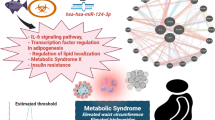
Abstract
A scarcity of research assesses the effects of exposure to a combination of chemicals on lipid profiles as well as molecular mechanisms related to dyslipidemia. A cross-sectional study of 3692 adults aims to identify the association between chemical mixtures, including blood and urine 26 chemicals, and lipid profiles among Korean adults (aged ≥ 18) using linear regression models, weighted quantile sum (WQS) regression, quantile g-computation (qgcomp), and Bayesian kernel machine regression (BKMR). In silico toxicogenomic data-mining, we assessed molecular mechanisms linked with dyslipidemia, including genes, miRNAs, pathways, biological processes, and diseases. In the linear regression models, heavy metals, volatile organic compound metabolites, and phthalate metabolites were found to be related to HDL-C, triglycerides, LDL-C, total lipids, and total cholesterol, and significant trends were observed for these chemical quartiles (p < 0.01). The WQS index was significantly linked with HDL-C, triglycerides, LDL-C, total cholesterol, and total lipids. The qgcomp index also found a significant association between chemicals and HDL-C, triglycerides, and total lipids. In BKMR analysis, the overall effect of the chemical mixture was significantly associated with HDL-C, triglycerides, total cholesterol, and total lipids. We found that mixed chemicals interacted with the PPARA gene and were linked with dyslipidemia. Several pathways (“SREBF and miR33 in cholesterol,” “estrogen receptor pathway and lipid homeostasis,” and “regulation of PGC-1α”), “negative regulation of hepatocyte apoptotic process,” “negative regulation of sequestering of triglycerides,” “regulation of hepatocyte apoptotic process,” and “negative regulation of cholesterol storage,” and “abdominal obesity metabolic syndrome” were identified as key molecular mechanisms that may be affected by mixed chemicals and implicated in the development of dyslipidemia. The highest interaction and expression of miRNAs involved in the process of dyslipidemia were also described. Especially, the cutoff levels for chemical exposure levels related to lipid profiles were also provided.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets examined during this study are available on request at the National Institute of Environmental Research, Environmental Health Research Department, http://www.nier.go.kr/NIER/kor/openapi/getEcoHealth.do?menuNo=14018.
Abbreviations
- MEHHP:
-
Mono-(2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexyl) phthalate
- MEOHP:
-
Mono-(2-ethyl-5-oxohexyl) phthalate
- MnBP:
-
Mono-n-butyl phthalate
- MBzP:
-
Mono-benzyl phthalate
- MECPP:
-
Mono-(2-ethyl-5-carboxypentyl) phthalate
- MCOP:
-
Mono-carboxyoctyl phthalate
- MCNP:
-
Mono-carboxy-isononyl phthalate
- MCPP:
-
Mono (3-carboxypropyl) phthalate
- ttMA:
-
t,t-Muconic acid
- BMA:
-
Benzylmercapturic acid
- 1OHP:
-
1-Hydroxypyrene
- 2NAP:
-
2-Naphthol
- 2OHFlu:
-
2-Hydroxyfluorene
- 1OHPhe:
-
1-Hydroxyphenanthrene
- BPA:
-
Bisphenol A
- BPF:
-
Bisphenol F
- BPS:
-
Bisphenol S
- TCS:
-
Triclosan
- MeP:
-
Methylparaben
- EtP:
-
Ethylparaben
- PrP:
-
Propylparaben
- 3PBA:
-
3-Phenoxybenzoic acid
- COT:
-
Cotinine
- BPb:
-
Blood lead
- BHg:
-
Blood mercury
- UHg:
-
Urine mercury
- UCd:
-
Urine cadmium
- EDCs:
-
Endocrine disrupting chemicals
- VOCs:
-
Volatile organic compounds
- PAH:
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
- BKMR:
-
Bayesian kernel machine regression
- QWS:
-
Weighted quantile sum
- Qgcomp:
-
Quantile g-computation
References
Andra SS, Makris KC (2012) Thyroid disrupting chemicals in plastic additives and thyroid health. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev 30:107–151
Ayotte P, Carrier A, Ouellet N, Boiteau V, Abdous B, Sidi EA, Château-Degat ML, Dewailly É (2011) Relation between methylmercury exposure and plasma paraoxonase activity in Inuit adults from Nunavik. Environ Health Perspect 119:1077–1083
Barbalata T, Zhang L, Dulceanu MD, Stancu CS, Devaux Y, Sima AV, Niculescu LS, CA EU-CCA. (2020) Regulation of microRNAs in high-fat diet induced hyperlipidemic hamsters. Sci Rep 10:20549
