Abstract
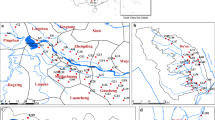
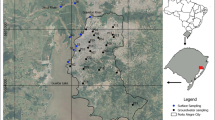
Recently, identifying the contamination status and assessing the health risk of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in surface water and groundwater have been of great significance. Eighteen individual PFASs were analyzed in thirty-three surface/groundwater samples during one period in a fluorine chemical park (Park A) and during two periods in Park B. The mean total concentration of 18 PFASs (∑PFASs) in Park A (9104.63 ng·L−1) was significantly higher than that in the wet season (WS) (801.68 ng·L−1) or DS (714.64 ng·L−1) in Park B. The perfluorobutane sulfonate (PFBS) was the predominant substance in the two parks, and the maximum concentration in groundwater exceeded 10,000 ng·L−1. The contamination status in the wet season (WS) was higher than that in the dry season (DS) in Park B. The ∑PFASs in Park A presented an increasing tendency following the groundwater flow direction, whereas this rule was limited to all periods in Park B. Two relative source contributions (RSCs) of 20% or 100% allowed assessing the PFASs risk to different age groups, and the results revealed that some PFASs (4 ≤ C ≤ 7 or 9 ≤ C ≤ 12) were identified as having a low risk quotient (RQ), except for perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and PFOA (C = 8). The RQmix value mainly relies on PFOA and PFOS, with a larger contribution rate of 80–90%. All assessed cases (case 1, case 2, case 3, and case 4) in all age groups revealed that infants were vulnerable to PFASs influence, followed by children, teenagers, and adults.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data generated or explored during the current work are contained in this article and its supporting information files.
References
Ahrens L, Taniyasu S, Yeung LW, Yamashita N, Lam PK, Ebinghaus R (2010) Distribution of polyfluoroalkyl compounds in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Tokyo Bay, Japan. Chemosphere 79:266–272
Ahrens L, Gashaw H, Sjoholm M, Gebrehiwot SG, Getahun A, Derbe E, Bishop K, Akerblom S (2016) Poly- and perfluoroalkylated substances (PFASs) in water, sediment and fish muscle tissue from Lake Tana, Ethiopia and implications for human exposure. Chemosphere 165:352–357
Awad E, Zhang X, Bhavsar SP, Petro S, Crozier PW, Reiner EJ, Fletcher R, Tittlemier SA, Braekevelt E (2011) Long-term environmental fate of perfluorinated compounds after accidental release at Toronto airport. Environ Sci Technol 45:8081–8089
Bao J, Li CL, Liu Y, Wang X, Yu WJ, Liu ZQ, Shao LX, Jin YH (2020) Bioaccumulation of perfluoroalkyl substances in greenhouse vegetables with long-term groundwater irrigation near fluorochemical plants in Fuxin, China. Environ Res 188:109751
Blaine AC, Rich CD, Sedlacko EM, Hyland KC, Stushnoff C, Dickenson ER, Higgins CP (2014) Perfluoroalkyl acid uptake in lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and strawberry (Fragaria ananassa) irrigated with reclaimed water. Environ Sci Technol 48:14361–14368
Cao X, Wang C, Lu Y, Zhang M, Khan K, Song S, Wang P, Wang C (2019) Occurrence, sources and health risk of polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in soil, water and sediment from a drinking water source area. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:208–217
Catherine M, Nadege B, Charles P, Yann A (2019) Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the marine environment: spatial distribution and temporal profile shifts in shellfish from French coasts. Chemosphere 228:640–648
Chen H, Zhang C, Han J, Sun R, Kong X, Wang X, He X (2015) Levels and spatial distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances in China Liaodong Bay basin with concentrated fluorine industry parks. Mar Pollut Bull 101:965–971
Chen H, Wang X, Zhang C, Sun R, Han J, Han G, Yang W, He X (2017) Occurrence and inputs of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) from rivers and drain outlets to the Bohai Sea, China. Environ Pollut 221:234–243
