Abstract
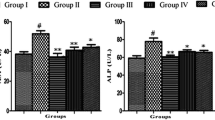
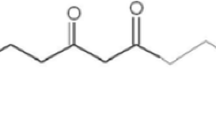
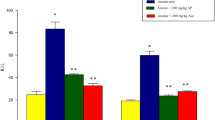
Arsenic (As) is known for its carcinogenic and hepatorenal toxic effects causing serious health problems in human beings. Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) extracted curcumin (Cur) is a polyphenolic antioxidant which has ability to combat hazardous environmental toxicants. This study (28 days) was carried out to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of different doses of Cur (Cur: 80, 160, 240 mg kg−1) against the oxidative damage in the liver and kidney of male rats caused by sodium arsenate (Na3AsO4) (10 mg L−1). As exposure significantly elevated the values of organ index, markers of hepatic injury (i.e., alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP)) and renal functions (i.e., total bilirubin, urea and creatinine, total cholesterol, total triglycerides, and lipid peroxidation malondialdehyde (MDA)). Moreover, different antioxidant markers such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and glutathione reductase (GR) activities in the liver and kidney tissues were reduced after As-induced toxicity. However, Na3AsO4 induced histopathological changes in various organs were minimized after the treatment with Cur. The alleviation effect of Cur was dosage dependent with an order of 240>160>80 mg kg−1. The oral administration of Cur prominently alleviated the As-induced toxicity in liver and kidney tissues by reducing lipid peroxidation, ALT, AST, ALP, total bilirubin, urea, creatinine, total cholesterol, total triglycerides, and low-density lipoproteins (LDL). In addition, Cur being an antioxidant improved defense system by enhancing activities of SOD, CAT, GPx, and GR. Overall, the findings explain the capability of Cur to counteract the oxidative alterations as well as hepatorenal injuries due to As intoxication.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aebi H (1984) Methods in enzymology, Volume. 105, Catalase in vitro. Chance, Britt. Acta Chem Scand 1:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Akcura M, Turan V, Kokten K, Kaplan M (2019) Fatty acid and some micro element compositions of cluster bean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba) genotype seeds growing under Mediterranean climate. Ind Crop Prod 128:140–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.10.062
Akman F, Turan V, Sayyed MI, Akdemir F, Kaçal MR, Durak R, Zaid MHM (2019) Comprehensive study on evaluation of shielding parameters of selected soils by gamma and X-rays transmission in the range 13.94–88.04 keV using WinXCom and FFAST programs. Results Phys 15:102751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102751
Allen T, Rana SVS (2007) Effect of n-propylthiouracil or thyroxine on arsenic trioxide toxicity in the liver of rat. J Trace Elem Med Biol 21:194–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2007.04.004
Anderson N, Borlak J (2008) Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets in steatosis and steatohepatitis. Pharmacol Rev 60:311–357. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.108.00001
Apaydin FG, Aslanturk A, Uzunhisarcikli M, Bas H, Kalender S, Kalender Y (2019) Histopathological and biochemical studies on the effect of curcumin and taurine against bisphenol A toxicity in male rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:12302–12310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04578-4
Bahrami A, Sathyapalan T, Moallem SA, Sahebkar A (2020) Counteracting arsenic toxicity: curcumin to the rescue? J Hazard Mater 400:123160
Belfield A, Goldberg DM (1971) Normal ranges and diagnostic value of serum 5′nucleotidase and alkaline phosphatase activities in infancy. Arch Dis Child 46:842–846. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.46.250.842
Bilen S, Bilen M, Turan V (2019) Relationships between cement dust emissionsand soil properties. Pol J Environ Stud 28:3089–3098. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/92521
Brown KG, Ross GL (2002) Arsenic, drinking water, and health: a position paper of the American Council on Science and Health. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 36:162–174. https://doi.org/10.1006/rtph.2002.1573
Brunati AM, Pagano MA, Bindoli A, Rigobello MP (2010) Thiol redox systems and protein kinases in hepatic stellate cell regulatory processes. Free Radic Res 44:363–378. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715760903555836
