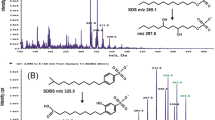
Abstract
The effects of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS), polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monolaurate (Tween 20), and their mixtures on the depuration of anthracene (Ant) and fluoranthene (Fla) individually adsorbed on the Kandelia obovata (Ko) leaf surfaces were in situ investigated. The Ko original leaf-wax microstructures have been destroyed by SDBS, Tween 20, and their mixtures at or above their critical micelle concentration (CMC). The volatilization rate constants (kV) of the adsorbed PAHs decreased with surfactants at or above their CMC resulting from the plasticizing effect and a decrease in the polarity of the Ko leaf-waxes induced by surfactants. Moreover, the photolysis rate constants (kP) of the adsorbed PAHs decreased with SDBS while increased with Tween 20 and their mixtures at or above their CMC, which can be attributed to effects of surfactants on the light adsorption behavior of Ko leaf-waxes. Overall, the effects of surfactants on the depuration of the adsorbed PAHs were dependent not only on the physical–chemical properties of surfactants but also on the micro-environment of the substrates adsorbed the PAHs. These results are of great significance for further understanding the accumulation of PAHs and could expand our knowledge about the migration mechanism of PAHs from the atmosphere by mangrove leaf surface micro-zones.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
Abbreviations
- SDBS:
-
Sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate
- Tween 20:
-
Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monolaurate
- Ant:
-
Anthracene
- Fla:
-
Fluoranthene
- K o :
-
Kandelia obovate
- CMC:
-
Critical micelle concentration
- POPs:
-
Persistent organic pollutants
- PAHs:
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- HOCs:
-
Hydrophobic organic contaminants
- Nap:
-
Naphthalene
- Flu:
-
Fluorine
- Phe:
-
Phenanthrene
- Pyr:
-
Pyrene
- LCSM:
-
Laser confocal scanning microscopy
- λ ex :
-
Excitation wavelength
- λ em :
-
Emission wavelength
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- RSD:
-
Relative standard deviation
- k T :
-
Total depuration rate constants
- k V :
-
Volatilization rate constants
- k P :
-
Photolysis rate constants
- C V1 :
-
The percentage contributions of volatilization
- C P1 :
-
The percentage contributions of photolysis
- LT:
-
Light-treated
- DT:
-
Dark-treated
- S:T:
-
Mass ratios of SDBD to Tween 20
- Brij35:
-
Polyoxyethyleneglycol dodecyl ether
References
Alsalahi MA, Latif MT, Ali MM, Magam SM, Wahid NBA, Khan MF, Suratmanet S (2014) Distribution of surfactants along the estuarine area of Selangor River, Malaysia. Mar Pollut Bull 80:344–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145076
Appah S, Jia WD, Ou MX, Wang P, Asante EA (2020) Analysis of potential impaction and phytotoxicity of surfactant-plant surface interaction in pesticide application. Crop Prot 127:104961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2019.104961
Bayen S, Estrada ES, Zhang H, Lee WK, Juhel G, Smedes F, Kelly BC (2019) Partitioning and bioaccumulation of legacy and emerging hydrophobic organic chemicals in mangrove ecosystems. Environ Sci Technol 53:2549–2558. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b06122
Cai ZQ, Liu W, Fu J, O’Reilly SE, Zhao DY (2017) Effects of oil dispersants on photodegradation of parent and alkylated anthracene in seawater. Environ Pollut 229:272–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.084
Chen BL, Johnson EJ, Chefetz B, Zhu LZ, Xing BS (2005) Sorption of polar and nonpolar aromatic organic contaminants by plant cuticular materials: role of polarity and accessibility. Environ Sci Technol 39:6138–6146. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050622q
Chen BL, Xing BS (2005) Sorption and conformational characteristics of reconstituted plant cuticular waxes on montmorillonite. Environ Sci Technol 39(21):8315–8323. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050840j
Chen L, Zhang Y, Liu BB (2010) In situ simultaneous determination the photolysis of multi-component PAHs adsorbed on the leaf surfaces of living Kandelia candel seedlings. Talanta 83(2):324–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2010.09.025
Damato TC, Carrasco DML, Carmona-Ribeiro AM, Luiz RV, Godoy R, Petri DFS (2017) The interactions between surfactants and the epicuticular wax on soybean or weed leaves: Maximal crop protection with minimal wax Solubilization. Crop Prot 91:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2016.09.019
Deng H, He JX, Feng D, Zhao YY, Sun W, Yu HM, Ge CJ (2021) Microplastics pollution in mangrove ecosystems: a critical review of current knowledge and future directions. Sci Total Environ 753:142041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142041
Fagerström A, Kocherbitov V, Ruzgas T, Westbye P, Bergström K, Engblom J (2013) Effects of surfactants and thermodynamic activity of model active ingredient on transport over plant leaf cuticle. Colloids Surf B 103:572–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.11.011
Gong P, Xu H, Wang CF, Chen Y, Guo LP, Wang XP (2021) Persistent organic pollutant cycling in forests. Nat Rev Earth Environ 2: 182–197. https://www.nature.com/articles/s43017-020-00137-5
Guo S, Chao XW, Zhu YX, Zhang Y (2021) The distribution and retained amount of benzo[a]pyrene at the micro-zones of mangrove leaf cuticles: results from a novel analytical method. Environ Pollut 287:117589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117589
