Abstract
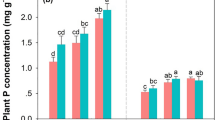
Climate warming changes the plant community composition and biodiversity. Dominate species or plant functional types (PFTs) loss may influence alpine ecosystem processes, but much uncertainty remains. This study tested whether loss of specific PFTs and vegetation variation would impact the metallic element release of mixed litter in an alpine treeline ecotone. Six representative PFTs in the alpine ecosystem on the eastern Tibetan Plateau were selected. Litterbags were used to determine the release of potassium, calcium, magnesium, sodium, manganese, zinc, copper, iron, and aluminum from litter loss of specific PFTs after 669 days of decomposition in coniferous forest (CF) and alpine shrubland (AS). The results showed that potassium, sodium, magnesium, and copper were net released, while aluminum, iron, and manganese were accumulated after 669 days. Functional type mixtures promoted the release of potassium, sodium, aluminum, and zinc (synergistic effect), while inhibiting the release of calcium, magnesium, and iron (antagonistic effect). Further, loss of specific plant functional type significantly affected the aluminum and iron release rates and the relatively mixed effects of the potassium, aluminum, and iron release rates. The synergistic effects on potassium, sodium, and aluminum in AS were greater than those in CF, while the antagonistic effect of manganese release in AS was lower than that in CF. Therefore, increased altitude may further promote the synergistic effect of potassium, sodium, and aluminum release and alleviate the antagonistic effect of manganese in mixed litter. Finally, the initial stoichiometric ratios regulate the mixed effects of elemental release rates, with the nitrogen-related stoichiometric ratios playing the most important role. The regulation of elements release by stoichiometric ratios requires more in-depth and systematic studies, which will help us to understand the influence mechanism of decomposition more comprehensively.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data is available on request to the corresponding author.
References
Adair EC, Parton WJ, Grosso S et al (2008) Simple three-pool model accurately describes patterns of long-term litter decomposition in diverse climates. Glob Change Biol 14(11):2636–2660. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2008.01674.x
Aerts R (2006) The freezer defrosting: global warming and litter decomposition rates in cold biomes. J Ecol 94(4):713–724. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2745.2006.01142.x
Aponte C, García LV, Maranón T (2012) Tree species effect on litter decomposition and nutrient release in Mediterranean oak forests changes over time. Ecosystems 15(7):1204–1218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-012-9577-4
Austin AT, Vivanco L (2006) Plant litter decomposition in a semi-arid ecosystem controlled by photo degradation. Nature 442:555–558. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05038
Baldy V, Gobert V, Guerold F et al (2007) Leaf litter breakdown budgets in streams of various trophic status: effects of dissolved inorganic nutrients on microorganisms and invertebrates. Freshw Biol 52:1322–1335. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2007.01768.x
Ball BA, Hunter MD, Kominoski JS et al (2008) Consequences of non-random species loss for decomposition dynamics: experimental evidence for additive and non-additive effects. J Ecol 96(2):303–313. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2745.2007.01346.x
Baptist F, Yoccoz NG, Choler P (2010) Direct and indirect control by snow cover over decomposition in alpine tundra along a snowmelt gradient. Plant Soil 328:397–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0119-6
Bardgett RD, van der Putten WH (2014) Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature 515(7528):505–511. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13855
Bardgett R, Wardle DA (2013) Aboveground-belowground linkages:biotic interactions, ecosystem processes, and global change. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 92(26):222–222. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011EO260011
Berg B, Davey MP, Marco AD et al (2010) Factors influencing limit values for pine needle litter decomposition: a synthesis for boreal and temperate pine forest systems. Biogeochemistry 100(1–3):57–73
Berg B, Mcclaugherty C (2020) Plant litter. Decomposition, Humus Formation, Carbon Sequestration. Berlin: Springer.