Becker K, Kaus S, Krause C, Lepom P, Schulz C, Seiwert M, Seifert B (2002) German Environmental Survey 1998 (GerES III): environmental pollutants in blood of the German population. Int J Hyg Environ Health 205:297–308
Bobb JF, Valeri L, Claus Henn B, Christiani DC, Wright RO, Mazumdar M, Godleski JJ, Coull BA (2015) Bayesian kernel machine regression for estimating the health effects of multi-pollutant mixtures. Biostatistics 16:493–508
Boucher JG, Ahmed S, Atlas E (2016) Bisphenol S Induces Adipogenesis in Primary Human Preadipocytes From Female Donors. Endocrinology 157:1397–1407
Bui TT, Giovanoulis G, Cousins AP, Magnér J, Cousins IT, de Wit CAJSotte. (2016) Human exposure, hazard and risk of alternative plasticizers to phthalate esters. Sci Total Environ 541:451–67
Buser MC, Murray HE, Scinicariello F (2014) Age and sex differences in childhood and adulthood obesity association with phthalates: analyses of NHANES 2007–2010. Int J Hyg Environ Health 217:687–694
Canada H (2010) Report on human biomonitoring of environmental chemicals in Canada. Results of the Canadian Health Measures Survey Cycle 1 (2007–2009). Book Report on human biomonitoring of environmental chemicals in Canada. Results of the Canadian Health Measures Survey Cycle 1 (2007–2009), City: Health Canada Ottawa, Ontario
Carrico C, Gennings C, Wheeler DC, Factor-Litvak P (2015) Characterization of weighted quantile sum regression for highly correlated data in a risk analysis setting. J Agric Biol Environ Stat 20:100–120
Carvalho CM, Chew EH, Hashemy SI, Lu J, Holmgren A (2008) Inhibition of the human thioredoxin system. A molecular mechanism of mercury toxicity. J Biol Chem 283:11913–23
Coker E, Chevrier J, Rauch S, Bradman A, Obida M, Crause M, Bornman R, Eskenazi B (2018) Association between prenatal exposure to multiple insecticides and child body weight and body composition in the VHEMBE South African birth cohort. Environ Int 113:122–132
Cozzolino R, De Giulio B, Marena P, Martignetti A, Günther K, Lauria F, Russo P, Stocchero M, Siani A (2017) Urinary volatile organic compounds in overweight compared to normal-weight children: results from the Italian I.Family cohort. Sci Rep 7:15636
Dong R, Zhou T, Chen J, Zhang M, Zhang H, Wu M, Li S, Zhang L (2017) Gender-and age-specific relationships between phthalate exposures and obesity in Shanghai adults. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 73:431–441
Duc HN, Oh H, Kim MS (2021b) Effects of antioxidant vitamins, curry consumption, and heavy metal levels on metabolic syndrome with comorbidities: A Korean community-based cross-sectional study. Antioxidants (basel) 10:808
Duc HN, Oh H, Yoon IM, Kim M-S (2021) Association between levels of thiamine intake, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and depression in Korea: a national cross-sectional study. J Nutri Sci 10:e31
Duc HN, Oh H, Kim M-S (2022) Association between exposure to chemical mixtures in relation to serum total IgE among adults 19–86 years old. Int Immunopharmacol 102:108428
Duc HN, Oh H, Kim M-S. (2021) The effect of mixture of heavy metals on obesity in individuals ≥50 years of age. Biol Trace Elem Research
El-Demerdash FM (2011) Lipid peroxidation, oxidative stress and acetylcholinesterase in rat brain exposed to organophosphate and pyrethroid insecticides. Food Chem Toxicol 49:1346–1352
Garey J, Wolff MSJB (1998) Estrogenic and antiprogestagenic activities of pyrethroid insecticides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 251:855–859
Grotto D, de Castro MM, Barcelos GR, Garcia SC, Barbosa F Jr (2009) Low level and sub-chronic exposure to methylmercury induces hypertension in rats: nitric oxide depletion and oxidative damage as possible mechanisms. Arch Toxicol 83:653–662
Gupta R, Kumar P, Fahmi N, Garg B, Dutta S, Sachar S, Matharu AS, Vimaleswaran KS (2020) Endocrine disruption and obesity: a current review on environmental obesogens. Curr Res Green Sustain Chem 3:100009
