Abstract
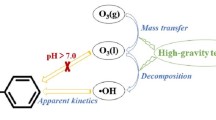
In this study, the high-gravity technique is used to intensify the heterogeneous catalytic ozonation with activated carbon (AC) as the catalyst for removal of phenol from wastewater in a rotating packed bed (RPB), and the effects of high-gravity factor, inlet O3 concentration, liquid–gas ratio, and initial pH on the degradation and mineralization of phenol at room temperature are investigated. It is revealed that the degradation rate of phenol reaches 100% at 10 min and the removal rate of total organic carbon (TOC) reaches 91% at 40 min under the conditions of high-gravity factor β = 40, inlet O3 concentration = 90 mg·L−1, liquid flow rate = 80 L·h−1, and initial pH = 11. Compared with the bubbling reactor (BR)/O3/AC and RPB/O3 systems, the mineralization rate of phenol by the RPB/O3/AC system is increased by 24.78% and 34.77%, respectively. Free radical quenching experiments are performed using tertiary butanol (TBA) and benzoquinone (BQ) as scavengers of ·OH and O2−, respectively. It is shown that the degradation and mineralization of phenol are attributed to the direct ozonation and the indirect oxidation by ·OH generated from the decomposition of O3 adsorbed on AC surface, respectively. ·OH and O2·− are also detected by electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR). Thus, it is concluded that AC-catalyzed ozonation and high-gravity technique have a synergistic effect on ·OH initiation, which in turn can significantly improve the degradation and mineralization of organic wastewater.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study were included in this article.
References
Abdedayem A, Guiza M, Ouederni A (2015) Copper supported on porous activated carbon obtained by wetness impregnation: effect of preparation conditions on the ozonation catalyst’s characteristics. CR Chim 18:100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2014.07.011
Afzal S, Quan X, Chen S, Wang J, Muhammad D (2016) Synthesis of manganese incorporated hierarchical mesoporous silica nanosphere with fibrous morphology by facile one-pot approach for efficient catalytic ozonation. J Hazard Mater 318:308–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.07.015
Afzal S, Pan K, Duan D, Wei Y, Chen L (2020) Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate with cobalt incorporated fibrous silica nanospheres for the degradation of organic pollutants in water. Appl Surf Sci 542:148674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148674
Ahmed S, Rasul MG, Martens WN, Brown R, Hashib MA (2010) Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of phenols in wastewater: a review on current status and developments. Desalination 261:3–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.04.062
Álvarez P, García-Araya J, Beltrán F, Masa FJ, Medina F (2005) Ozonation of activated carbons: effect on the adsorption of selected phenolic compounds from aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 283:503–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.09.014
Banat F, Al-Asheh S, Al-Makhadmeh L (2010) Utilization of raw and activated date pits for the removal of phenol from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng Technol 27:80–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.200401868
Bhausaheb S, Korake S (2016) Review on removal of phenol from wastewater using low cost adsorbent. Int J Eng Sci 6:2278–7798
Bing J, Hu C, Nie Y, Min Y, Qu J (2015) Mechanism of catalytic ozonation in Fe2O3/Al2O3@SBA-15 aqueous suspension for destruction of ibuprofen. Environ Sci Technol 49:1690–1697. https://doi.org/10.1021/es503729h
Chen YH, Chiu CY, Chang CY, Huang YH, Yu YH, Chiang PC, Shie JL, Chiou CS (2005) Modeling ozonation process with pollutant in a rotating packed bed. Ind Eng Chem Res 44:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie0401657
Chen YH, Chang CY, Su WL, Chiu CY, Yu H, Chiang PC, Chang CF, Shie JL, Chiou CS, Chiang SI (2010) Ozonation of CI reactive black 5 using rotating packed bed and stirred tank reactor. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 80:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.1159
Elovitz MS, Gunten UV (1999) Hydroxyl radical/ozone ratios during ozonation processes. I. The Rct concept. Ozone-Sci Eng 21:239–260. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919519908547239
Huang K, Wang J, Wu D, Lin S (2015) Copper hydroxyl sulfate as a heterogeneous catalyst for the catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of phenol. Rsc Adv 5:8455–8462. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA15878D
Jaafarzadeh N, Ghanbari F, Ahmadi M (2017) Efficient degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by peroxymonosulfate/magnetic copper ferrite nanoparticles/ozone: a novel combination of advanced oxidation processes. Chem Eng J 320:436–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.036
Jans U, Hoigné J (1998) Activated carbon and carbon black catalyzed transformation of aqueous ozone into OH-radicals. Ozone-Sci Eng 20(1):67–90. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919519808547291