Chen H, Yao Y, Zhao Z, Wang Y, Wang Q, Ren C, Wang B, Sun H, Alder AC, Kannan K (2018) Multimedia distribution and transfer of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) surrounding two fluorochemical manufacturing facilities in Fuxin, China. Environ Sci Technol 52:8263–8271
Choi HG, Moon HB, Choi M, Yu J (2011) Monitoring of organic contaminants in sediments from the Korean coast: spatial distribution and temporal trends (2001–2007). Mar Pollut Bull 62:1352–1361
Dun Y, Tang C, Shen Y (2013) Identifying interactions between river water and groundwater in the North China Plain using multiple tracers. Environ Earth Sci 72:99–110
Etchepare R, van der Hoek JP (2015) Health risk assessment of organic micropollutants in greywater for potable reuse. Water Res 72:186–198
Fu Y, Wang T, Wang P, Fu Q, Lu Y (2014) Effects of age, gender and region on serum concentrations of perfluorinated compounds in general population of Henan, China. Chemosphere 110:104–110
Gagliano E, Sgroi M, Falciglia PP, Vagliasindi FGA, Roccaro P (2020) Removal of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from water by adsorption: role of PFAS chain length, effect of organic matter and challenges in adsorbent regeneration. Water Res 171:115381
Gan CD, Gan ZW, Cui SF, Fan RJ, Fu YZ, Peng MY, Yang JY (2021) Agricultural activities impact on soil and sediment fluorine and perfluorinated compounds in an endemic fluorosis area. Sci Total Environ 771:144809
Gao Y, Liang Y, Gao K, Wang Y, Wang C, Fu J, Wang Y, Jiang G, Jiang Y (2019) Levels, spatial distribution and isomer profiles of perfluoroalkyl acids in soil, groundwater and tap water around a manufactory in China. Chemosphere 227:305–314
Gao L, Liu J, Bao K, Chen N, Meng B (2020) Multicompartment occurrence and partitioning of alternative and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in an impacted river in China. Sci Total Environ 729:138753
Gebbink WA, Bossi R, Rigét FF, Rosing-Asvid A, Sonne C, Dietz R (2016) Observation of emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in Greenland marine mammals. Chemosphere 144:2384–2391
Gobelius L, Lewis J, Ahrens L (2017) Plant uptake of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances at a contaminated fire training facility to evaluate the phytoremediation potential of various plant species. Environ Sci Technol 51:12602–12610
Gobelius L, Hedlund J, Durig W, Troger R, Lilja K, Wiberg K, Ahrens L (2018) Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in Swedish groundwater and surface water: implications for environmental quality standards and drinking water guidelines. Environ Sci Technol 52:4340–4349
Gomez-Canela C, Barth JA, Lacorte S (2012) Occurrence and fate of perfluorinated compounds in sewage sludge from Spain and Germany. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 19:4109–4119
Graetz S, Ji M, Hunter S, Sibley PK, Prosser RS (2020) Deterministic risk assessment of firefighting water additives to aquatic organisms. Ecotoxicology 29:1377–1389
Han T, Gao L, Chen J, He X, Wang B (2020) Spatiotemporal variations, sources and health risk assessment of perfluoroalkyl substances in a temperate bay adjacent to metropolis, North China. Environ Pollut 265:115011
He X, Li A, Wang S, Chen H, Yang Z (2018) Perfluorinated substance assessment in sediments of a large-scale reservoir in Danjiangkou, China. Environ Monit Assess 190:66
Hongkachok C, Boontanon SK, Boontanon N, Fujii S, Tanaka S, Suzuki Y (2018) Levels of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in groundwater around improper municipal and industrial waste disposal sites in Thailand and health risk assessment. Water Sci Technol 2017:457–466
Ikkere LE, Perkons I, Sire J, Pugajeva I, Bartkevics V (2018) Occurrence of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, perfluorinated compounds, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in freshwater mussels from Latvia. Chemosphere 213:507–516
Jin H, Zhang Y, Zhu L, Martin JW (2015) Isomer profiles of perfluoroalkyl substances in water and soil surrounding a Chinese fluorochemical manufacturing park. Environ Sci Technol 49:4946–4954