Celik I, Gallicchio L, Boyd K, Lam TK, Matanoski G, Tao X, Shiels M, Hammond E, Chen L, Robinson KA, Caulfield LE, Herman JG, Guallar E, Alberg AJ (2008) Arsenic in drinking water and lung cancer: a systematic review. Environ Res 108:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2008.04.001
Cheraghi E, Roshanaei K (2019) The protective effect of curcumin against aluminum chloride-induced oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity in rats. Pharm Biomed Res. https://doi.org/10.18502/pbr.v5i1.761
Chromý V, Rozkošná K, Sedlák P (2008) Determination of serum creatinine by Jaffe method and how to calibrate to eliminate matrix interference problems. Clin Chem Lab Med 46:1127–1133. https://doi.org/10.1515/CCLM.2008.224
Conterato GMM, Augusti PR, Somacal S, Einsfeld L, Sobieski R, Torres JRV, Emanuelli T (2007) Effect of lead acetate on cytosolic thioredoxin reductase activity and oxidative stress parameters in rat kidneys. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 101:96–100. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2007.00084.x
Czeczot H, Ścibior D, Skrzycki M, Podsiad M (2006) Glutathione and GSH-dependent enzymes in patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Biochim Pol 53:237–241. https://doi.org/10.18388/abp.2006_3384
El-Demerdash FM, Yousef MI, Radwan FME (2009) Ameliorating effect of curcumin on sodium arsenite-induced oxidative damage and lipid peroxidation in different rat organs. Food Chem Toxicol 47:249–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2008.11.013
Ercal N, Neal R, Treeratphan P, Lutz PM, Hammond TC, Dennery PA, Spitz DR (2000) A role for oxidative stress in suppressing serum immunoglobulin levels in lead-exposed fisher 344 rats. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:251–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010102
Fahad S, Sönmez O, Saud S, Wang D, Wu C, Adnan M, Turan V (2021a) Plant growth regulators for climate-smart agriculture. In: Footprints of climate variability on plant diversity, 1st edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Fahad S, Sonmez O, Saud S, Wang D, Wu C, Adnan M, Turan V (2021b) Climate change and plants: biodiversity, growth and interactions. In: Footprints of climate variability on plant diversity, 1st edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Fahad S, Sonmez O, Saud S, Wang D, Wu C, Adnan M, Turan V (2021c) Developing climate resilient crops: improving global food security and safety. In: Footprints of climate variability on plant diversity, 1st edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Fahad S, Sönmez O, Turan V, Adnan M, Saud S, Wu C, Wang D (2021d) Sustainable soil and land management and climate change. In: Footprints of climate variability on plant diversity, 1st edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Farkhondeh T, Samarghandian S (2016) The hepatoprotective effects of curcumin against drugs and toxic agents: an updated review. Toxin Rev 35:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2016.1215333
Flora SJS, Mehta A (2009) Monoisoamyl dimercaptosuccinic acid abrogates arsenic-induced developmental toxicity in human embryonic stem cell-derived embryoid bodies: comparison with in vivo studies. Biochem Pharmacol 78:1340–1349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009.07.003
Flora SJS, Pachauri V (2010) Chelation in metal intoxication. Int J Environ Res Public Health 7:2745–2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7072745
Garber CC (1981) Jendrassik-Grof analysis for total and direct bilirubin in serum with a centrifugal analyzer. Clin Chem 27:1410–1416. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/27.8.1410
Ghosh D, Ghosh S, Sarkar S, Ghosh A, Das N, Saha KD, Mandal AK (2010) Quercetin in vesicular delivery systems: evaluation in combating arsenic-induced acute liver toxicity associated gene expression in rat model. Chem Biol Interact 186:61–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2010.03.048
Guo X, Liu X, Wang J, Fu X, Yao J, Zhang X, Jackson S, Li J, Zhang W, Sun D (2020) Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) ameliorates arsenic-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction in rats and toxicity in endothelial EA.hy926 cells. Environ Res 186:109506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109506
Gupta SC, Sung B, Kim JH, Prasad S, Li S, Aggarwal BB (2013) Multitargeting by turmeric, the golden spice: from kitchen to clinic. Mol Nutr Food Res 57:1510–1528. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201100741
Hashish EA, Elgaml SA (2016) Hepatoprotective and nephroprotective effect of curcumin against copper toxicity in rats. Indian J Clin Biochem 31:270–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-015-0527-8
