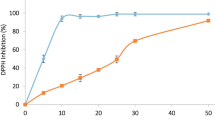
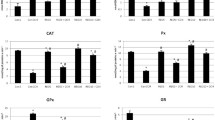
Abstract
Curcumin is a natural anti-inflammatory and antioxidant with several potential health benefits. Although it has been examined in several metals toxicity studies, but its role in the protection against copper toxicity has not been investigated. In this study; the detoxification and antioxidant effect of curcumin were examined to determine its prophylactic/therapeutic role experimentally in rats. Forty albino rats were divided into five groups; control, CuSO4 (4 mg/kg body weight), curcumin (80 mg/kg body weight), curcumin post-treatment (CuSO4 for 15 days followed by curcumin for the next 15 days) and curcumin co-treatment (CuSO4 plus curcumin for 30 days). All rats were treated orally by stomach tube for 30 days/once a day. Changes were observed in hepatic marker enzymes such as: aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine transaminase-(ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT), besides the serum total protein, urea and creatinine. Concentration of liver and kidney antioxidants such as: catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), reduced glutathione-(GSH) and malondialdehyde (MDA) were measured. An increased in the activities of liver marker enzymes, urea, creatinine and the MDA contents were detected after exposure to CuSO4. Meanwhile, the activities of serum total protein, hepatic and renal antioxidants were decreased. Changes in all biochemical parameters were alleviated by the post-treatment and co-treatment of curcumin. Our finding suggests that the curcumin showed protective effects on CuSO4-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trumbo P, Yates AA, Schlicker S, Poos M. Dietary reference intakes: vitamin A, vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, silicon, vanadium, and zinc. J Am Diet Assoc. 2001;101(3):294–301.
Barceloux DG. Copper. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1999;37(2):217–30.
Abuja PM, Albertini R. Methods for monitoring oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation and oxidation resistance of lipoproteins. Clin Chim Acta. 2001;306(1–2):1–17.
Hassan S, Shaikh MU, Ali N, Riaz M. Copper sulphate toxicity in a young male complicated by methemoglobinemia, rhabdomyolysis and renal failure. J Coll Phys Surg-Pak: JCPSP. 2010;20(7):490–1.
Galhardi CM, Diniz YS, Faine LA, Rodrigues HG, Burneiko RC, Ribas BO, et al. Toxicity of copper intake: lipid profile, oxidative stress and susceptibility to renal dysfunction. Food Chem Toxicol. 2004;42(12):2053–60.
Jurenka JS. Anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin, a major constituent of Curcuma longa: a review of preclinical and clinical research. Altern Med Rev. 2009;14(2):141–53.
Eigner D, Scholz D. Ferula asa-foetida and Curcuma longa in traditional medical treatment and diet in Nepal. J Ethnopharmacol. 1999;67(1):1–6.
El-Masry AA. Toxicity and hepatorenal response to acute copper exposure in rats. Glob Adv Res J Biochem Bioinform. 2012;1(1):1–6.
Agarwal R, Goel SK, Behari JR. Detoxification and antioxidant effects of curcumin in rats experimentally exposed to mercury. J of Appl Toxicol. 2010;30(5):457–68.
Reitman S, Frankel S. A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957;28(1):56–63.
Seligman AM, Chauncey HH, Nachlas MM, Manheimer LH, Ravin HA. Colorimetric determination of serum alkaline phosphatases in human serum. J Biol Chem. 1951;190:7–15.
Fuke H, Yagi H, Takegoshi C, Kondo T. A sensitive automated colorimetric method for the determination of serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Clin Chim Acta. 1976;69(1):43–51.
Krohn RI. The colorimetric detection and quantitation of total protein. Current protocols in cell biology/editorial board, Juan S Bonifacino et al. 2002; Appendix 3:Appendix 3H.
Tabacco A, Meiattini F, Moda E, Tarli P. Simplified enzymic/colorimetric serum urea nitrogen determination. Clin Chem. 1979;25(2):336–7.