Knutsen H, Maehlum T, Haarstad K, Slinde GA, Arp HPH (2019) Leachate emissions of short- and long-chain per- and polyfluoralkyl substances (PFASs) from various Norwegian landfills. Environ Sci Process Impacts 21:1970–1979
Lapworth DJ, Gooddy DC, Allen D, Old GH (2009) Understanding groundwater, surface water, and hyporheic zone biogeochemical processes in a Chalk catchment using fluorescence properties of dissolved and colloidal organic matter. J Geophys Res 114:G00F02. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009jg000921
Lee JW, Lee HK, Lim JE, Moon HB (2020) Legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the coastal environment of Korea: occurrence, spatial distribution, and bioaccumulation potential. Chemosphere 251:126633
Lee YM, Lee JY, Kim MK, Yang H, Lee JE, Son Y, Kho Y, Choi K, Zoh KD (2020) Concentration and distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the Asan Lake area of South Korea. J Hazard Mater 381:120909
Li X, Shang X, Luo T, Du X, Wang Y, Xie Q, Matsuura N, Chen J, Kadokami K (2016) Screening and health risk of organic micropollutants in rural groundwater of Liaodong Peninsula, China. Environ Pollut 218:739–748
Li P, Oyang X, Zhao Y, Tu T, Tian X, Li L, Zhao Y, Li J, Xiao Z (2019) Occurrence of perfluorinated compounds in agricultural environment, vegetables, and fruits in regions influenced by a fluorine-chemical industrial park in China. Chemosphere 225:659–667
Li BB, Hu LX, Yang YY, Wang TT, Liu C, Ying GG (2020a) Contamination profiles and health risks of PFASs in groundwater of the Maozhou River basin. Environ Pollut 260:113996
Li X, Tian T, Shang X, Zhang R, Xie H, Wang X, Wang H, Xie Q, Chen J, Kadokami K (2020b) Occurrence and health risks of organic micro-pollutants and metals in groundwater of Chinese rural areas. Environ Health Perspect 128:107010
Li Y, Barregard L, Xu Y, Scott K, Pineda D, Lindh CH, Jakobsson K, Fletcher T (2020c) Associations between perfluoroalkyl substances and serum lipids in a Swedish adult population with contaminated drinking water. Environ Health 19:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-020-00588-9
Lindstrom AB, Strynar MJ, Delinsky AD, Nakayama SF, McMillan L, Libelo EL, Neill M, Thomas L (2011) Application of WWTP biosolids and resulting perfluorinated compound contamination of surface and well water in Decatur, Alabama, USA. Environ Sci Technol 45:8015–8021
Lu Z, Lu R, Zheng H, Yan J, Song L, Wang J, Yang H, Cai M (2018) Risk exposure assessment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in drinking water and atmosphere in central eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:9311–9320
Ma X, Shan G, Chen M, Zhao J, Zhu L (2018) Riverine inputs and source tracing of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in Taihu Lake, China. Sci Total Environ 612:18–25
Miranda DA, Benskin JP, Awad R, Lepoint G, Leonel J, Hatje V (2021) Bioaccumulation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in a tropical estuarine food web. Sci Total Environ 754:142146
Naile JE, Khim JS, Hong S, Park J, Kwon BO, Ryu JS, Hwang JH, Jones PD, Giesy JP (2013) Distributions and bioconcentration characteristics of perfluorinated compounds in environmental samples collected from the west coast of Korea. Chemosphere 90:387–394
Nascimento RA, Nunoo DBO, Bizkarguenaga E, Schultes L, Zabaleta I, Benskin JP, Spanó S, Leonel J (2018) Sulfluramid use in Brazilian agriculture: a source of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) to the environment. Environ Pollut 242:1436–1443
Ojemaye CY, Petrik L (2019) Occurrences, levels and risk assessment studies of emerging pollutants (pharmaceuticals, perfluoroalkyl and endocrine disrupting compounds) in fish samples from Kalk Bay harbour, South Africa. Environ Pollut 252:562–572
Pan CG, Yu KF, Wang YH, Zhang W, Zhang J, Guo J (2019) Perfluoroalkyl substances in the riverine and coastal water of the Beibu Gulf, South China: spatiotemporal distribution and source identification. Sci Total Environ 660:297–305