Hossain K, Suzuki T, Hasibuzzaman MM, Islam MS, Rahman A, Paul SK, Tanu T, Hossain S, Saud ZA, Rahman M, Nikkon F, Miyataka H, Himeno S, Nohara K (2017) Chronic exposure to arsenic, LINE-1 hypomethylation, and blood pressure: a cross-sectional study in Bangladesh. Environ Health A Glob Access Sci Source 16:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-017-0231-7
Hossen MS, Tanvir EM, Prince MB, Paul S, Saha M, Ali MY, Gan SH, Khalil MI, Karim N (2017) Protective mechanism of turmeric (Curcuma longa) on carbofuran-induced hematological and hepatic toxicities in a rat model. Pharm Biol 55:1937–1945. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2017.1345951
Iftikhar S, Turan V, Tauqeer HM, Rasool B, Zubair M, Mahmood-ur-Rahman, Khan MA, Akhtar S, Khan SA, Basharat Z, Zulfiqar I, Iqbal J, Iqbal M, Ramzani PMA (2021) Phytomanagement of As-contaminated matrix: physiological and molecular basis. In: Handbook of Bioremediation. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 61–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819382-2.00005-3
Jagadeesan G, Bharathi E (2014) In vivo restoration of hepatic and nephro protective potential of hesperidin and ellagic acid against mercuric chloride intoxicated rats. Biomed Aging Pathol 4:219–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomag.2014.01.008
Jiang JQ, Ashekuzzaman SM, Jiang A, Sharifuzzaman SM, Chowdhury SR (2013) Arsenic contaminated groundwater and its treatment options in bangladesh. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:18–46. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10010018
Kamran M, Malik Z, Parveen A, Huang L, Riaz M, Bashir S, Mustafa A, Abbasi GH, Xue B, Ali U (2020) Ameliorative effects of biochar on rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) growth and heavy metal immobilization in soil irrigated with untreated wastewater. J Plant Growth Regul 39:266–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-09980-3
Kamran M, Danish M, Saleem MH, Malik Z, Parveen A, Abbasi GH, Jamil M, Ali S, Afzal S, Riaz M, Rizwan M, Ali M, Zhou Y (2021) Application of abscisic acid and 6-benzylaminopurine modulated morpho-physiological and antioxidative defense responses of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) by minimizing cobalt uptake. Chemosphere 263:128169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128169
Kaya C, Aydemir S, Sonmez O, Ashraf M, Dikilitas M (2013) Regulation of growth and some key physiological processes in salt-stressed maize (Zea mays L.) plants by exogenous application of asparagine and glycerol. Acta Bot Croat 72(1):157–168
Kim JY, Paik JK, Kim OY, Park HW, Lee JH, Jang Y, Lee JH (2011) Effects of lycopene supplementation on oxidative stress and markers of endothelial function in healthy men. Atherosclerosis 215:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.11.036
Lakhani HV, Sharma D, Dodrill MW, Nawab A, Sharma N, Cottrill CL, Shapiro JI, Sodhi K (2018) Phenotypic alteration of hepatocytes in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Med Sci 15:1591–1599. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.27953
Lawrence RA, Burk RF (1976) Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 71:952–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291X(76)90747-6
Mahdavinia M, Alizadeh S, Vanani AR, Dehghani MA, Shirani M, Alipour M, Shahmohammadi HA, Asl SR (2019) Effects of quercetin on bisphenol A-induced mitochondrial toxicity in rat liver. Iran J Basic Med Sci 22:499–505. https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2019.32486.7952
Mailafiya MM, Abubakar K, Chiroma SM, Danmaigoro A, Rahim EBA, Mohd Moklas MA, Zakaria ZAB (2020) Curcumin-loaded cockle shell-derived calcium carbonate nanoparticles: a novel strategy for the treatment of lead-induced hepato-renal toxicity in rats. Saudi J Biol Sci 27:1538–1552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.03.009
Mehrzadi S, Fatemi I, Malayeri AR, Khodadadi A, Mohammadi F, Mansouri E, Rashno M, Goudarzi M (2018) Ellagic acid mitigates sodium arsenite-induced renal and hepatic toxicity in male Wistar rats. Pharmacol Rep 70:712–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2018.02.007
Mershiba SD, Dassprakash MV, Saraswathy SD (2013) Protective effect of naringenin on hepatic and renal dysfunction and oxidative stress in arsenic intoxicated rats. Mol Biol Rep 40:3681–3691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2444-8
Mishra D, Mehta A, Flora SJS (2008) Reversal of arsenic-induced hepatic apoptosis with combined administration of DMSA and its analogues in guinea pigs: role of glutathione and linked enzymes. Chem Res Toxicol 21:400–407. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx700315a