Berthelsen BO, Steinnes E, Solberg W et al (1995) Heavy metal concentrations in plants in relation to atmospheric heavy metal deposition. J Environ Qual 24:1018–1026. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1995.00472425002400050034x
Bokhorst S, Metcalfe DB, Wardle DA (2013) Reduction in snow depth negatively affects decomposers but impact on decomposition rates is substrate dependent. Soil Biol Biochem 62:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.03.016
Butchart SHM, Walpole M, Collen B et al (2010) Global biodiversity: indicators of recent declines. Science 328:1164–1168. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1187512
Butenschoen O, Krashevska V, Maraun M et al (2014) Litter mixture effects on decomposition in tropical montane rainforests vary strongly with time and turn negative at later stages of decay. Soil Biol Biochem 77:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.06.019
Chapin FS, Bret-Harte MS, Zhong HH (1996) Plant functional types as predictors of transient responses of arctic vegetation to global change. J Veg Sci 7:347–358. https://doi.org/10.2307/3236278
Chapin FS, Sturm M, Serreze MC et al (2005) Role of land surface changes in Arctic summer warming. Science 310:57–660. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1117368
Chen D, Pan Q, Bai Y et al (2016) Effects of plant functional group loss on soil biota and net ecosystem exchange: a plant removal experiment in the Mongolian grassland. J Ecol 104(3):734–743. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12541
Chen YM, Zhang J, Liu Y et al (2021) Effects of single plant functional type loss on microbial community composition and litter decomposition in an alpine timberline ecotone. Eur J Soil Biol 104:103318
Cornelissen J (1996) An experimental comparison of leaf decomposition rates in a wide range of temperate plant species and types. J Ecol 573-582.https://doi.org/10.2307/2261479
Cotrufo MF, Soong JL, Horton AJ et al (2015) Formation of soil organic matter via biochemical and physical pathways of litter mass loss. Nat Geosci 8:776–779. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2520
Crowther TW, Riggs C, Lind EM et al (2019) Sensitivity of global soil carbon stocks to combined nutrient enrichment. Ecol Lett 22(6):936–945. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.13258
Davey MP, Berg B, Emmett BA, Rowland P (2007) Decomposition of oak leaf litter is related to initial litter Mn concentrations. Can J Bot 85:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1139/b06-150
Edmonds R L, Tuttle K M (2010) Red alder leaf decomposition and nutrient release in alder and conifer riparian patches in western Washington, USA. For Ecol Manag 2010, 259(12): 2375-2381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2010.03.011
Eisenhauer N, BeßLer H, Engels C et al (2010) Plant diversity effects on soil microorganisms support the singular hypothesis. Ecology 91(2):485–496. https://doi.org/10.1890/08-2338.1
Elliott J (2013) Evaluating the potential contribution of vegetation as a nutrient source in snowmelt runoff. Can J Soil Sci 93:435–443. https://doi.org/10.4141/CJSS2012-050
Fanin N, Kardol P, Farrell M et al (2019) Effects of plant functional group removal on structure and function of soil communities across contrasting ecosystems. Ecol Lett 22:1095–1103. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.13266
Fernández-Martínez M, Vicca S, Janssens IA et al (2014) Nutrient availability as the key regulator of global forest carbon balance. Nat Clim Chang 4:471–476
Gadd GM, Griffiths AJ (1978) Microorganisms and heavy metal toxicity. Microb Ecol 4:303–317
Gartner TB, Cardon ZG (2004) Decomposition dynamics in mixed-species leaf litter. Oikos 104(2):230–246. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0030-1299.2004.12738.x
Geerling JC, Loewy AD (2008) Central regulation of sodium appetite. Experimental Physiol 93:177–209. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2007.039891
Gong ZT, Zhang GL, Chen ZC et al (2007) Pedogenesis and soil taxonomy. Science Press 35
Grace J (2002) Impacts of climate change on the treeline. Ann Bot 90:537–544. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcf222
Hagedorn F, Gavazov K, Alexander JM (2019) Above- and belowground linkages shape responses of mountain vegetation to climate change. Science 365:1119–1123. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aax4737