Jain B, Singh AK, Hashmi A, Abu Bin Hasan Susan M, Lellouche JP (2020) Surfactant-assisted cerium oxide and its catalytic activity towards fenton process for non-degradable dye. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 3:430–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-020-00159-z
Jiao WZ, Liu YZ, Qi GS (2010) Gas pressure drop and mass transfer characteristics in a cross-flow rotating packed bed with porous plate packing. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:3732–3740. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie9009777
Jiao W, Luo S, He Z, Liu Y (2016) Applications of high gravity technologies for wastewater treatment: a review. Chem Eng J 313:912–927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.125
Ku Y, Huang YJ, Chen HW, Hou WM (2011) Decomposition of acetone by hydrogen peroxide/ozone process in a rotating packed contactor. Water Environ Res 83:588–593. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143010X12851009156961
Lei L, Li G, Zhang X, Su Y (2007) Catalytic oxidation of highly concentrated real industrial wastewater by integrated ozone and activated carbon. Appl Catal A Gen 327:287–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2007.05.027
Li W, Yan J, Yan Z, Song Y, Jiao W, Qi G, Liu Y (2018) Adsorption of phenol by activated carbon in rotating packed bed: experiment and modeling. Appl Therm Eng 142:760–766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.07.051
Li S, Tang Y, Zhang J, Hao W, Chen W, Gu F, Hu Z, Li L (2019) Advanced and green ozonation process for removal of clofibric acid in water system: preparation and mechanism analysis of efficient copper-substituted MCM-48. Sep Purif Technol 211:684–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.10.031
Li P, Wei X, Shao S, Gao W, Liu Y (2020a) Degradation of nitrobenzene in wastewater by O3/FeOOH in a rotating packed bed. Chem Eng Process 153:107981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2020.107981
Li X, Ma J, He H (2020b) Recent advances in catalytic decomposition of ozone. J Environ Sci 94:14–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.03.058
Ma D, Chen L, Wu Y, Liu R (2016) Evaluation of the removal of antiestrogens and antiandrogens via ozone and granular activated carbon using bioassay and fluorescent spectroscopy. Chemosphere 153:346–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.073
Miao Q, Tang Y, Xu J, Liu X, Xiao L, Chen Q (2013) Activated carbon prepared from soybean straw for phenol adsorption. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 44:458–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2012.12.006
Mousavi S, Dehghanzadeh R, Ebrahimi SM (2017) Comparative analysis of ozonation (O3) and activated carbon catalyzed ozonation (ACCO) for destroying chlorophyll a and reducing dissolved organic carbon from a eutrophic water reservoir. Chem Eng J 314:396–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.159
Naguib DM, Badawy NM (2019) Phenol removal from wastewater using waste products. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103592
Nawrocki J (2013) Catalytic ozonation in water: controversies and questions. discussion paper. Appl Catal B Environ 142:465–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.05.061
Qian Z, Chen Q, Grossmann IE (2017) Optimal synthesis of rotating packed bed reactor. Comput Chem Eng 105:152–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-64241-7.50391-8
Qiao J, Luo S, Yang P, Jiao W, Liu Y (2019) Degradation of nitrobenzene-containing wastewater by ozone/persulfate oxidation process in a rotating packed bed. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 99:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.02.015
Qin YJ, Luo S, Geng S, Jiao WZ, Liu YZ (2018) Degradation and mineralization of aniline by O3/Fenton process enhanced using high-gravity technology. Chin J Chem Eng 26:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2018.01.018
Rivera-Utrilla J, Sánchez-Polo M, Gómez-Serrano V, Álvarez P, Alvim-Ferraz M, Dias JM (2011) Activated carbon modifications to enhance its water treatment applications. An overview. J Hazard Mater 187:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.01.033
Shao S, Lei D, Song Y, Liang L, Jiao W (2021) Cu–MnOX /γ-Al2O3 catalyzed ozonation of nitrobenzene in a high-gravity rotating packed bed. Ind Eng Chem Res 60:2123–2135. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c05751
Singh N, Jana S, Singh GP, Dey RK (2020) Graphene-supported TiO2: study of promotion of charge carrier in photocatalytic water splitting and methylene blue dye degradation. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 3:127–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-020-00140-w
Staehelin J, Hoigne J (1982) Decomposition of ozone in water: rate of initiation by hydroxide ions and hydrogen peroxide. Environ Sci Technol 16:621–653. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00104a009
Turhan K, Uzman S (2008) Removal of phenol from water using ozone. Desalination 229:257–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.09.012
Wang J, Chen H (2020) Catalytic ozonation for water and wastewater treatment: Recent advances and perspective. Sci Total Environ 704:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135249
Wang D, Liu L, Ma L, Wang F, Shao L (2019a) Modeling and experimental studies on ozone absorption into phenolic solution in a rotating packed bed. Ind Eng Chem Res 58:7052–7062. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b00787
Wang X, Xu J, Liu J, Liu J, Liu W (2019b) Mechanism of Cr(VI) removal by magnetic greigite/biochar composites. Sci Total Environ 700:134414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134414
Wei X, Shao S, Ding X, Jiao W, Liu Y (2020) Degradation of phenol with heterogeneous catalytic ozonation enhanced by high gravity technology. J Cleaner Prod 248:119179.1-119179.10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119179
Wu TW, Hung YT, Chen MT, Tan CS (2017) CO2 capture from natural gas power plants by aqueous PZ/DETA in rotating packed bed. Sep Purif Technol 186:309–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.05.040
Wu ZW, Zhang GQ, Zhang RY, Yang FL (2018) Insights into mechanism of catalytic ozonation over practicable mesoporous Mn-CeOx /γ-Al2O3 Catalysts. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:1943–1953. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b04516
Xiong W, Cui W, Li R, Feng C, Chen N (2020) Mineralization of phenol by ozone combined with activated carbon: performance and mechanism under different pH levels. Environ Sci Technol 1:100005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2019.100005
Xta B, Cw A, Fga B, Wen HA, Hya B, Sza B, Yza B, Yl A (2020) Mn-Fe-Ce multiple oxides with Al2O3 coating supported onto honeycomb cordierite monoliths for NO catalytic oxidation. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 611:125790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125790
Yang G, Mo S, Xing B, Dong J, Yuan J (2019a) Effective degradation of phenol via catalytic wet peroxide oxidation over N, S, and Fe-tridoped activated carbon. Environ Pollut 258:113687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113687
Yang PA, Luo SB, Liu HA, Jiao WA, Liu YA (2019b) Aqueous ozone decomposition kinetics in a rotating packed bed. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 96:11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.10.027
Yu G, Wang Y, Cao H, Zhao H, Xie Y (2020) Reactive oxygen species and catalytic active sites in heterogeneous catalytic ozonation for water purification. Environ Sci Technol 54:5931–5946. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c00575
Zeng Z, Zou H, Li X, Arowo M, Sun B, Chen J, Chu G, Shao L (2013) Degradation of phenol by ozone in the presence of fenton reagent in a rotating packed bed. Chem Eng J 229:404–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.018
Zhang M, Zhang Z, Liu S, Peng Y, Ki SY (2020a) Ultrasound-assisted electrochemical treatment for phenolic wastewater. Ultrason Sonochem 65:105058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105058
Zhang YQ, Cheng XQ, Jiang X, Urban JJ, Lau CH, Liu SQ, Shao L (2020b) Robust natural nanocomposites realizing unprecedented ultrafast precise molecular separations. Mater Today 36:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2020.02.002
Zhang M, Yin D, Guo J, Wu H, Feng X (2021a) Ternary catalyst Mn-Fe-Ce/Al2O3 for the ozonation of phenol pollutant: performance and mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut 28:32921–32932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13006-5
Zhang YQ, Guo J, Han G, Bai YP, Ge QC, Ma J, Lau CH, Shao L (2021) Molecularly soldered covalent organic frameworks for ultrafast precision sieving. Mater Sci 7:eabe8706. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abe8706
Funding
This work was supported by the Fund for Shanxi “1331 Project” (nuc2021-006), Key Research & Development Plan of Shanxi Province (201903D321059), Scientific Activities of Selected Returned Overseas Professionals in Shanxi Province (20200004), and Transformation and Cultivation Projects of Scientific and Technological Achievements in Universities of Shanxi Province Institutions (2020CG040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shengjuan Shao and Xin Ding were in charge of the experiment. Youzhi Liu, Zhixing Li, and Jiaxin Jing analyzed the experimental data. Jingwen Zhang and Weizhou Jiao were major contributors in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors of this manuscript have directly participated in the planning, execution, and analyses of this study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Shao, S., Ding, X. et al. Removal of phenol from wastewater by high-gravity intensified heterogeneous catalytic ozonation with activated carbon. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 34830–34840 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18093-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18093-y