salimath BP (2017) Suppression of VEGF-induced angiogenesis and tumor growth by Eugenia jambolana, Musa paradisiaca, and Coccinia indica extracts. Pharm Biol 55(1):1489–1499. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2017.1307422
Maes H, Olmeda D, Soengas MS, Agostinis P (2016) Vesicular trafficking mechanisms in endothelial cells as modulators of the tumor vasculature and targets of antiangiogenic therapies. FEBS J 283:25–38
Mahmoudinia S, Niapour A, Ghasemi Hamidabadi H, Mazani M (2019) 2,4-D causes oxidative stress induction and apoptosis in human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:26170–26183
Man S, Gao W, Zhang Y, Huang L, Liu C (2010) Chemical study and medical application of saponins as anti-cancer agents. Fitoterapia 81:703–714
Melzig MF, Hebestreit P, Gaidi G, Lacaille-Dubois MA (2005) Structure-activity-relationship of saponins to enhance toxic effects of agrostin. Planta Med 71:1088–1090
Min JK, Han KY, Kim EC, Kim YM, Lee SW, Kim OH, Kim KW, Gho YS, Kwon YG (2004) Capsaicin inhibits in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis. Cancer Res 64:644–651
Mohammadi-Motlagh HR, Shokohinia Y, Mojarrab M, Rasouli H, Mostafaie A (2017) 2-Methylpyridine-1-ium-1-sulfonate from Allium hirtifolium: an anti-angiogenic compound which inhibits growth of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells through cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction. Biomed Pharmacother 93:117–129
Nam SH, Lkhagvasuren K, Seo HW, Kim JK (2017) Antiangiogenic effects of ziyuglycoside II, a major active compound of Sanguisorba officinalis L. Phytother Res 31:1449–1456
Niapour A, Bohlooli S, Sharifi Pasandi M, Mohammadi-ghalehbin B (2018) In vitro anti leishmanial effect of Agrostemma githago extract on leishmania major promastigotes by cell count and MTT assay. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci 28:13–23
Niapour A, Ghasemi Hamidabadi H, Niapour N, Mohammadi P, Sharifi Pasandi M, Malekzadeh V (2019) Pharmacological Notch pathway inhibition leads to cell cycle arrest and stimulates ascl1 and neurogenin2 genes expression in dental pulp stem cells-derived neurospheres. Biotechnol Lett 41:873–887
Niapour A, Seyedasli N (2022) Acquisition of paclitaxel resistance modulates the biological traits of gastric cancer AGS cells and facilitates epithelial to mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 395:515–533
Niapour N, Niapour A, Sheikhkanloui Milan H, Amani M, Salehi H, Najafzadeh N, Gholami MR (2015) All trans retinoic acid modulates peripheral nerve fibroblasts viability and apoptosis. Tissue Cell 47:61–65
Phng LK, Gerhardt H (2009) Angiogenesis: a team effort coordinated by Notch. Dev Cell 16:196–208
Podolak I, Galanty A, Sobolewska D (2010) Saponins as cytotoxic agents: a review. Phytochem Rev 9:425–474
Saadati H, Noroozzadeh S, Esmaeili H, Amirshahrokhi K, Shadman J, Niapour A (2021) The neuroprotective effect of mesna on cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity: behavioral, electrophysiological, and molecular studies. Neurotox Res 39:826–840
Schrot J, Weng A, Melzig MF (2015) Ribosome-inactivating and related proteins. Toxins (basel) 7:1556–1615
Senger DR, Davis GE (2011) Angiogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3:a005090
Sharifi Pasandi M, Hosseini Shirazi F, Gholami MR, Salehi H, Najafzadeh N, Mazani M, Ghasemi Hamidabadi H, Niapour A (2017) Epi/perineural and Schwann cells as well as perineural sheath integrity are affected following 2,4-D exposure. Neurotox Res 32:624–638
Thomas JL, Baker K, Han J, Calvo C, Nurmi H, Eichmann AC, Alitalo K (2013) Interactions between VEGFR and Notch signaling pathways in endothelial and neural cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 70:1779–1792
Thurston G, Daly C (2012) The complex role of angiopoietin-2 in the angiopoietin-tie signaling pathway. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a006550
Tian F, Zhang X, Tong Y, Yi Y, Zhang S, Li L, Sun P, Lin L, Ding J (2005) PE, a new sulfated saponin from sea cucumber, exhibits anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activities in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther 4:874–882
Tiemeijer LA, Ristori T, Stassen O, Ahlberg JJ, de Bijl JJJ, Chen CS, Bentley K, Bouten CVC, Sahlgren CM (2022) Engineered patterns of Notch ligands Jag1 and Dll4 elicit differential spatial control of endothelial sprouting. iScience 25:104306
Ugarte-Berzal E, Redondo-Munoz J, Eroles P, Del Cerro MH, Garcia-Marco JA, Terol MJ, Garcia-Pardo A (2010) VEGF/VEGFR2 interaction down-regulates matrix metalloproteinase-9 via STAT1 activation and inhibits B chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell migration. Blood 115:846–849
Velasquez C, Mansouri S, Mora C, Nassiri F, Suppiah S, Martino J, Zadeh G, Fernandez-Luna JL (2019) Molecular and clinical insights into the invasive capacity of glioblastoma cells. J Oncol 2019:1740763
Vincken JP, Heng L, de Groot A, Gruppen H (2007) Saponins, classification and occurrence in the plant kingdom. Phytochemistry 68:275–297
Wei J, Zhang L, Ren L, Zhang J, Yu Y, Wang J, Duan J, Peng C, Sun Z, Zhou X (2017) Endosulfan inhibits proliferation through the Notch signaling pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Environ Pollut 221:26–36
Woltje K, Jabs M, Fischer A (2015) Serum induces transcription of Hey1 and Hey2 genes by Alk1 but not Notch signaling in endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 10:e0120547
Xing Y, Tu J, Zheng L, Guo L, Xi T (2015) Anti-angiogenic effect of tanshinone IIA involves inhibition of the VEGF/VEGFR2 pathway in vascular endothelial cells. Oncol Rep 33:163–170
Yang Y, Duan W, Liang Z, Yi W, Yan J, Wang N, Li Y, Chen W, Yu S, Jin Z, Yi D (2013) Curcumin attenuates endothelial cell oxidative stress injury through Notch signaling inhibition. Cell Signal 25:615–629
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Bohlooli for providing the A. githago githago seed extract.
Funding
This study was financially supported by Ardabil University of Medical Sciences (Grant No. arums-199).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Estimation of total phenol and flavonoid of the extract and LC–MS performance and interpretation were done by M.M. HUVECs, T98G, and HGF2PI2 culture, MTT assay, cell cycle analysis, annexin V-PI, caspase 3/7 assay, ROS, and ELISA kits were done by A.N. Primer design and real-time PCR were performed and interpreted by F.N and A.N. Study design: A.N. and N.S did statistical analyses and manuscript preparation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the ethical committee of Ardabil University of Medical Sciences (IR.ARUMS.REC.1397.211).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Niapour, A., Miran, M., Seyedasli, N. et al. Anti-angiogenic effects of aqueous extract from Agrostemma githago L. seed in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via regulating Notch/VEGF, MMP2/9, ANG2, and VEGFR2. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 22413–22429 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23510-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23510-x