Hall EK, Maixner F, Franklin O et al (2011) Linking microbial and ecosystem ecology using ecological stoichiometry: a synthesis of conceptual and empirical approaches. Ecosystems 14(2):261–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-010-9408-4
Handa T, Aerts R, Berendse F et al (2014) Consequences of biodiversity loss for litter decomposition across biomes. Nature 509:218–221. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13247
Hansen RA (2000) Effects of habitat complexity and composition on a diverse litter microarthropod assemblage. Ecology 81:1120–1132. https://doi.org/10.2307/177183
Harpole WS, Ngai JT, Cleland EE et al (2011) Nutrient co-limitation of primary producer communities. Ecol Lett 14:852–862. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01651.x
Hättenschwiler S, Tiunov AV, Scheu S (2005) Biodiversity and litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. Ann Rev Ecol Evol Syst 36:191–218. https://doi.org/10.2307/30033802
He J, Yang WQ, Xu L et al (2015) Copper and zinc dynamics in foliar litter during decomposition from gap center to closed canopy in an alpine forest. Scand J For Res. https://doi.org/10.1080/02827581.2015.1078405
Hemkemeyer M, Schwalb SA, Heinze S (2021) Functions of elements in soil microorganisms. Microbiol Res 252:126832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2021.126832
Hobbie SE, Nadelhoffer KJ, Hgberg PA (2002) Synthesis: the role of nutrients as constraints on carbon balances in boreal and arctic regions. Plant Soil 242(1):163–170. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019670731128
Hooper DU, Chapin FS, Ewel JJ et al (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: a consensus of current knowledge. Ecol Monogr 75(1). https://doi.org/10.2307/4539083
Hooper DU, Adair EC, Cardinale BJ et al (2012) A global synthesis reveals biodiversity loss as a major driver of ecosystem change. Nature. 486, 105-108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11118
Jeffries TW, Choi S, Kirk TK (1981) Nutritional regulation of lignin degradation by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microb 42(2):290–296. https://doi.org/10.1159/000263266
Jia Y, Kong X, Weiser MD et al (2015) Sodium limits litter decomposition rates in a subtropical forest: additional tests of the sodium ecosystem respiration hypothesis. Appl Soil Ecol 93:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2015.04.012
Johnson NC (2010) Resource stoichiometry elucidates the structure and function of arbuscular mycorrhizas across scales. New Phytol 185:631–647. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03110.x
Jonczak J, Parzych A, Sobisz Z (2014) Dynamics of Cu, Mn, Ni, Sr and Zn release during decomposition of four types of litter in headwater riparian forests in northern Poland. For Res Papers 75(2):1–8. https://doi.org/10.2478/frp-2014-0018
Jones ME, LaCroix RE, Zeigler J et al (2020) Enzymes, manganese, or iron? Drivers of oxidative organic matter decomposition in soils. Environ Sci Technol 54(21):14114–14123. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c04212
Kaspari M (2020) The seventh macronutrient: how sodium shortfall ramifies through populations, food webs and ecosystems. Ecol Lett 23:1153–1168. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.13517
Kerkhoff AJ, Fagan WF, Elser JJ et al (2006) Phylogenetic and growth form variation in the scaling of nitrogen and phosphorus in the seed plants. Am Nat 168:E103–E122. https://doi.org/10.1086/507879
Laskowski R, Maria N, Maciej M (1995) The dynamics of chemical elements in forest litter. Ecology 76(5):1393–1406. https://doi.org/10.2307/1938143
Lecerf A, Marie G, Kominoski JS et al (2011) Incubation time, functional litter diversity, and habitat characteristics predict litter-mixing effects on decomposition. Ecology 92:160–169. https://doi.org/10.2307/29779584
Lenior L, Gegout J, Marquet P et al (2008) A significant upward shift in plant species optimum elevation during the 20th century. Science 320:1768–1771. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1156831
Leroy CJ, Marks JC (2006) Litter quality, stream characteristics and litter diversity influence decomposition rates and macroinvertebrates. Freshw Biol 51:605–617. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2006.01512.x