Qi Y, Huo S, Hu S, Xi B, Su J, Tang Z (2016) Identification, characterization, and human health risk assessment of perfluorinated compounds in groundwater from a suburb of Tianjin. China. Environ Earth Sci 75(5):432–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5415-x
Shigei M, Ahrens L, Hazaymeh A, Dalahmeh SS (2020) Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water and soil in wastewater-irrigated farmland in Jordan. Sci Total Environ 716:137057
Ssebugere P, Sillanpaa M, Matovu H, Wang Z, Schramm KW, Omwoma S, Wanasolo W, Ngeno EC, Odongo S (2020) Environmental levels and human body burdens of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances in Africa: a critical review. Sci Total Environ 739:139913
Sun R, Wu M, Tang L, Li J, Qian Z, Han T, Xu G (2018) Perfluorinated compounds in surface waters of Shanghai, China: source analysis and risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 149:88–95
Thomaidi VS, Tsahouridou A, Matsoukas C, Stasinakis AS, Petreas M, Kalantzi OI (2020) Risk assessment of PFASs in drinking water using a probabilistic risk quotient methodology. Sci Total Environ 712:136485
Xie H, Chen J, Huang Y, Zhang R, Chen CE, Li X, Kadokami K (2020) Screening of 484 trace organic contaminants in coastal waters around the Liaodong Peninsula, China: occurrence, distribution, and ecological risk. Environ Pollut 267:115436
Xie LN, Wang XC, Dong XJ, Su LQ, Zhu HJ, Wang C, Zhang DP, Liu FY, Hou SS, Dong B, Shan GQ, Zhang X, Zhu Y (2021) Concentration, spatial distribution, and health risk assessment of PFASs in serum of teenagers, tap water and soil near a Chinese fluorochemical industrial plant. Environ Int 146:106166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106166
Xu C, Liu Z, Song X, Ding X, Ding D (2021) Legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in multi-media around a landfill in China: implications for the usage of PFASs alternatives. Sci Total Environ 751:141767
Yang L, Zhu L, Liu Z (2011) Occurrence and partition of perfluorinated compounds in water and sediment from Liao River and Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere 83:806–814
Zhang DQ, Wang M, He Q, Niu X, Liang Y (2020) Distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in aquatic plant-based systems: from soil adsorption and plant uptake to effects on microbial community. Environ Pollut 257:113575
Zhao YG, Wan HT, Law AY, Wei X, Huang YQ, Giesy JP, Wong MH, Wong CK (2011) Risk assessment for human consumption of perfluorinated compound-contaminated freshwater and marine fish from Hong Kong and Xiamen. Chemosphere 85:277–283
Zhao Z, Cheng X, Hua X, Jiang B, Tian C, Tang J, Li Q, Sun H, Lin T, Liao Y, Zhang G (2020) Emerging and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water, sediment, and air of the Bohai Sea and its surrounding rivers. Environ Pollut 263:114391
Zheng P, Liu M, Yin H, Shen L, Wang Y, Wu Q (2020) Analysis of 58 poly-/perfluoroalkyl substances and their occurrence in surface water in a high-technology industrial park. Environ Pollut 267:115381
Funding
This work was supported by Liaoning BaiQianWan Talents Program (2021921100) and Integration of ecosystem restoration and management technologies and demonstration of ecological industry development in northwest Liaoning Province (2020JH1/10300006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors made contributions to the study conception and design. J. X. T. conceived of the experiment and drafted the manuscripts, Y. L. Z. conducted the experiment, collected samples and drafted the manuscripts, Y. L., B. X., and T. T. collected the samples and conducted the experiment. Q. L. and L. Y. L. tested all the samples. All the authors reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Roland Peter Kallenborn
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Zhu, Y., Li, Y. et al. Occurrence characteristics and health risk assessment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances from water in residential areas around fluorine chemical industrial areas, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 60733–60743 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20155-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20155-8