Hao C, Cheng X, Xia H, Ma X (2012) The endocrine disruptor mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate promotes adipocyte differentiation and induces obesity in mice. Biosci Rep 32:619–629
Heindel JJ, Blumberg B, Cave M, Machtinger R, Mantovani A, Mendez MA, Nadal A, Palanza P, Panzica G, Sargis R et al (2017) Metabolism disrupting chemicals and metabolic disorders. Reprod Toxicol 68:3–33
Hellerstein MK, Benowitz NL, Neese RA, Schwartz JM, Hoh R, Jacob P 3rd, Hsieh J, Faix D (1994) Effects of cigarette smoking and its cessation on lipid metabolism and energy expenditure in heavy smokers. J Clin Invest 93:265–72
Houston MC (2011) Role of mercury toxicity in hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and stroke. J Clin Hypertens (greenwich) 13:621–627
Howe CG, Margetaki K, Vafeiadi M, Roumeliotaki T, Karachaliou M, Kogevinas M, McConnell R, Eckel SP, Conti DV, Kippler M et al (2021) Prenatal metal mixtures and child blood pressure in the Rhea mother-child cohort in Greece. Environ Health 20:1
Ibhazehiebo K, Koibuchi N (2011) Thyroid hormone receptor-mediated transcription is suppressed by low dose phthalate. Niger J Physiol Sci 26:143–149
Janesick A, Blumberg B (2011) Minireview: PPARγ as the target of obesogens. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 127:4–8
Jia Z, Zhang H, Ong CN, Patra A, Lu Y, Lim CT, Venkatesan T (2018) Detection of lung cancer: concomitant volatile organic compounds and metabolomic profiling of six cancer cell lines of different histological origins. ACS Omega 3:5131–5140
Jiang WC, Wu SY, Ke YB (2016) Association of exposure to environmental chemicals with risk of childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 50:893–899
Jiang Y, Wang W, Liu Z-Y, Xie Y, Qian Y, Cai X-N (2018) Overexpression of miR-130a-3p/301a-3p attenuates high glucose-induced MPC5 podocyte dysfunction through suppression of TNF-α signaling. Exp Ther Med 15:1021–1028
Kang Y, Park J, Youn K (2019) Association between urinary phthalate metabolites and obesity in adult Korean population: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS), 2012–2014. Ann Occup Environ Med 31:1132937
Keil AP, Buckley JP, O’Brien KM, Ferguson KK, Zhao S, White AJ (2020) A quantile-based g-computation approach to addressing the effects of exposure mixtures. Environ Health Perspect 128:047004
Khan MA, Wang F (2009) Mercury-selenium compounds and their toxicological significance: toward a molecular understanding of the mercury-selenium antagonism. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1567–1577
Kim J, Lee K (2020) Changes in urinary cotinine concentrations in non-smoking adults from the Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) II (2012–2014) after implementation of partial smoke-free regulations. Int J Hyg Environ Health 224:113419
Kojima M, Nemoto K, Murai U, Yoshimura N, Ayabe Y, Degawa MJAot. (2002) Altered gene expression of hepatic lanosterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51) in lead nitrate-treated rats. Arch Toxicol 76:398–403
Lang AL, Beier JI (2018) Interaction of volatile organic compounds and underlying liver disease: a new paradigm for risk. J Biol Chem 399:1237–1248
Le Magueresse-Battistoni B, Labaronne E, Vidal H, Naville D (2017) Endocrine disrupting chemicals in mixture and obesity, diabetes and related metabolic disorders. World J Biol Chem 8:108–119
Lee I, Park YJ, Kim MJ, Kim S, Choi S, Park J, Cho YH, Hong S, Yoo J, Park H et al (2021) Associations of urinary concentrations of phthalate metabolites, bisphenol A, and parabens with obesity and diabetes mellitus in a Korean adult population: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) 2015–2017. Environ Int 146:106227
Li N, Wang D, Zhou Y, Ma M, Li J, Wang Z (2010) Dibutyl phthalate contributes to the thyroid receptor antagonistic activity in drinking water processes. Environ Sci Technol 44:6863–6868
Li F, Xiang B, Jin Y, Li C, Li J, Ren S, Huang H, Luo Q (2019) Dysregulation of lipid metabolism induced by airway exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in C57BL/6 mice. Environ Pollut 245:986–93
Li R, Yang S, Gao R, Deng Y, Liu J, Yuan C, Yao Q, Lv X, Wang K, Ye X et al (2020) RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE ENVIRONMENTAL ENDOCRINE DISRUPTOR BISPHENOL A AND DYSLIPIDEMIA: A FIVE-YEAR PROSPECTIVE STUDY. Endocr Pract 26:399–406
Licursi V, Conte F, Fiscon G, Paci P (2019) MIENTURNET: an interactive web tool for microRNA-target enrichment and network-based analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 20:545
Liu B, Lehmler H-J, Sun Y, Xu G, Liu Y, Zong G, Sun Q, Hu FB, Wallace RB, Bao W (2017) Bisphenol A substitutes and obesity in US adults: analysis of a population-based, cross-sectional study. Lancet Planet Health 1:e114–e122
Lopez S, Bermudez B, Montserrat-de la Paz S, Abia R, Muriana FJG (2018) A microRNA expression signature of the postprandial state in response to a high-saturated-fat challenge. J Nutr Biochem 57:45–55
Loughery JR, Kidd KA, Mercer A, Martyniuk CJ (2018) Part A: temporal and dose-dependent transcriptional responses in the liver of fathead minnows following short term exposure to the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon phenanthrene. Aquat Toxicol 199:90–102
Luo G, Hu S, Lai T, Wang J, Wang L, Lai S (2020) MiR-9-5p promotes rabbit preadipocyte differentiation by suppressing leptin gene expression. Lipids Health Dis 19:126
Ma J, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Xiao L, Cen X, Li W, Guo Y, Kim M, Yuan J, Chen W (2019) Association between urinary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolites and dyslipidemias in the Chinese general population: a cross-sectional study. Environ Pollut 245:89–97
Marill KA (2004) Advanced statistics: linear regression, part II: multiple linear regression. Acad Emerg Med 11:94–102
Meng Z, Wang D, Liu W, Li R, Yan S, Jia M, Zhang L, Zhou Z, Zhu W (2019) Perinatal exposure to Bisphenol S (BPS) promotes obesity development by interfering with lipid and glucose metabolism in male mouse offspring. Environ Res 173:189–198
National Institute of Environmental Research SK. (2015) Research development and planning for Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) (III). Book Research development and planning for Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) (III), City
Nguyen HD, Kim MS (2021) Effects of heavy metal, vitamin, and curry consumption on metabolic syndrome during menopause: a Korean community-based cross-sectional study. J Menopause 28:949–959
Nguyen HD, Oh H, Hoang NHM, Jo WH, Kim MS (2021) Environmental science and pollution research role of heavy metal concentrations and vitamin intake from food in depression: a national cross-sectional study (2009–2017). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:1–13
Nguyen HD, Oh H, Hoang NHM, Kim M-S (2021b) Association between heavy metals, high-sensitivity C-reaction protein and 10-year risk of cardiovascular diseases among adult Korean population. Sci Rep 11:14664
Nguyen HD, Oh H, Kim MS (2021) Effects of heavy metals on hypertension during menopause: a Korean community-based cross-sectional study. Menopause 28:1400–1409
Nguyen HD, Oh H, Kim M-S (2022) Mixtures modeling identifies vitamin B1 and B3 intakes associated with depression. J Affect Disord 301:68–80
Nguyen HD, Oh H, Jo WH, Hoang NHM, Kim MS. (2021) Mixtures modeling identifies heavy metals and pyrethroid insecticide metabolites associated with obesity. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int
Nishino T, Horie T, Baba O, Sowa N, Hanada R, Kuwabara Y, Nakao T, Nishiga M, Nishi H, Nakashima Y et al (2018) SREBF1 MicroRNA-33b axis exhibits potent effect on unstable atherosclerotic plaque formation in vivo. ATVB 38:2460–73
Organization WH. (2021) Cardiovascular diseases. Book Cardiovascular diseases, City
Palmisano BT, Zhu L, Stafford JM (2017) Role of estrogens in the regulation of liver lipid metabolism. Adv Exp Med Biol 1043:227–256
Patel CJ, Cullen MR, Ioannidis JP, Butte AJ (2012) Systematic evaluation of environmental factors: persistent pollutants and nutrients correlated with serum lipid levels. Int J Epidemiol 41:828–843
Pollack AZ, Sjaarda L, Ahrens KA, Mumford SL, Browne RW, Wactawski-Wende J, Schisterman EF (2014) Association of cadmium, lead and mercury with paraoxonase 1 activity in women. PLoS One 9:e92152