Liu Y, Chen YM, Zhang J et al (2016) Changes in foliar litter decomposition of woody plants with elevation across an alpine forest-tundra ecotone in eastern Tibet Plateau. Plant Ecol 217:495–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-016-0594-9
Liu L, Zhang X, Yu Y et al (2017) Detecting spatiotemporal changes of peak foliage coloration in deciduous and mixed forests across the Central and Eastern United States. Envirol Res Lett 12(2):024013. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aa5b3a
Liu Y, Chen QM, Wang ZX et al (2019) Nitrogen addition alleviates microbial nitrogen limitations and promotes soil respiration in a subalpine coniferous forest. Forests 10(11):1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10111038
Lukumbuzya TK, Fyles JW, Cote B (1994) Effects of base-cation fertilization on litter decomposition in a sugar maple forest in southern Quebec. Can J Forest Res 24:447–452. https://doi.org/10.1139/x94-061
Maisto G, Marco AD, Meola A et al (2011) Nutrient dynamics in litter mixtures of four Mediterranean maquis species decomposing in situ. Soil Biol Biochem 43(3):520–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.11.017
Makkonen M, Berg MP, van Logtestijn RSP et al (2013) Do physical plant litter traits explain non-additivity in litter mixtures? A test of the improved microenvironmental conditions theory. Oikos 122:987–997. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0706.2012.20750.x
Manzoni S, Trofymow JA, Jackson RB et al (2010) Stoichiometric controls on carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus dynamics in decomposing litter. Ecol Monogr 80:89–106. https://doi.org/10.1890/09-0179.1
Martínez A, Larrañaga A, Pérez J, Descals E, Pozo J (2014) Temperature affects leaf litter decomposition in low-order forest streams: field and microcosm approaches. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 87:257–267. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6941.12221
Mayor JR, Sanders NJ, Classen AT et al (2017) Elevation alters ecosystem properties across temperate treelines globally. Nature 542:91–95. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21027
McGroddy ME, Daufresne T, Hedin LO (2004) Scaling of C : N : P stoichiometry in forests worldwide: implications of terrestrial redfield-type ratios. Ecology 85:2390–2401. https://doi.org/10.1890/03-0351
Mclaren J R, Turkington R (2010) Plant functional group identity differentially affects leaf and root decomposition. Glob Chang Biol 16(11). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02151.x
Mooshammer M, Wanek W, Schnecker J et al (2012) Stoichiometric controls of nitrogen and phosphorus cycling in decomposing beech leaf litter. Ecology 93:770–782. https://doi.org/10.1890/11-0721.1
Newingham BA, Callaway R, Bassiridad H (2007) Allocating nitrogen away from a herbivore: a novel compensatory response to root herbivory. Oecologia 153:913–920
Ni XY, Yang WQ, Li H et al (2014) Effects of snowpack on early foliar litter humification during winter in a subalpine forest of western Sichuan. Chin J Plant Ecol 38:540–549. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1258.2014.00050
Odum WE, Drifmeyer JE (1978) Sorption of pollutants by plant detritus: a review. Environ Health Perspect 27:133–137. https://doi.org/10.2307/3428872
Olsen I, Jantzen E (2001) Sphingolipids in bacteria and fungi. Anaerobe 7(2):103-112
Peñuelas J, Fernandez-Martinez M, Ciais P et al (2019) The bioelements, the elementome, and the biogeochemical. Ecology 100(5):e02652. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.2652
Perez J, Jeffries TW (1992) Roles of manganese and organic acid chelators in regulating lignin degradation and biosynthesis of peroxidases by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2402–2409. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.58.8.2402-2409.1992
Salinas N, Malhi Y, Meir P et al (2011) The sensitivity of tropical leaf litter decomposition to temperature: results from a large-scale leaf translocation experiment along an elevation gradient in Peruvian forests. New Phytol 189:967–977. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03521.x
Sardans J, Peñuelas J (2015) Potassium: a neglected nutrient in global change. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 24:261–275. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12259
