Abstract
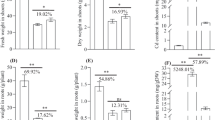
Boron (B) has previously been shown to inhibit cadmium (Cd) uptake in wheat. Here, we investigated the physiological response of external B application (C for no B added, B for B added, B+Cd for B and Cd added, B/Cd for B 24 h pretreatment before Cd added, B and Cd were 46.2 μM and 5 μM, respectively) on wheat growth under Cd stress. The results showed that the wheat growth was significantly weaker under Cd treatment, while B application did not significantly improve the wheat growth under Cd stress. However, B application decreased Cd concentrations and malondialdehyde (MDA) concentrations of shoot and root. The key enzyme activities including superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD) significantly increased under Cd treatments while decreased under B treatments. Further, a total of 198, 680 and 204 of the differential metabolites were isolated between B and C treatment, Cd and C treatment and B+Cd and Cd treatment, respectively. The metabolites with up-accumulation in B application (B+Cd) roots were mainly galactaric acid, citric acid, N6-galacturonyl-L-lysine, D-glucose, while the metabolites with down-accumulation were mainly threoninyl-tryptophan and C16 sphinganine. The differential metabolic pathways were mainly concentrated in linoleic acid metabolism, galactose metabolism, sphingolipid metabolism, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, propanoate metabolism in diabetic complications between B+Cd treatment and B treatment. The results indicate that B alleviates Cd toxicity in winter wheat by inhibiting Cd uptake, increasing antioxidant enzyme activity and changing metabolites.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Abbasi GH, Akhtar J, Anwar-ul-Haq M, Malik W, Ali S, Chen ZH, Zhang G (2015) Morpho-physiological and micrographic characterization of maize hybrids under NaCl and Cd stress. Plant Growth Regul 75:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-014-9936-6
Astolfi S, Zuchi S, Neumann G, Cesco S, Sanità di Toppi L, Pinton R (2012) Response of barley plants to Fe deficiency and Cd contamination as affected by S starvation. J Exp Bot 63:1241–1250. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err344
Bali AS, Sidhu GPS, Kumar V (2020) Root exudates ameliorate cadmium tolerance in plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 18:1243–1275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01012-x
Bellaloui N (2012) Phomopsis seed infection effects on soybean seed phenol, lignin, and isoflavones in maturity group V genotypes differing in phomopsis resistance. J Crop Improv 26:693–710. https://doi.org/10.1080/15427528.2012.671236
Chen D, Chen D, Xue R, Long J, Lin X, Lin Y, Jia L, Zeng R, Song Y (2019) Effects of boron, silicon and their interactions on cadmium accumulation and toxicity in rice plants. J Hazard Mater 367:447–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.111
Chen Q, Lu X, Guo X, Pan Y, Yu B, Tang Z, Guo Q (2018) Differential responses to Cd stress induced by exogenous application of Cu, Zn or Ca in the medicinal plant Catharanthus roseus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 157:266–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.055
Clemens S, Aarts MG, Thomine S, Verbruggen N (2013) Plant science the key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning. Trends Plant Sci 18:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2012.08.003
Dong XC, Liu GD, Wu XW, Lu XP, Muhammad R, Yan L, Muhammad R, Shah A, Wu L, Jiang CC (2016) Different metabolite profile and metabolic pathway with leaves and roots in response to boron deficiency at the initial stage of citrus rootstock growth. Plant Physiol Biochem 108:121–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.07.007
Duan MM, Wang S, Huang DY, Zhu QH, Liu SL, Zhang Q, Zhu HH, Xu C (2018) Effectiveness of simultaneous applications of lime and zinc/iron foliar sprays to minimize cadmium accumulation in rice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:510–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.037
Ernst WHO, Krauss GJ, Verkleij JAC, Wesenberg D (2008) Interaction of heavy metals with the sulphur metabolism in angiosperms from an ecological point of view. Plant Cell Environ 31:123–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01746.x
Fahad S, Hussain S, Khan F, Wu C, Saud S, Hassan S, Ahmad N, Gang D, Ullah A, Huang J (2015) Effects of tire rubber ash and zinc sulfate on crop productivity and cadmium accumulation in five rice cultivars under field conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:12424–12434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4518-3
Feki-Tounsi M, Hamza-Chaffai A (2014) Cadmium as a possible cause of bladder cancer: a review of accumulated evidence. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:10561–10573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2970-0
Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Iannone MF, Rosales EP, Zawoznika MS, Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2012) Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83:33–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.04.006
Garg N, Manchanda G (2009) ROS generation in plants: boon or bane? Plant Biosys 143:81–96. https://doi.org/10.1080/11263500802633626
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutase: 1 Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.59.2.309
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016
He P, Lu Y, Liang Y, Chen B, Wu M, Li S, He G, Jin T (2013) Exposure assessment of dietary cadmium: findings from Shanghainese over 40 years China. BMC Public Health 13:590. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-13-590
Hseu Z, Su S, Lai H, Guo H, Chen T, Chen Z (2010) Remediation techniques and heavy metal uptake by different rice varieties in metal-contaminated soils of Taiwan: new aspects for food safety regulation and sustainable agriculture. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 56:31–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0765.2009.00442.x
Hu Y, Norton GJ, Duan G, Huang Y, Liu Y (2014) Effect of selenium fertilization on the accumulation of cadmium and lead in rice plants. Plant Soil 384:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2189-3
Jasinski M, Ducos E, Martinoia E, Bountry M (2003) The ATP-binding cassette transporters: structure, function, and gene family comparison between rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 131:1169–1177. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.102.014720
Li X, Li Y, Mai J, Tao L, Qu M, Liu J, Shen R, Xu G, Feng Y, Xiao H, Wu L, Shi L, Guo S, Liang J, Zhu Y, He Y, Baluška F, Shabala S, Yu M (2018) Boron alleviates aluminum toxicity by promoting root alkalization in transition zone via polar auxin transport. Plant Physiol 177:1254–1266. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.00188
Lin L, Zhou W, Dai H, Cao F, Zhang G, Wu F (2012) Selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice. J Hazard Mater 235–236:343–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.08.012
Lu L, Tian S, Zhang J, Yang X, Labavitch JM, Webb SM, Latimer M, Brown PH (2013) Efficient xylem transport and phloem remobilization of Zn in the hyperaccumulator plant species Sedum alfredii. New Phytol 198:721–731. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12168
Ma J, Cai H, He C, Zhang W, Wang L (2015) A hemicellulose-bound form of silicon inhibits cadmium ion uptake in rice (Oryza sativa) cells. New Phytol 206:1063–1074. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13276
Ma JF, Shen RF, Shao JF (2021) Transport of cadmium from soil to grain in cereal crops: a review. Pedosphere 31(1):3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(20)60015-7
Meda AR, Scheuermann EB, Prechsl UE, Erenoglu B, Schaaf G, Hayen H, Weber G, von Wiren N (2007) Iron acquisition by phytosiderophores contributes to cadmium tolerance. Plant Physiol 143:1761–1773. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.094474
Molins H, Michelet L, Lanquar V, Agorio A, Giraudat J, Roach T, Krieger-Liszkay A, Thomine S (2013) Mutants impaired in vacuolar metal mobilization identify chloroplasts as a target for cadmium hypersensitivity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 36(4):804–817. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12016
Nakamura S, Suzuic N, Yin Y, Ishii S, Fujimaki S, Kawachi N, Rai H, Matsumoto T, Sato-Izawa K, Ohkama-Ohtsu N (2020) Effects of enhancing endogenous and exogenous glutathione in roots on cadmium movement in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci 290:110304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110304
Qin S, Sun X, Hu C, Tan Q, Zhao X, Xin J, Wen X (2017) Effect of NO3−:NH4+ ratios on growth, root morphology and leaf metabolism of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) seedlings. Acta Physiol Plant 39(9):198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2491-9
Qin S, Liu H, Nie Z, Gao W, Li C, Lin Y, Zhao P (2018) AsA-GSH cycle and antioxidant enzymes play important roles in Cd tolerance of wheat. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101:684–690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2471-9
Qin S, Liu H, Nie Z, Rengel Z, Gao W, Li C, Zhao P (2020) Toxicity of cadmium and its competition with mineral nutrients for uptake by plants: a review. Pedosphere 30(2):168–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(20)60002-9
Qin S, Liu H, Rengel Z, Gao W, Nie Z, Li C, Hou M, Cheng J, Zhao P (2020) Boron inhibits cadmium uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum) by regulating gene expression. Plant Sci 297:110522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110522
Qin X, Nie Z, Liu H, Zhao P, Qin S, Shi Z (2018) Influence of selenium on root morphology and photosynthetic characteristics of winter wheat under cadmium stress. Environ Exp Bot 150:232–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.03.024
