Abstract
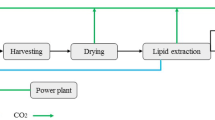
Recently, with efficient methods of cultivating microalgae at hand, researchers and investors have paid considerable attention to the production of different environmentally friendly biofuel products. In this study, a two-stage deterministic model is proposed to design a microalgae-based biofuel and co-product supply chain network (MBCSCN). In the first stage, appropriate locations to cultivate microalgae are identified through the analytical hierarchy process (AHP). In the second stage, a deterministic mathematical mixed integer linear programming (MILP) model is developed for a period of 5 years based on economic and environmental impacts as two criteria. The economic objective function maximizes the overall profit, while the objective function of the environmental impacts seeks to minimize fossil fuel consumption throughout the supply chain. Then, a multi-objective MILP optimization problem is solved using the ε-constraint method. The proposed model is evaluated through a case study in Iran. It has helped to identify appropriate locations for the cultivation of microalgae and to specify the required quantity of feedstock, the species of microalgae, the required technology, and the transportation modes in each step of the supply chain.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files
Notes
Iranian Rial currency
Qeshm Microalgae Bio-refinery (QMAB)
References
Adeniyi OM, Azimov U, Burluka A (2018) Algae biofuel: current status and future applications. Renew Sust Energ Rev 90:316–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.03.067
Adenle AA, Haslam GE, Lee L (2013) Global assessment of research and development for algae biofuel production and its potential role for sustainable development in developing countries. Energy Policy 61:182–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2013.05.088
Ahn Y-C, Lee I-B, Lee K-H, Han J-H (2015) Strategic planning design of microalgae biomass-to-biodiesel supply chain network: multi-period deterministic model. Appl Energy 154:528–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2015.05.047
Akbarian-Saravi N, Mobini M, Rabbani M (2020) Development of a comprehensive decision support tool for strategic and tactical planning of a sustainable bioethanol supply chain: real case study, discussions and policy implications. J Clean Prod 244:11887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118871
Akgul O, Shah N, Papageorgiou LG (2012) An optimisation framework for a hybrid first/second generation bioethanol supply chain. Comput Chem Eng 42:101–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2012.01.012
Aliyu A, Lee J, Harvey A (2021) Microalgae for biofuels via thermochemical conversion processes: a review of cultivation, harvesting and drying processes, and the associated opportunities for integrated production. Bioresour Technol Rep:100676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2021.100676
An H, Wilhelm WE, Searcy SW (2011) A mathematical model to design a lignocellulosic biofuel supply chain system with a case study based on a region in Central Texas. Bioresour Technol 102:7860–7870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.05.060
Andrade DS, Telles TS, Castro GHL (2020) The Brazilian microalgae production chain and alternatives for its consolidation. J Clean Prod 250:119526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119526
Arabi M, Yaghoubi S, Tajik J (2019a) Algal biofuel supply chain network design with variable demand under alternative fuel price uncertainty: a case study. Comput Chem Eng 130:106528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2019.106528
Arabi M, Yaghoubi S, Tajik J (2019b) A mathematical model for microalgae-based biobutanol supply chain network design under harvesting and drying uncertainties. Energy J 179:1004–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.04.219
Asadi E, Habibi F, Nickel S, Sahebi H (2018) A bi-objective stochastic location-inventory-routing model for microalgae-based biofuel supply chain. Appl Energy 228:2235–2261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.07.067
Babazadeh R, Razmi J, Rabbani M, Pishvaee MS (2015) An integrated data envelopment analysis–mathematical programming approach to strategic biodiesel supply chain network design problem. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.09.038
Babazadeh R, Ghaderi H, Pishvaee MS (2019) A benders-local branching algorithm for second-generation biodiesel supply chain network design under epistemic uncertainty. Comput Chem Eng 124:364–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2019.01.013
Bahadar A, Khan MB (2013) Progress in energy from microalgae: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 27:128–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.06.029
Bai Y, Ouyang Y, Pang J-S (2012) Biofuel supply chain design under competitive agricultural land use and feedstock market equilibrium. Energy Econ 34:1623–1633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2012.01.003
Balaman ŞY, Selim H (2014) A network design model for biomass to energy supply chains with anaerobic digestion systems. Appl Energy 130:289–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.05.043
Barros AI, Gonçalves AL, Simões M, Pires JC (2015) Harvesting techniques applied to microalgae: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 41:1489–1500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.09.037
Barry A, Wolfe A, English C, Ruddick C, Lambert D (2016) 2016 National Algal Biofuels Technology Review, USDOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE). Bioenergy
Beiki H, Seyedhosseini SM, Mihardjo LW, Seyedaliakbar SM (2021) Multiobjective location-routing problem of relief commodities with reliability. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11891-w
Branke J, Deb K, Miettinen K, Slowiński R (2008) Multiobjective optimization: interactive and evolutionary approaches. Springer
Branyikova I, Prochazkova G, Potocar T, Jezkova Z, Branyik T (2018) Harvesting of microalgae by flocculation. Fermentation 4:93. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation4040093
Chen G, Zhao L, Qi Y (2015) Enhancing the productivity of microalgae cultivated in wastewater toward biofuel production: a critical review. Appl Energy 137:282–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.10.032
Chisti Y (2013) Constraints to commercialization of algal fuels. J Biotechnol 167:201–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2013.07.020
Chu R, Li S, Zhu L, Yin Z, Hu D, Liu C, Mo F (2021) A review on co-cultivation of microalgae with filamentous fungi: efficient harvesting, wastewater treatment and biofuel production. Renew Sust Energ Rev 139:110689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110689
Coleman AM, Abodeely JM, Skaggs RL, Moeglein WA, Newby DT, Venteris ER, Wigmosta MS (2014) An integrated assessment of location-dependent scaling for microalgae biofuel production facilities. Algal Res 5:79–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2014.05.008
Davis R, Aden A, Pienkos PT (2011) Techno-economic analysis of autotrophic microalgae for fuel production. Appl Energy 88:3524–3531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.04.018
Efroymson RA, Jager HI, Mandal S, Parish ES, Mathews TJ (2020) Better management practices for environmentally sustainable production of microalgae and algal biofuels. J Clean Prod:125150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125150
Fallahpour A, Nayeri S, Sheikhalishahi M, Wong KY, Tian G, Fathollahi-Fard AM (2021) A hyper-hybrid fuzzy decision-making framework for the sustainable-resilient supplier selection problem: a case study of Malaysian Palm oil industry. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12491-y
Fathollahi-Fard AM, Ahmadi A, Al-e-Hashem SM (2020) Sustainable closed-loop supply chain network for an integrated water supply and wastewater collection system under uncertainty. J Environ Manag 275:111277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111277
Ghaderi H, Moini A, Pishvaee MS (2018) A multi-objective robust possibilistic programming approach to sustainable switchgrass-based bioethanol supply chain network design. J Clean Prod 179:368–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.218
Ghosh T, Bakshi BR (2019) Designing biofuel supply chains while mitigating harmful algal blooms with treatment wetlands. Comput Chem Eng 126:113–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2019.03.041
Golmohammadi A-M, Honarvar M, Hosseini-Nasab H, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2020) A bi-objective optimization model for a dynamic cell formation integrated with machine and cell layouts in a fuzzy environment. Fuzzy Inf Eng:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/16168658.2020.1747162
Gong J, You F (2015) An efficient global optimization algorithm for mixed-integer nonlinear fractional programs with separable concave terms, American Control Conference (ACC), 2015. IEEE, pp 547-552
Gutiérrez-Arriaga CG, Serna-González M, Ponce-Ortega JM, El-Halwagi MM (2014) Sustainable integration of algal biodiesel production with steam electric power plants for greenhouse gas mitigation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:1388–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc400436a
Hadian H, Chahardoli S, Golmohammadi A-M, Mostafaeipour A (2020) A practical framework for supplier selection decisions with an application to the automotive sector. Int J Prod Res 58:2997–3014. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2019.1624854
Hosseinalizadeh R, Khamseh AA, Akhlaghi MM (2019) A multi-objective and multi-period model to design a strategic development program for biodiesel fuels. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 36:100545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2019.100545
Idrees M (2014) Making biofuels from microalgae-a review of technologies. J Food Sci Technol 1:007–014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.10.009
Ismail MM, Ismail GA, El-Sheekh MM (2020) Potential assessment of some micro-and macroalgal species for bioethanol and biodiesel production. Energ Source Part A:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1758853
Jian H, Jing Y, Peidong Z (2015) Life cycle analysis on fossil energy ratio of algal biodiesel: effects of nitrogen deficiency and oil extraction technology. Sci World J 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/920968
Karimi SK, Naini SGJ, Sadjadi SJ (2021) An integration of environmental awareness into flexible supply chains: a trade-off between costs and environmental pollution. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13454-z
Kim J, Yoo G, Lee H, Lim J, Kim K, Kim CW, Park MS, Yang J-W (2013) Methods of downstream processing for the production of biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 31:862–876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.04.006
Li Z, Xie C, Peng P, Gao X, Wan Q (2021) Multi-objective location-scale optimization model and solution methods for large-scale emergency rescue resources. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12753-9
Mahjoub N, Sahebi H, Mazdeh M, Teymouri A (2020) Optimal design of the second and third generation biofuel supply network by a multi-objective model. J Clean Prod 256:120355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120355
Mata TM, Martins AA, Caetano NS (2010) Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14:217–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.07.020
Mavrotas G (2009) Effective implementation of the ε-constraint method in multi-objective mathematical programming problems. Appl Math Comput 213:455–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2009.03.037
Mohseni S, Pishvaee MS, Sahebi H (2016) Robust design and planning of microalgae biomass-to-biodiesel supply chain: a case study in Iran. Energy J 111:736–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.06.025