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)45228-9
Mittal M, Flora SJS (2007) Vitamin E supplementation protects oxidative stress during arsenic and fluoride antagonism in male mice. Drug Chem Toxicol 30:263–281. https://doi.org/10.1080/01480540701380075
Mohamed AA-R, El-Houseiny W, Abd Elhakeem E-M, Ebraheim LLM, Ahmed AI, Abd El-Hakim YM (2020) Effect of hexavalent chromium exposure on the liver and kidney tissues related to the expression of CYP450 and GST genes of Oreochromis niloticus fish: Role of curcumin supplemented diet. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 188:109890
Moon K, Guallar E, Navas-Acien A (2012) Arsenic exposure and cardiovascular disease: an updated systematic review. Curr Atheroscler Rep 14:542–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-012-0280-x
Moron MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B (1979) Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 582:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4165(79)90289-7
Namgyal D, Ali S, Mehta R, Sarwat M (2020) The neuroprotective effect of curcumin against Cd-induced neurotoxicity and hippocampal neurogenesis promotion through CREB-BDNF signaling pathway. Toxicology 442:152542
Navas-Acien A, Sharrett AR, Silbergeld EK, Schwartz BS, Nachman KE, Burke TA, Guallar E (2005) Arsenic exposure and cardiovascular disease: a systematic review of the epidemiologic evidence. Am J Epidemiol 162:1037–1049. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwi330
Ogun M, Ozcan A, Karaman M, Merhan O, Ozen H, Kukurt A, Karapehlivan M (2016) Oleuropein ameliorates arsenic induced oxidative stress in mice. J Trace Elem Med Biol 36:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2016.03.006
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Oyedemi SO, Bradley G, Afolayan AJ (2010) In -vitro and -vivo antioxidant activities of aqueous extract of Strychnos henningsii Gilg. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol 4:070–078
Pandey A, Chaturvedi M, Mishra S, Kumar P, Somvanshi P, Chaturvedi R (2020) Reductive metabolites of curcumin and their therapeutic effects. Heliyon 6:e05469
Parveen A, Hamzah Saleem M, Kamran M, Zulqurnain Haider M, Chen JT, Malik Z, Shoaib Rana M, Hassan A, Hur G, Tariq Javed M, Azeem M (2020) Effect of citric acid on growth, ecophysiology, chloroplast ultrastructure, and phytoremediation potential of jute (Corchorus capsularis l.) seedlings exposed to copper stress. Biomolecules 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040592
Rabbani U, Fatmi Z (2020) Arsenic contamination of drinking water and mitigation in Pakistan: a case of Indus river basin, pp 273–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-21258-2_12
Rees H, Duncan S, Gould P, Wells R, Greenwood M, Brabbs T, Hall A (2019) A high-throughput delayed fluorescence method reveals underlying differences in the control of circadian rhythms in Triticum aestivum and Brassica napus. Plant Methods 15:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-019-0436-6
Reitman S, Frankel S (1957) A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol 28:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcp/28.1.56
Saber TM, Abo-Elmaaty AMA, Abdel-Ghany HM (2019) Curcumin mitigates mancozeb-induced hepatotoxicity and genotoxicity in rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 183:109467
Sahne F, Mohammadi M, Najafpour GD, Moghadamnia AA (2016) Extraction of bioactive compound curcumin from turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) via different routes: a comparative study. Pakistan J. Biotechnol. 13:173–180
Sankar P, Gopal Telang A, Kalaivanan R, Karunakaran V, Manikam K, Sarkar SN (2015) Effects of nanoparticle-encapsulated curcumin on arsenic-induced liver toxicity in rats. Environ Toxicol 30:628–637. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.21940
Sayyed MI, Akman F, Turan V, Araz A (2019) Evaluation of radiation absorption capacity of some soil samples. Radiochim Acta 107:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1515/ract-2018-2996
Seif MM, Madboli AN, Marrez DA, Aboulthana WMK (2019) Hepato-renal protective effects of Egyptian purslane extract against experimental cadmium toxicity in rats with special emphasis on the functional and histopathological changes. Toxicol Rep 6:625–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.06.013
Seo EY, Ha AW, Kim WK (2012) α-lipoic acid reduced weight gain and improved the lipid profile in rats fed with high fat diet. Nutr Res Pract 6:195–200. https://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2012.6.3.195