Ramtahal G, Umaharan P, Hanuman A, Davis C, Ali L (2019) The effectiveness of soil amendments, biochar and lime, in mitigating cadmium bioaccumulation in Theobroma cacao L. Sci Total Environ 693:133563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.369
Rizwan M, Ali S, Abbas T, Zia-Ur-Rehman M, Hannan F, Keller C, Al-Wabel MI, Ok YS (2016) Cadmium minimization in wheat: a critical review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 130:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.04.001
Schat H, Llugany M, Vooijs R, Hartley-Whitaker J, Bleeker PM (2002) The role of phytochelatins in constitutive and adaptive heavy metal tolerance in hyperaccumulator and non-hyperaccumulator metallophytes. J Exp Bot 53:2381–2392. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erf107
Semane B, Cuypers A, Smeets K, Van Belleghem F, Horemans N, Schat H, Vangronsveld J (2007) Cadmium responses in Arabidopsis thaliana: glutathione metabolism and antioxidative defence system. Physiol Plant 129:519–528. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2006.00822.x
Shireen F, Nawaz MA, Chen C, Zhang Q, Zheng Z, Sohail H, Sun JY, Cao HS, Huang Y, Bie Z (2018) Boron: functions and approaches to enhance its availability in plants for sustainable agriculture. Int J Mol Sci 19:1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071856
Uraguchi S, Fujiwara T (2012) Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation. Rice 5:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1939-8433-5-5
Wang S, Wang F, Gao S (2015) Foliar application with nano-silicon alleviates Cd toxicity in rice seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:2837–2845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3525-0
Wang MY, Chen AK, Wong MH, Qiu L, Cheng H, Ye ZH (2011) Cadmium accumulation in and tolerance of rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties with different rates of radial oxygen loss. Environ Pollut 159:1730–1736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.02.025
Wu X, Liu G, Riaz M, Yan L, Jiang C (2018) Metabolic changes in roots of trifoliate orange [Poncirus trifoliate (L.) Raf.] as induced by different treatments of boron deficiency and resupply. Plant Soil 434:217–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3684-8
Wu X, Riaz M, Yan L, Du C, Liu Y, Jiang C (2017) Boron deficiency in Trifoliate orange induces changes in pectin composition and architecture of components in root cell walls. Front Plant Sci 8:1882. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01882
Wu Z, Liu S, Zhao J, Wang F, Du Y, Zou S, Li H, Wen D, Huang Y (2017) Comparative responses to silicon and selenium in relation to antioxidant enzyme system and the glutathione-ascorbate cycle in flowering Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis var. utilis) under cadmium stress. Environ Exp Bot 133:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.09.005
Wu Z, Wang F, Liu S, Du Y, Li F, Du R, Wen D, Zhao J (2016) Comparative responses to silicon and selenium in relation to cadmium uptake, compartmentation in roots, and xylem transport in flowering Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis var. utilis) under cadmium stress. Environ Exp Bot 131:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.07.012
Zhang M, Hu C, Zhao X, Tan Q, Sun X, Cao A, Cui M, Zhang Y (2012) Molybdenum improves antioxidant and osmotic-adjustment ability against salt stress in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. Pekinensis). Plant Soil 355:375–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-1109-z
Zimeri AM, Dhankher OP, Mccaig B, Meagher RB (2005) The plant MT1 metallothioneins are stabilized by binding cadmiums and are required for cadmium tolerance and accumulation. Plant Mol Biol 58(6):839–855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-005-8268-3
Funding
This research was funded by the Chinese State Natural Science Foundation (32002128), the Scientific and Technological Key Projects of Henan Province (212102310979, 202102110213) and Key Scientific Research Project of the Higher Education Institutions of Henan Province (20A210018). We thank Shanghai Lu Ming Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) for assistance with LC-MS metabonomics analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SQ and PZ conceived and designed the research. SQ, ZN, CL and YX perform all the experiments, supervised the study, implemented the method and performed data analysis, interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript. WG and HL supervised the study and checked the results. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, S., Xu, Y., Nie, Z. et al. Metabolomic and antioxidant enzyme activity changes in response to cadmium stress under boron application of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 34701–34713 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17123-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17123-z