Sardans J, Alonso R, Janssens IA et al (2016) Foliar and soil concentrations and stoichiometry of nitrogen and phosphorous across European Pinus sylvestris forests: relationships with climate, N deposition and tree growth. Funct Ecol 30(5):676–689. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12541
Sardans J, Grau O, Chen HYH et al (2017) Changes in nutrient concentrations of leaves and roots in response to global change factors. Glob Chang Biol 23(9):3849–3856. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13721
Scherer-Lorenzen M (2008) Functional diversity affects decomposition processes in experimental grasslands. Funct Ecol 22(3):547–555. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2435.2008.01389.x
Setiawan NN, Vanhellemont M, Schrijver AD et al (2016) Mixing effects on litter decomposition rates in a young tree diversity experiment. Acta Oecol 70:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actao.2015.12.003
Sinsabaugh RL, Manzoni S, Moorhead DL et al (2013) Carbon use efficiency of microbial communities: stoichiometry, methodology and modelling. Ecol Lett 16:930–939. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12113
Srivastava DS, Cardinale BJ, Downing AL et al (2009) Diversity has stronger top-down than bottom-up effects on decomposition. Ecology 90:1073–1083. https://doi.org/10.1890/08-0439.1
Staaf H, Berg B (1982) Accumulation and release of plant nutrients in decomposing Scots pine needle litter. Long-term decomposition in a Scots pine forest II. Can J Bot 60:1561–1568
Sterner RW, Elser JJ (2002) Ecological Stoichiometry. The Biology of Elements From Molecules to the Biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Stock WD, Verboom GA (2012) Phylogenetic ecology of foliar N and P concentrations and N: P ratios across Mediterranean-type ecosystems. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 21:1147–1156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-8238.2011.00752.x
Sun T, Cui YL, Berg B et al (2018) A test of manganese effects on decomposition in forest and cropland sites. Soil Biol Biochem 129:178–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.11.018
Sundqvist MK, Sanders NJ, Wardle DA et al (2013) Community and ecosystem responses to elevational gradients: processes, mechanisms, and insights for global change. Annu Rev Ecol Evol S 44:261–280. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110512-135750
Swan CM, Boyero L, Canhoto C (2021) The ecology of plant litter decomposition in stream ecosystems. First ed. Springer International Publishing.
Szanser M, Ilieva-Makulec K, Kajak A et al (2011) Impact of litter species diversity on decomposition processes and communities of soil organisms. Soil Biol Biochem 43:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.08.031
Tape K, Sturm M, Racine C et al (2006) The evidence for shrub expansion in Northern Alaska and the Pan-Arctic. Glob Chang Biol 12:686–702. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2006.01128.x
Tian DS, Niu SL et al (2015) A global analysis of soil acidification caused by nitrogen addition. Environ Res Lett 10:024019
Tian DS, Reich PB, Chen HYH et al (2019) Global changes alter plant multi-element stoichiometric coupling. New Phytol 221:807–817. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15428
Urbina I, Sardans J, Grau O et al (2017) Plant community composition affects the species biogeochemical niche. Ecosphere 8(5):e01801. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.1801
Verbruggen N, Hermans C (2013) Physiological and molecular responses to magnesium nutritional imbalance in plants. Plant Soil 368:87–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1589-0
Wang LF, Zhang J, He RL et al (2018) Impacts of soil fauna on lignin and cellulose degradation in litter decomposition across an alpine forest-tundra ecotone. Eur J Soil Biol 87:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2018.05.004
Wang C, Gao Q, Yu M (2019) Quantifying trends of land change in Qinghai-Tibet plateau during 2001–2015. Remote Sens 11:2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202435
Wang LF, Chen YM, Zhou Y et al (2021) Litter chemical traits strongly drove the carbon fractions loss during decomposition across an alpine treeline ecotone. Sci Total Environ 753:142287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142287
