Abstract
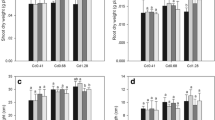
Selenium (Se), iron (Fe), and humic acid (HA) are beneficial fertilizers that inhibit cadmium (Cd) uptake in crops and are crucial for agricultural yields as well as human health. However, the joined effect of Se, Fe, and HA on Cd uptake in rice are still poorly understood. Therefore, a hydroponic culture experiment was established to evaluate the combined effect of Se (Se4+ or Se6+), Fe, and HA on the biomass, Cd uptake, and Cd translocation of/in rice seedlings. Compared to Se6+ application, Se4+ application in most treatments resulted in lower Cd translocations from roots to shoots, leading to a significant decrease in shoot Cd concentrations. Compared to the treatments with Se4+ or Fe2+ application, joined application of Se4+ and Fe2+ inhibited Cd uptake in shoots by decreasing Cd adsorption onto (iron plaque) and uptake by roots, and alleviating Cd translocation from root to shoot. Compared to the treatments with Se6+ or Fe2+ application, joined application of Se6+ and Fe2+ inhibited Cd uptake in shoots by sequestering (retaining) Cd onto root surface (iron plaque). HA inhibited Cd uptake in all treatments by decreasing the bioavailability of Cd in the nutrient solution through complexation. The simultaneous application of Se, Fe, and HA decreased the shoot Cd concentrations the most, followed by the combined application of two fertilizers and their individual application; the mean shoot Cd concentration in the Fe-SeIV-HA2 treatment was the lowest among all the treatments, at only 11.39 % of those in the control treatments. The 3-way ANOVA results indicated that the Cd concentrations in shoots were significantly affected by Se, Fe, HA, and certain of their interactions (Fe×Se and Se×HA) (p< 0.05). The above findings suggest that the joined application of Se, Fe, and HA ameliorated Cd uptake mainly by inhibiting Cd adsorption onto (iron plaque) and uptake by roots and the translocation from roots to shoots (Fe×Se4+), retaining (sequestering) Cd in iron plaque (Fe×Se6+), and decreasing Cd availability in nutrient solution (HA).
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data sets supporting the results of this article are included within the article and its additional files.
References
Baik MH, Lee SY, Jeong J (2013) Sorption and reduction of selenite on chlorite surfaces in the presence of Fe(II) ions. J Environ Radioact 126:209–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2013.08.005
Bashir K, Ishimaru Y, Nishizawa NK (2010) Iron uptake and loading into rice grains. Rice 3:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12284-010-9042-y
Bouis HE, Welch RM (2010) Biofortification-a sustainable agricultural strategy for reducing micronutrient malnutrition in the global south. Crop Sci 50:S20–S30. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2009.09.0531
Cabrera D, Young SD, Rowell DL (1988) The toxicity of cadmium to barley plants as affected by complex formation with humic acid. Plant Soil 105:195–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02376783
Chang H, Zhou XB, Wang WH, Zhou YX, Dai WC, Zhang CM, Yu SH (2013) Effects of selenium application in soil on formation of iron plaque outside roots and cadmium uptake by rice. Adv Mater Res 750-752:1573–1576. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.750-752.1573
Chen MX, Cao L, Song X, Wang XY, Qian QP, Liu W (2014) Effect of iron plaque and selenium on cadmium uptake and translocation in rice seedlings (Oryza sativa) grown in solution culture. Int J Agric Biol 16:1159–1164. https://doi.org/10.1092/2014/16-6-1159-1164
Chen C, Xia SG, Deng RB, Liu CF, Shi GR (2017) AhIRT1 and AhNRAMP1 metal transporter expression correlates with Cd uptake in peanuts under iron deficiency. PLoS ONE 12:e0185144. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185144
Connorton JM, Balk J (2019) Iron biofortification of staple crops: lessons and challenges in plant genetics. Plant Cell Physiol 60:1447–1456. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcz079
Cui JH, Liu TX, Li YD, Li FB (2018) Selenium reduces cadmium uptake into rice suspension cells by regulating the expression of lignin synthesis and cadmium-related genes. Sci Total Environ 644:602–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.002
Ding YZ, Feng RW, Wang RG, Guo JK, Zheng XQ (2014) A dual effect of Se on Cd toxicity: evidence from plant growth, root morphology and responses of the antioxidative systems of paddy rice. Plant Soil 375:289–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1966-8
Duan MM, Wang S, Huang DY, Zhu QH, Liu SL, Zhang Q, Zhu HH, Xu C (2018) Effectiveness of simultaneous applications of lime and zinc/iron foliar sprays to minimize cadmium accumulation in rice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:510–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.037
Evangelou MW, Daghan H, Schaeffer A (2004) The influence of humic acids on the phytoextraction of cadmium from soil. Chemosphere 57:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.06.017
Fu YQ, Yang XJ, Shen H (2018) Root iron plaque alleviates cadmium toxicity to rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 161:534–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.06.015
Gao L, Chang JD, Chen RJ, Li HB, Lu HF, Tao LX, Xiong J (2016) Comparison on cellular mechanisms of iron and cadmium accumulation in rice: prospects for cultivating Fe-rich but Cd-free rice. Rice 9:39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-016-0112-7
García AC, Santos LA, Izquierdo FG, Sperandio MVL, Castro RN, Berbara RLL (2012) Vermicompost humic acids as an ecological pathway to protect rice plant against oxidative stress. Ecol Eng 47:203–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.06.011
García AC, Santos LA, Izquierdo FG, Rumjanek VM, Castro RN, Santos FSD, Souza LGAD, Berbara RLL (2014) Potentialities of vermicompost humic acids to alleviate water stress in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). J Geochem Explor 136:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.10.005
García AC, Santos LA, Souza LGAD, Tavares OCH, Zonta E, Gomes ETM, García-Mina JM, Berbara RLL (2016) Vermicompost humic acids modulate the accumulation and metabolism of ROS in rice plants. J Plant Physiol 192:56–63
Gustafsson JP, Pechova P, Berggren D (2003) Modeling metal binding to soils: the role of natural organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 37:2767–2774. https://doi.org/10.1021/es026249t
Hamid Y, Tang L, Hussain B, Usman M, Lin Q, Rashid M, He ZL, Yang XE (2020) Organic soil additives for the remediation of cadmium contaminated soils and their impact on the soil-plant system: a review. Sci Total Environ 707:136121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136121
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. California Agricultural Experiment Station, California
Hu Y, Norton GJ, Duan G, Huang YC, Liu YX (2014) Effect of selenium fertilization on the accumulation of cadmium and lead in rice plants. Plant Soil 384:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2189-3
Hu Y, Cheng H, Tao S (2016) The challenges and solutions for cadmium-contaminated rice in China: a critical review. Environ Int 92-93:515–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.04.042
Huang QQ, