Abstract
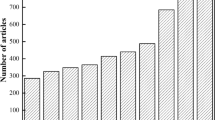
The recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) is both essential to sustainable resource utilization and environmental conservation. While spent batteries possess a resource value, they pose an environmental hazard at the same time. Since the start of development to recycle spent LIBs in 1990s, important contributions have been made and a number of achievements have been accomplished by scholars globally. Therefore, it is valuable to summarize the developments on spent LIB recycling and to analyze the characteristics and trends comprehensively. A review of the progress in this field will provide guidance for future development. In this study, recycling characteristics and developing trends including the research foundation, milestone, research hotspot, key technologies, and emerging trends were identified based on visual scientometric analysis followed by a discussion on future research directions in this area. For the analysis, 1041 publications in English were collected, summarized, and categorized. The distribution of scientific publications on spent LIB recycling from 1995 to 2020 displayed an increasing trend in numbers. China made the biggest contribution with 528 publications and basically cooperated with all other countries. The research fields with the highest contributions were “engineering”, “chemistry”, and “environmental science and technology”. The keywords recovery, lithium ion battery, and cobalt appeared in high frequency. “Metal value” was identified as the most frequently used keyword which began to burst in 2005 and ended in 2013.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Chen CM (2006) CiteSpace II: detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 57(3):359–377. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.20317
Commission, E. (2017). The European Commission (EC) launched the European Battery Alliance (EBA). Retrieved from https://energypost.eu/europe-needs-its-own-ev-battery-recycling-industry/
Du S, Li H (2019) The knowledge mapping of mobile commerce research: a visual analysis based on I-model. Sustainability 11(6):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061580
EPA. (March 22, 2018). Safe Battery Collection & Recycling. Retrieved from https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2018-03/documents/smith_epa_webinar_03_22_18.pdf
Fang Y, Yin J, Wu BH (2018) Climate change and tourism: a scientometric analysis using CiteSpace. J Sustain Tour 26(1):108–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2017.1329310
Frohlich S, Sewing D (1995) The BATENUS process for recycling mixed battery waste. J Power Sources 57(1–2):27–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-7753(95)02234-1
Fu YP, He YQ, Qu LL, Feng Y, Li JL, Liu JS, Xie WN (2019) Enhancement in leaching process of lithium and cobalt from spent lithium-ion batteries using benzenesulfonic acid system. Waste Manage 88:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.03.044
Guo MM, Li K, Zhang HB, Min X, Liang JX, Hu XF, Sun TH (2020) Promotional removal of oxygenated VOC over manganese-based multi oxides from spent lithium-ions manganate batteries: modification with Fe, Bi and Ce dopants. Sci Total Environ 740:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139951
He SC, Wilson BP, Lundstrom M, Liu ZH (2020) Clean and efficient recovery of spent LiCoO2 cathode material: water-leaching characteristics and low-temperature ammonium sulfate calcination mechanisms. J Clean Prod 268:15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122299
Huang T, Liu LF, Zhang SW (2019) Recovery of cobalt, lithium, and manganese from the cathode active materials of spent lithium-ion batteries in a bio-electro-hydrometallurgical process. Hydrometallurgy 188:101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.06.011
Japan, B. A. o. (April 2001). Law for Promotion of Effective Utilization of Resources. Retrieved from http://www.baj.or.jp/e/recycle/recycle04.html
Kunugita E, Kim JH, Komasawa I (1989) A process for recovery of lithium from spent lithium batteries. Kagaku Kogaku Ronbunshu 15(4):857–862. https://doi.org/10.1252/kakoronbunshu.15.857
Lei SY, Cao Y, Cao XF, Sun W, Weng YQ, Yang Y (2020) Separation of lithium and transition metals from leachate of spent lithium-ion batteries by solvent extraction method with Versatic 10. Sep Purif Technol 250:7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117258
Li J, Lai YM, Zhu XQ, Liao Q, Xia A, Huang Y, Zhu X (2020) Pyrolysis kinetics and reaction mechanism of the electrode materials during the spent LiCoO2 batteries recovery process. J Hazard Mater 398:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122955
Li M, Lu J, Chen ZW, Amine K (2018) 30 Years of lithium-ion batteries. Adv Mater 30(33):24. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201800561
Liu CW, Lin J, Cao HB, Zhang Y, Sun Z (2019) Recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries in view of lithium recovery: a critical review. J Clean Prod 228:801–813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.304
Lugo M, Ail SS, Castaldi MJ (2020) Approaching a zero-waste strategy by reuse in New York City: challenges and potential. Waste Manage Res 38(7):734–744. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242x20919496
Ma TF, Guo ZX, ShenZ, Wu QY, Li YH & Yang G (2020) Molten salt-assisted regeneration and characterization of submicron-sized LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 crystals from spent lithium ion batteries Journal of Alloys and Compounds 848 9 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156591
P MeshramA Mishra Abhilash & Sahu R 2020 Environmental impact of spent lithium ion batteries and green recycling perspectives by organic acids — a review Chemosphere 242 16 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125291
Miatto A, Reck BK, West J, Graedel TE (2020) The rise and fall of American lithium. Resour Conserv Recycl 162:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105034
Naseri T, Bahaloo-Horeh N, Mousavi SM (2019) Environmentally friendly recovery of valuable metals from spent coin cells through two-step bioleaching using Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. J Environ Manage 235:357–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.01.086
Natarajan S, Boricha AB, Bajaj HC (2018) Recovery of value-added products from cathode and anode material of spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manage 77:455–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.04.032
Ouyang W, Wang YD, Lin CY, He MC, Hao FH, Liu HB, Zhu WH (2018) Heavy metal loss from agricultural watershed to aquatic system: a scientometrics review. Sci Total Environ 637:208–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.434
Sommerville R, Shaw-Stewart J, Goodship V, Rowson N, Kendrick E (2020) A review of physical processes used in the safe recycling of lithium ion batteries. Sustain Mater Technol 25:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2020.e00197
Song JB, Zhang HL, Dong WL (2016) A review of emerging trends in global PPP research: analysis and visualization. Scientometrics 107(3):1111–1147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-1918-1
Tang YQ, Zhang BL, Xie HW, Qu X, Xing PF, Yin HY (2020) Recovery and regeneration of lithium cobalt oxide from spent lithium-ion batteries through a low-temperature ammonium sulfate roasting approach. J Power Sources 474:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228596
Xu CP, Nasrollahzadeh M, Selva M, Issaabadi Z, Luque R (2019) Waste-to-wealth: biowaste valorization into valuable bio(nano)materials. Chem Soc Rev 48(18):4791–4822. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cs00543e
Yadav P, Jie CJ, Tan S, Srinivasan M (2020) Recycling of cathode from spent lithium iron phosphate batteries. J Hazard Mater 399:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123068
Zhang BL, Xie HW, Lu BH, Chen X, Xing PF, Qu JK, Yin HY (2019a) A green electrochemical process to recover Co and Li from spent LiCoO2-based batteries in molten salts. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(15):13391–13399. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02657
Zhang GW, He YQ, Feng Y, Wang HF, Zhu XN (2018) Pyrolysis-ultrasonic-assisted flotation technology for recovering graphite and LiCoO2 from spent lithium-ion batteries. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(8):10896–10904. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02186
Zhang GW, He YQ, Wang HF, Feng Y, Xie WN, Zhu XN (2019b) Application of mechanical crushing combined with pyrolysis-enhanced flotation technology to recover graphite and LiCoO2 from spent lithium-ion batteries. J Clean Prod 231:1418–1427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.279
Zhang YN, Zhang YY, Zhang YJ, Dong P, Meng Q, Xu ML (2019c) Novel efficient regeneration of high-performance Li-1.2 Mn0.56Ni0.16Co0.08 O-2 cathode materials from spent LiMn2O4 batteries. J Alloy Compd 783:357–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.359
S Zhao W Zhang G Li H Zhu J Huang W He 2020a Ultrasonic renovation mechanism of spent LCO batteries: a mild condition for cathode materials recycling ResourConserv Recycl 162 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105019
Zhao SQ, Li GM, He WZ, Huang JW, Zhu HC (2019) Recovery methods and regulation status of waste lithium-ion batteries in China: a mini review. Waste Manage Res 37(11):1142–1152. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242x19857130
Zhao SQ, Zhang WX, Li GM, Zhu HC, Huang JW, He WZ (2020b) Ultrasonic renovation mechanism of spent LCO batteries: a mild condition for cathode materials recycling. Resour Conserv Recycl 162:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105019
Zheng CJ, Yuan JF, Zhu L, Zhang YJ, Shao QH (2020) From digital to sustainable: a scientometric review of smart city literature between 1990 and 2019. J Clean Prod 258:24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120689
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Funding of Shanghai Institute of Pollution Control and Ecological Security (HJGFXK-2017–002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Siqi Zhao: Conceptualization and Writing—original draft preparation; Jiawei Quan, Tianya Wang: Methodology; Duanmei Song: Formal analysis and investigation; Wenzhi He: Writing—review and editing; Juwen Huang: Resources; Guangming Li: Funding acquisition and Supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S., Quan, J., Wang, T. et al. Unveiling the recycling characteristics and trends of spent lithium-ion battery: a scientometric study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 9448–9461 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17814-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17814-7