Rager JE, Clark J, Eaves LA, Avula V, Niehoff NM, Kim YH, Jaspers I, Gilmour MI (2021) Mixtures modeling identifies chemical inducers versus repressors of toxicity associated with wildfire smoke. Sci Total Environ 775:145759
Ranjbar M, Rotondi MA, Ardern CI, Kuk JL (2015) Urinary biomarkers of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are associated with cardiometabolic health risk. PLoS One 10:e0137536
Rao ChS, Subash YE (2013) The effect of chronic tobacco smoking and chewing on the lipid profile. J Clin Diagn Res 7:31–34
Renzetti S, Curtin P, Just A, Gennings C (2016) Gwqs: generalized weighted quantile sum regression. 1
Ribeiro CM, Beserra BTS, Silva NG, Lima CL, Rocha PRS, Coelho MS, Neves FdAR, Amato AA (2020) Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals and anthropometric measures of obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 10:e033509
Rochester JR, Bolden AL (2015) Bisphenol S and F: A systematic review and comparison of the hormonal activity of bisphenol a substitutes. Environ Health Perspect 123:643–650
Rupprecht LE, Smith TT, Donny EC, Sved AF (2017) Self-administered nicotine differentially impacts body weight gain in obesity-prone and obesity-resistant rats. Physiol Behav 176:71–75
Scinicariello F, Buser MC (2014) Urinary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and childhood obesity: NHANES (2001–2006). Environ Health Perspect 122:299–303
Sedgeman LR, Michell DL, Vickers KC (2019) Integrative roles of microRNAs in lipid metabolism and dyslipidemia. Curr Opin Lipidol 30:165–171
Shen O, Du G, Sun H, Wu W, Jiang Y, Song L, Wang X (2009) Comparison of in vitro hormone activities of selected phthalates using reporter gene assays. Toxicol Lett 191:9–14
Shih DM, Xia YR, Wang XP, Miller E, Castellani LW, Subbanagounder G, Cheroutre H, Faull KF, Berliner JA, Witztum JL et al (2000) Combined serum paraoxonase knockout/apolipoprotein E knockout mice exhibit increased lipoprotein oxidation and atherosclerosis. J Biol Chem 275:17527–17535
Shih Y-H, Howe CG, Scannell Bryan M, Shahriar M, Kibriya MG, Jasmine F, Sarwar G, Graziano JH, Persky VW, Jackson B et al (2021) Exposure to metal mixtures in relation to blood pressure among children 5–7 years old: An observational study in Bangladesh. Environ Epidemiol 5:e135
Shim YH, Ock JW, Kim Y-J, Kim Y, Kim SY, Kang D (2019) Association between heavy metals, bisphenol a, volatile organic compounds and phthalates and metabolic syndrome. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:671
Shrestha S, Mishra DR, Dhakal N, Bhandari S, Khanal S, Lamsal M (2019) Correlation of urinary cotinine with cardiovascular risk factors in pan masala tobacco users. Indian Heart J 71:459–463
Sohn SH, Heo HC, Jo S, Park C, Sakong J (2020) The association between mercury concentrations and lipid profiles in the Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) cycle 3. Ann Occup Environ Med 32:e19–e19
Stahr S, Chiang T-c, Bauer MA, Runnells GA, Rogers LJ, Do HV, Kadlubar SA, Su LJ (2021) Low-level environmental heavy metals are associated with obesity among postmenopausal women in a southern state. Expo Health 13:269–280
Steinberg D, Parthasarathy S, Carew TE, Khoo JC, Witztum JL (1989) Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med 320:915–24
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D, Hassoun E, Bagchi M (2001) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of chromium and cadmium ions. J Environ Pathol, Toxicol Oncol 20:12
Supruniuk E, Mikłosz A, Chabowski A (2017) The implication of PGC-1α on fatty acid transport across plasma and mitochondrial membranes in the insulin sensitive tissues. Front Physiol 8:923–1023
Tsiloulis T, Pike J, Powell D, Rossello FJ, Canny BJ, Meex RC, Watt MJ (2017) Impact of endurance exercise training on adipocyte microRNA expression in overweight men. Faseb j 31:161–171
van der Meer TP, van Faassen M, van Beek AP, Snieder H, Kema IP, Wolffenbuttel BHR, van Vliet-Ostaptchouk JV (2020) Exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals in the Dutch general population is associated with adiposity-related traits. Sci Rep 10:9311