Sharma RA, Hill KA, Williams ML, Steward WP, Ireson CR, Verschoyle RD, Leuratti C, Manson MM, Gescher A, Marnett LJ (2001) Effects of dietary curcumin on glutathione S-transferase and malondialdehyde-DNA adducts in rat liver and colon mucosa: Relationship with drug levels. Clin Cancer Res 7:1452–1458
Shirzadfar H, Amirzadeh P, Hajinoroozi MH (2019) A comprehensive study over the jaundice causes and effects on newborns and reviewing the treatment effects. Int J Biosens Bioelectron 5:107–112
Soliman MM, Baiomy AA, Yassin MH (2015) Molecular and histopathological study on the ameliorative effects of curcumin against lead acetate-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrototoxicity in Wistar rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 167:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0280-0
Sonmez O, Aydemir S, Kaya C (2009) Mitigation effects of mycorrhiza on boron toxicity in wheat (Triticum durum) plants. N Z J Crop Hortic Sci 37(2):99–104
Sonmez O, Turan V, Kaya C (2016) The effects of sulfur, cattle, and poultry manure addition on soil phosphorus. Turk J Agric For 40:536–541. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1601-41
Sreejayan N, Rao MNA (1994) Curcuminoids as potent inhibitors of lipid peroxidation. J Pharm Pharmacol 46:1013–1016. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.1994.tb03258.x
Strimpakos AS, Sharma RA (2008) Curcumin: Preventive and therapeutic properties in laboratory studies and clinical trials. Antioxid Redox Signal 10:511–546. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2007.1769
Sun Q, Yang Q, Xu H, Xue J, Chen C, Yang X, Gao X, Liu Q (2019) MiR-149 negative regulation of mafA is involved in the arsenite-induced dysfunction of insulin synthesis and secretion in pancreatic beta cells. Toxicol Sci 167:4–125. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfy150
Tauqeer HM, Fatima M, Rashid A, Shahbaz AK, Ramzani PMA, Farhad M, Basharat Z, Turan V, Iqbal M (2021a) The current scenario and prospects of immobilization remediation technique for the management of heavy metals contaminated soils. In: Hasanuzzaman M (ed) Approaches to the Remediation of Inorganic Pollutants. Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp 155–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6221-1_8
Tauqeer HM, Karczewska A, Lewińska K, Fatima M, Khan SA, Farhad M, Turan V, Ramzani PMA, Iqbal M (2021b) Environmental concerns associated with explosives (HMX, TNT, and RDX), heavy metals and metalloids from shooting range soils: Prevailing issues, leading management practices, and future perspectives. In: Handbook of Bioremediation. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 569–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819382-2.00036-3
Tripoli E, La Guardia M, Giammanco S, Di Majo D, Giammanco M (2007) Citrus flavonoids: Molecular structure, biological activity and nutritional properties: a review. Food Chem 104:466–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.11.054
Trujillo J, Chirino YI, Molina-Jijón E, Andérica-Romero AC, Tapia E, Pedraza-Chaverrí J (2013) Renoprotective effect of the antioxidant curcumin: Recent findings. Redox Biol 1:448–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2013.09.003
Turan V (2019) Confident performance of chitosan and pistachio shell biochar on reducing Ni bioavailability in soil and plant plus improved the soil enzymatic activities, antioxidant defense system and nutritional quality of lettuce. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 183:109594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109594
Turan V (2020) Potential of pistachio shell biochar and dicalcium phosphate combination to reduce Pb speciation in spinach, improved soil enzymatic activities, plant nutritional quality, and antioxidant defense system. Chemosphere 245:125611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125611
Turan V (2021a) Calcite in combination with olive pulp biochar reduces Ni mobility in soil and its distribution in chili plant. Int J Phytoremediation:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2021.1929826
Turan V (2021b) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and pistachio husk biochar combination reduces Ni distribution in mungbean plant and improves plant antioxidants and soil enzymes. Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13490
Turan V, Schröder P, Bilen S, Insam H, Fernández-Delgado Juárez M (2019) Co-inoculation effect of Rhizobium and Achillea millefolium L. oil extracts on growth of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and soil microbial-chemical properties. Sci Rep 9:15178. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51587-x