Guo YJ, Jetter R (2017) Comparative analyses of cuticular waxes on various organs of potato (Solanum tuberosum L). J Agric Food Chem 65(19):3926–3933. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00818
Hanif NM, Latif MT, Othman MR (2015) Atmospheric surfactants around lake ecosystem of Tasik Kenyir, Terengganu Malaysia. J Anal Atom Spectrom 15: 1–7. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/256547334
Hu XZ, Pambou E, Gong HN, Liao MR, Hollowell P, Liu HY, Wang WM, Bawn C, Cooper J, Campana M, Ma K, Li PX, Webster JRP, Padia F, Bell G, Lu JR (2020a) How does substrate hydrophobicity affect the morphological features of reconstituted wax films and their interactions with nonionic surfactant and pesticide? J Colloid Interface Sci 575:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.04.043
Hu YX, Sun YX, Pei NC, Zhang ZW, Li HW, Wang WW, Xie JL, Xu XR, Luo XJ, Mai BX (2020b) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and alternative halogenated flame retardants in mangrove plants from Futian National Nature Reserve of Shenzhen City. South China Environ Pollut 260:114087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114087
Huang YZ, Xiao X, Effiong K, Xu CC, Su ZN, Hu J, Jiao SJ, Holmer M (2021) New insights into the microplastic enrichment in the blue carbon ecosystem: evidence from seagrass meadows and mangrove forests in coastal South China Sea. Environ Sci Technol 55(8):4804–4812. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c07289
Jannis W, Urs VG, Canonica SC (2011) Effect of dissolved organic matter on the transformation of contaminants induced by excited triplet states and the hydroxyl radical. Environ Sci Technol 45:1334–1340. https://doi.org/10.1021/es102212t
Jia JP, Bi CJ, Jin XP, Zeng YS, Deng L, Wang XP, Chen ZL (2021) Uptake, translocation, and risk assessment of PAHs in contaminated soil-air-vegetable systems based on a field simulation experiment. Environ Pollut 271:116361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116361
Kobayashi R, Cahill TM, Okamoto RA, Maddalena RL, Kado NY (2007) Controlled exposure chamber study of uptake and clearance of airborne polycyclicaromatic hydrocarbons by wheat grain. Environ Sci Technol 41(22):7934–7940. https://doi.org/10.1021/es071459x
Li BX, Liu Y, Zhang P, Li XX, Pang XY, Zhao YH, Li H, Liu F, Lin J, Mu W (2019) Selection of organosilicone surfactants for tank-mixed pesticides considering the balance between synergistic effects on pests and environmental risks. Chemosphere 217:591–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.061
Li F, Zeng XK, Yang JD, Zhou K, Zan QJ, Lei A, Tam NFY (2014) Contamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments and plants of mangrove swamps in Shenzhen, China. Mar Pollut Bull 85:590–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.02.025
Li QQ, Li YG, Zhu LZ, Xing BS, Chen BL (2017) Dependence of plant adsorption and diffusion of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on the leaf surfaces morphology and micro-structures of cuticular waxes. Sci Rep 7: 1–11. https://www.nature.com/articles/srep46235
Li RL, Sun HF, Wang SP, Wang YH, Yu KF (2018) Retention of CdS/ZnS quantum dots (QDs) on the root epidermis of woody plant and its implications by benzo[a]pyrene: evidence from the in situ synchronous nanosecond time-resolved fluorescence spectra method. J Agric Food Chem 66(4):814–821. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b04258
Li YG, Chen BL (2009) Phenanthrene sorption by fruit cuticles and potato periderm with different compositional characteristics. J Agric Food Chem 57(2):637–644. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf802719h
Li YG, Chen BL, Chen ZM, Zhu LZ (2009) Surfactant effects on the affinity of plant cuticles with organic pollutants. J Agric Food Chem 57(9):3681–3688. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf803917w
Naidoo G, Naidoo K (2016) Uptake of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their cellular effects in the mangrove Bruguiera gymnorrhiza. Mar Pollut Bull 113:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.09.012
Niu JF, Chen JW, Martens D, Henkelmann B, Quan X, Yang FL, Seidlitz HK, Schramm KW (2004) The role of UV-B on the degradation of PCDD/Fs and PAHs sorbed on surfaces of spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.) needles. Sci Total Environ 322:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2003.09.017
Pambou E, Hu XZ, Li ZY, Campana M, Hughes A, Li P, Webster JRP, Bell G, Lu JR (2018) Structural features of reconstituted cuticular wax films upon interaction with nonionic surfactant C12E6. Langmuir 34:3395–3404. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b00143
Paris F, Krzyżaniak Y, Gauvrit C, Jamois F, Domergue F, Joubès J, Ferrières V, Adrian M, Legentil L, Daire X, Trouvelot S (2016) An ethoxylated surfactant enhances the penetration of the sulfated laminarin through leaf cuticle and stomata, leading to increased induced resistance against grapevine downy mildew. Physiol Plant 156(3): 338–350. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ppl.12394
Qiu YW, Qiu HL, Li J, Zhang G (2018) Bioaccumulation and cycling of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in typical mangrove wetlands of Hainan Island, South China. Arch. Environ Contam Toxicol 75: 464–475. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00244-018-0548-4