Heinegard D, Tiderstrom G. Determination of serum creatinine by a direct colorimetric method. Clin Chim Acta. 1973;43(3):305–10.
Sidhu P, Garg ML, Dhawan DK. Protective effects of zinc on oxidative stress enzymes in liver of protein-deficient rats. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2005;28(2):211–30.
Aebi H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:121–6.
Weydert CJ, Cullen JJ. Measurement of superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in cultured cells and tissue. Nat Protoc. 2010;5(1):51–66.
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH. Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem. 1968;25:14.
Valenzuela A. The biological significance of malondialdehyde determination in the assessment of tissue oxidative stress. Life Sci. 1991;48(4):301–9.
Suvarna SK, Layton C, Bancroft JD. Bancroft’s theory and practice of histological techniques. 7th ed. England: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2013.
Bewick V, Cheek L, Ball J. Statistics review 9: one-way analysis of variance. Crit Care. 2004;8(2):130–6.
Leong PK, Chiu PY, Ko KM. Prooxidant-induced glutathione antioxidant response in vitro and in vivo: a comparative study between schisandrin B and curcumin. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(4):464–72.
Eybl V, Kotyzova D, Bludovska M. The effect of curcumin on cadmium-induced oxidative damage and trace elements level in the liver of rats and mice. Toxicol Lett. 2004;151(1):79–85.
Wang T, Long X, Cheng Y, Liu Z, Yan S. The potential toxicity of copper nanoparticles and copper sulphate on juvenile Epinephelus coioides. Aquat Toxicol. 2014;152:96–104.
Sharma S, Kulkarni SK, Chopra K. Curcumin, the active principle of turmeric (Curcuma longa), ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2006;33(10):940–5.
Tirkey N, Kaur G, Vij G, Chopra K. Curcumin, a diferuloylmethane, attenuates cyclosporine-induced renal dysfunction and oxidative stress in rat kidneys. BMC Pharmacol. 2005;5:15.
Zhang SS, Noordin MM, Rahman SO, Haron J. Effects of copper overload on hepatic lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense in rats. Vet Hum Toxicol. 2000;42(5):261–4.
Trujillo J, Chirino YI, Molina-Jijon E, Anderica-Romero AC, Tapia E, Pedraza-Chaverri J. Renoprotective effect of the antioxidant curcumin: recent findings. Redox Biol. 2013;1(1):448–56.
Pinlaor S, Yongvanit P, Prakobwong S, Kaewsamut B, Khoontawad J, Pinlaor P, et al. Curcumin reduces oxidative and nitrative DNA damage through balancing of oxidant-antioxidant status in hamsters infected with Opisthorchis viverrini. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2009;53(10):1316–28.
Hwang DF, Wang LC, Cheng HM. Effect of taurine on toxicity of copper in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 1998;36(3):239–44.
Bruzell EM, Morisbak E, Tonnesen HH. Studies on curcumin and curcuminoids. XXIX. Photoinduced cytotoxicity of curcumin in selected aqueous preparations. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2005;4(7):523–30.
Joe B, Lokesh BR. Role of capsaicin, curcumin and dietary n-3 fatty acids in lowering the generation of reactive oxygen species in rat peritoneal macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1224(2):255–63.
Lagasse E, Connors H, Al-Dhalimy M, Reitsma M, Dohse M, Osborne L, et al. Purified hematopoietic stem cells can differentiate into hepatocytes in vivo. Nat Med. 2000;6(11):1229–34.
Ikarashi K, Li B, Suwa M, Kawamura K, Morioka T, Yao J, et al. Bone marrow cells contribute to regeneration of damaged glomerular endothelial cells. Kidney Int. 2005;67(5):1925–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in the current work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashish, E.A., Elgaml, S.A. Hepatoprotective and Nephroprotective Effect of Curcumin Against Copper Toxicity in Rats. Ind J Clin Biochem 31, 270–277 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-015-0527-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-015-0527-8