Vom Saal FS, Nagel SC, Coe BL, Angle BM, Taylor JA (2012) The estrogenic endocrine disrupting chemical bisphenol A (BPA) and obesity. Molec Cell Endocrinol 354:74–84
Wang Q, Xu X, Zeng Z, Hylkema MN, Cai Z, Huo X (2020) PAH exposure is associated with enhanced risk for pediatric dyslipidemia through serum SOD reduction. Environ Int 145:106132
Xihua L, Shengjie T, Weiwei G, Matro E, Tingting T, Lin L, Fang W, Jiaqiang Z, Fenping Z, Hong L (2019) Circulating miR-143-3p inhibition protects against insulin resistance in Metabolic Syndrome via targeting of the insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor. Transl Res 205:33–43
Xu X, Cook RL, Ilacqua VA, Kan H, Talbott EO, Kearney G (2010) Studying associations between urinary metabolites of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and cardiovascular diseases in the United States. Sci Total Environ 408:4943–4948
Yaghjyan L, Sites S, Ruan Y, Chang SH (2015) Associations of urinary phthalates with body mass index, waist circumference and serum lipids among females: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2004. Int J Obes (lond) 39:994–1000
Ye X, Wong L-Y, Zhou X, Calafat AM (2014) Urinary concentrations of 2, 4-dichlorophenol and 2, 5-dichlorophenol in the US population (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2003–2010): trends and predictors. Environ Health Perspect 122:351–55
Yoo M, Lim Y-H, Kim T, Lee D, Hong Y-C (2016) Association between urinary 3-phenoxybenzoic acid and body mass index in Korean adults: 1st Korean National Environmental Health Survey. Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine 28:2
Zhang M, Sun W, Zhou M, Tang Y (2017) MicroRNA-27a regulates hepatic lipid metabolism and alleviates NAFLD via repressing FAS and SCD1. Sci Rep 7:14493
Zhang Y, Dong T, Hu W, Wang X, Xu B, Lin Z, Hofer T, Stefanoff P, Chen Y, Wang X et al (2019) Association between exposure to a mixture of phenols, pesticides, and phthalates and obesity: Comparison of three statistical models. Environ Int 123:325–336
Zhang J, Jazii FR, Haghighi MM, Alvares D, Liu L, Khosraviani N, Adeli K (2020) miR-130b is a potent stimulator of hepatic very-low-density lipoprotein assembly and secretion via marked induction of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Matabol 318:E262–E75
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to all research staff for their excellent contributions in data collection in the survey.
Funding
This work is supported by grants National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MEST) (grant nos. NRF2013R1A1A3008851, and 2018R1D1A1B07049610).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hai Duc Nguyen: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, visualization.
Min-Sun Kim: visualization, project administration, supervision.
Hojin Oh: visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All participants in KoNEHS provided written informed consent. The KoNEHS dataset has been de-identified and made publicly available. This survey was approved by the institutional review board of the NIER in Korea (NIER-2016-BR-003–01, NIER-2016-BR-003–03).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
- The combined effect of 26 chemicals on lipid profiles was identified.
- A mixture of chemical exposures was associated with the risk of dyslipidemia.
- HDL-C, TG, total cholesterol, and lipids were related to mixture of chemical exposure.
- Molecular mechanisms related to dyslipidemia were provided.
- The cutoff levels for chemical levels related to dyslipidemia were reported.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, H., Oh, H. & Kim, MS. The effects of chemical mixtures on lipid profiles in the Korean adult population: threshold and molecular mechanisms for dyslipidemia involved. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 39182–39208 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18871-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18871-2