Qu YJ, Gong YW, Ma J, Wei HY, Liu QY, Liu LL, Wu HW, Yang SH, Chen YX (2020) Potential sources, influencing factors, and health risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the surface soil of urban parks in Beijing. China Environ Pollut 260:114016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114016
Schonherr J, Baur P, Uhlig BA (2000) Rates of cuticular penetration of 1-naphthylacetic acid (NAA) as affected by adjuvants, temperature, humidity and water quality. Plant Growth Regul 31: 61–74. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1006354732358
Shi TR, Tian K, Bao HY, Wu FY (2017) Variation in foliar uptake of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in six varieties of winter wheat. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24: 27215–27224. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11356-017-0312-8
Sun HF, Li RL, Zhu YX, Zhang Y (2013a) In situ determination mechanism for the depuration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons adsorbed onto the leaf surfaces of living mangrove seedlings. J Hazard Mater 262:339–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.08.064
Sun HF, Yang YN, Zhu YX, Zhang Y (2013b) In situ investigation of the depuration of fluoranthene adsorbed on the leaf surfaces of living mangrove seedlings. Talanta 116:441–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.07.018
Sun HF, Guo S, Zhu N, Sang N, Chen Z (2016a) In situ determination of multiple polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons adsorption by crop leaf surfaces using multi-way models. Environ Pollut 218:523–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.07.032
Sun HF, Wang WP, Guo S, Zhang Y (2016b) In situ investigation into surfactant effects on the clearance of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons adsorbed onto soybean leaf surfaces. Environ Pollut 210:330–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.01.036
Sun HF, Guo S, Nan YL, Ma RY (2018) Direct determination of surfactant effects on the uptake of gaseous parent and alkylated PAHs by crop leaf surfaces. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 154:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.02.045
Tamura H, Knoche M, Bukovac MJ (2001). Evidence for surfactant solubilization of plant epicuticular wax. J Agric Food Chem 49(4): 1809–1816. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf000608r
Wang DG, Chen JW, Xu Z, Qiao XL (2005) Disappearance of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons sorbed on surfaces of pine [Pinua thunbergii] needles under irradiation of sunlight: volatilization and photolysis. Atmos Environ 39:4583–4591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.04.008
Wang P, Du KZ, Zhu YX, Zhang Y (2008) A novel analytical approach for investigation of anthracene adsorption onto mangrove leaves. Talanta 76:1177–1182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.05.021
Wei J, Huang GH, Zhu L, Zhao S, An CJ, Fan YR (2012) Enhanced aqueous solubility of naphthalene and pyrene by binary and ternary Gemini cationic and conventional nonionic surfactants. Chemosphere 89:1347–1353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.05.091
Wild E, Dent J, Thomas GO, Jones KC (2006) Visualizing the air-to-leaf transfer and within-leaf movement and distribution of phenanthrene: further studies utilizing two-photon excitation microscopy. Environ Sci Technol, 40, 907–916. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/es0515046
Yang B, Liu S, Liu Y, Lin XB, Liu M, Liu XR (2017) PAHs uptake and translocation in Cinnamomum camphora leaves from Shanghai, China. Sci Total Environ 574:358–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.058
Yang XJ, Lu GN, She BJ, Liang XL, Yin RR, Guo CL, Yi XY, Dang Z (2015) Cosolubilization of 4,4’-dibromodiphenyl ether, naphthalene and pyrene mixtures in various surfactant micelles. Chem Eng J 260:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.08.101
Zhu Y, Huang HJ, Zhang YH, Xiong GN, Zhang QH, Li YJ, Tao S, Liu WX (2021) Evaluation of PAHs in edible parts of vegetables and their human health risks in Jinzhong City, Shanxi Province, China: a multimedia modeling approach. Sci Total Environ 773:145076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145076
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge senior engineer Fang Wu of College of the Environment and Ecology (Xiamen University) for helping to use the apparatus.
Funding
We acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21627814).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shuai Guo: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing-Original Draft, Visualization. Chaoxian Wei: Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Resources, Visualization. Yaxian Zhu: Data curation, Visualization, Project administration. Yong Zhang: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Writing-Review and Editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ester Heath
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Material
(DOCX 940 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, S., Wei, C., Zhu, Y. et al. How surfactants affect the depuration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons adsorbed on the mangrove leaf surfaces: insight from an in situ method. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 31413–31425 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18469-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18469-0