Uzunhisarcikli M, Aslanturk A (2019) Hepatoprotective effects of curcumin and taurine against bisphenol A-induced liver injury in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:37242–37253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06615-8
Uzunhisarcikli M, Aslanturk A, Kalender S, Apaydin FG, Bas H (2016) Mercuric chloride induced hepatotoxic and hematologic changes in rats: the protective effects of sodium selenite and vitamin E. Toxicol Ind Health 32:1651–1662
Vahouny GV, Khalafi R, Satchithanandam S, Watkins DW, Story JA, Cassidy MM, Kritchevsky D (1987) Dietary fiber supplementation and fecal bile acids, neutral steroids and divalent cations in rats. J Nutr 117:2009–2015. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/117.12.2009
Visnagri A, Adil M, Kandhare AD, Bodhankar SL (2015) Effect of naringin on hemodynamic changes and left ventricular function in renal artery occluded renovascular hypertension in rats. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 7:121–127. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-7406.154437
Wybenga DR, Di Giorgio J, Pileggi VJ (1971) Manual and automated methods for urea nitrogen measurement in whole serum. Clin Chem 17:891–895. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/17.9.891
Yadav RS, Sankhwar ML, Shukla RK, Chandra R, Pant AB, Islam F, Khanna VK (2009) Attenuation of arsenic neurotoxicity by curcumin in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 240:367–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2009.07.017
Yadav A, Lomash V, Samim M, Flora SJS (2012) Curcumin encapsulated in chitosan nanoparticles: a novel strategy for the treatment of arsenic toxicity. Chem Biol Interact 199:49–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2012.05.011
Yang Q, Xie RJ, Geng XX, Luo XH, Han B, Cheng ML (2005) Effect of Danshao Huaxian capsule on expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in fibrotic liver of rats. World J Gastroenterol 11:4953–4956. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i32.4953
Yoon KN, Alam N, Lee JS, Cho HJ, Kim HY, Shim MJ, Lee MW, Lee TS (2011) Antihyperlipidemic effect of dietary Lentinus edodes on plasma, feces and hepatic tissues in hypercholesterolemic rats. Mycobiology 39:96–102. https://doi.org/10.4489/MYCO.2011.39.2.096
Yousef MI, Omar SAM, El-Guendi MI, Abdelmegid LA (2010) Potential protective effects of quercetin and curcumin on paracetamol-induced histological changes, oxidative stress, impaired liver and kidney functions and haematotoxicity in rat. Food Chem Toxicol 48:3246–3261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.08.034
Yu C, Mei XT, Zheng YP, Xu DH (2014) Zn(II)-curcumin protects against hemorheological alterations, oxidative stress and liver injury in a rat model of acute alcoholism. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37:729–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2014.02.011
Acknowledgements
The authors highly acknowledge the Department of Chemistry and Faculty of Veterinary Sciences at The University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, for providing experimental materials and analyzing the samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Ali Hassan, Muhammad Kamran, Shah Fahad; data curation: Anam Ishaq, Muhammad Riaz, Aasma Parveen; formal analysis: Anam Ishaq, Huma Gulzar; Muhammad Sohaib Chattha, Noman Walayat; investigation: Anam Ishaq, Huma Gulzar; methodology: Anam Ishaq, Sana Fatima; resources: Muhammad Riaz, Ali Hassan, Muhammad Kamran; writing—original draft: Anam Ishaq, Huma Gulzar, Muhammad Kamran; writing—review and editing: Shah Fahad, Muhammad Sohaib Chattha, Sobia Afzal, Muhammad Kamran; supervision: Shah Fahad, Ali Hassan
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
We all declare this manuscript reporting studies does not involve any human participants, human data, or human tissue. So ethics approval and consent to participate is not applicable.
Consent for publication
Our manuscript does not contain data from any individual person, so consent for publication is not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishaq, A., Gulzar, H., Hassan, A. et al. Ameliorative mechanisms of turmeric-extracted curcumin on arsenic (As)-induced biochemical alterations, oxidative damage, and impaired organ functions in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 66313–66326 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15695-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15695-4