Watanabe T, Broadley MR, Jansen S et al (2007) Evolutionary control of leaf element composition in plants. New Phytol 174:516–523. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02078.x
Wieder W, Cleveland CC, Smith WK et al (2015) Future productivity and carbon storage limited by terrestrial nutrient availability. Nat Geosci 8:441–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2413
Windham L, Weis J S, Weis P (2004) Metal dynamics of plant litter of Spartina alterniflora and Phragmites australis in metal-contaminated salt marshes. Part 1: patterns of decomposition and metal uptake. Environ Toxicol Chem 2010, 23(6). https://doi.org/10.1897/03-284
Yuan ZY, Chen HYH (2009) Global trends in senesced-leaf nitrogen and phosphorus. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 18:532–542. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-8238.2009.00474.x
Yuan ZY, Chen HYH (2015) Decoupling of nitrogen and phosphorus in terrestrial plants associated with global changes. Nat Clim Chang 5(5):465–469. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2549
Yuan ZY, Chen HYH, Reich PB (2011) Global-scale latitudinal patterns of plant fine-root nitrogen and phosphorus. Nat Commun 2(1):344. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1346
Yue K, Yang WQ, Peng Y et al (2016) Dynamics of multiple metallic elements during foliar litter decomposition in an alpine forest river. Ann for Sci 73(2):547–557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13595-016-0549-2
Yue K, García-Palacios P, Parsons SA et al (2018) Assessing the temporal dynamics of aquatic and terrestrial litter decomposition in an alpine forest. Funct Ecol 32:2464–2475. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.13143
Zhang KR, Cheng XL, Dang HS et al (2020) Biomass:N:K:Ca:Mg: P ratios in forest stands world-wide: biogeographical variations and environmental controls. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 29(12):2176–2189. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.13187
Zheng HF, Chen YM, Liu Y et al (2021) Effects of litter quality diminish and effects of vegetation type develop during litter decomposition of two shrub species in an alpine treeline ecotone. Ecosystems 24(4) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-020-00512-9
Zhou Y, Wang LF, Chen YM et al (2020) Litter stoichiometric traits have stronger impact on humification than environment conditions in an alpine treeline ecotone. Plant Soil 453(1796):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04586-1
Zhou Y, Wang LF, Chen YM et al (2021) Temporal dynamics of mixed litter humification in an alpine treeline ecotone. Sci Total Environ 803:150122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150122
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Xian Shen, Yamei Chen, Lifeng Wang, and others at the Institute of Ecology and Forestry, Sichuan Agricultural University, for assistance with field sampling and laboratory analyses. We also want to thank Jian Zhang and Yang Liu for reviewing the paper.
Funding
This work was financially supported by projects from the Science and Technology Development Project of the central government guided in Sichuan (2020ZYD049); National Natural Science Foundation of China (31570605); and the project supported by the Foundation of Key Laboratory of Southwest China Wildlife Resources Conservation, China West Normal University, Ministry of Education, Nanchong, 637009, P. R. China (XNYB21-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yang Liu, Yamei Chen, Lifeng Wang, Yu Zhou, and Xian Shen designed the study. Data collection were performed by Xian Shen. The analysis was performed and the first draft of the manuscript was written by Yu Zhou. Jian Zhang, Zhenfeng Xu, Li Guo, Bo Tan, Lixia Wang, Chengming You, and Yang Liu read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Shen, X., Chen, Y. et al. Both specific plant functional type loss and vegetation change influence litter metallic element release in an alpine treeline ecotone. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 41544–41556 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18778-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18778-y