Mohtashami Z, Aghsami A, Jolai F (2020) A green closed loop supply chain design using queuing system for reducing environmental impact and energy consumption. J Clean Prod 242:118452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118452
Mohtashami Z, Bozorgi-Amiri A, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2021) A two-stage multi-objective second generation biodiesel supply chain design considering social sustainability: A case study. Energy J:121020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121020
Mojtahedi M, Fathollahi-Fard AM, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Newton S (2021) Sustainable vehicle routing problem for coordinated solid waste management. J Ind Inf Integr 23:100220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jii.2021.100220
Najafi G, Ghobadian B, Yusaf TF (2011) Algae as a sustainable energy source for biofuel production in Iran: a case study. Renew Sust Energ Rev 15:3870–3876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.07.010
Nasr N, Niaki STA, Kashan AH, Seifbarghy M (2021) An efficient solution method for an agri-fresh food supply chain: hybridization of Lagrangian relaxation and genetic algorithm. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13718-8
Pahlevan SM, Hosseini SMS, Goli A (2021) Sustainable supply chain network design using products’ life cycle in the aluminum industry. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12150-8
Parsaeifar S, Bozorgi-Amiri A, Naimi-Sadigh A, Sangari MS (2019) A game theoretical for coordination of pricing, recycling, and green product decisions in the supply chain. J Clean Prod 226:37–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.343
Pokoo-Aikins G, Nadim A, El-Halwagi MM, Mahalec V (2010) Design and analysis of biodiesel production from algae grown through carbon sequestration. Clean Techn Environ Policy 12:239–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-009-0215-6
Quinn JC, Davis R (2015) The potentials and challenges of algae based biofuels: a review of the techno-economic, life cycle, and resource assessment modeling. Bioresour Technol 184:444–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.075
Rabbani M, Momen S, Akbarian-Saravi N, Farrokhi-Asl H, Ghelichi Z (2020) Optimal design for sustainable bioethanol supply chain considering the bioethanol production strategies: A case study. Comput Chem Eng 134:106720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2019.106720
Rahemi H, Torabi SA, Avami A, Jolai F (2020) Bioethanol supply chain network design considering land characteristics. Renew Sust Energ Rev 119:109517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109517
Rizwan M, Lee JH, Gani R (2013) Optimal processing pathway for the production of biodiesel from microalgal biomass: a superstructure based approach. Comput Chem Eng 58:305–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2013.08.002
Salomon V (2018) Multi-criteria methods and techniques applied to supply chain management. BoD–Books on Demand
Shabbir MS, Mahmood A, Setiawan R, Nasirin C, Rusdiyanto R, Gazali G, Arshad MA, Khan S, Batool F (2021) Closed-loop supply chain network design with sustainability and resiliency criteria. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12980-0
Sharma B, Brandes E, Khanchi A, Birrell S, Heaton E, Miguez F (2015) Evaluation of microalgae biofuel production potential and cultivation sites using geographic information systems: a review. Bioenergy Res 8:1714–1734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-015-9623-0
Shi R, Handler RM, Shonnard DR (2019) Life cycle assessment of novel technologies for algae harvesting and oil extraction in the renewable diesel pathway. Algal Res 37:248–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2018.12.005
Slade R, Bauen A (2013) Micro-algae cultivation for biofuels: cost, energy balance, environmental impacts and future prospects. Biomass Bioenergy 53:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.12.019
Sun L, Jin Y, Shen J, You F (2021) Sustainable residential micro-cogeneration system based on a fuel cell using dynamic programming-based economic day-ahead scheduling. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 9:3258–3266. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c08725
Tzeng G-H, Huang J-J (2011) Multiple attribute decision making: methods and applications, p CRC Press
Van Boxtel A, Perez-Lopez P, Breitmayer E, Slegers P (2015) The potential of optimized process design to advance LCA performance of algae production systems. Appl Energy 154:1122–1127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.01.036
Zhang L (2013) Biofuel supply chain and bottom-up market equilibrium model for production and policy analysis
Zhang K, Zhang F, Wu Y-R (2021) Emerging technologies for conversion of sustainable algal biomass into value-added products: a state-of-the-art review. Sci Total Environ:147024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147024
Zhou W, Chen P, Min M, Ma X, Wang J, Griffith R, Hussain F, Peng P, Xie Q, Li Y (2014) Environment-enhancing algal biofuel production using wastewaters. Renew Sust Energ Rev 36:256–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.04.073
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study conception and design, data collection, analysis, and writing of the first draft were performed by MEZ. The critical reviews, commentaries, and revision of the translations were performed by ABA. The validation of the data, verification of the research outputs, critical reviews, commentaries, and revision of the translations were performed by AMG. FJ commented on the final version of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zerafati, M.E., Bozorgi-Amiri, A., Golmohammadi, AM. et al. A multi-objective mixed integer linear programming model proposed to optimize a supply chain network for microalgae-based biofuels and co-products: a case study in Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19465-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19465-8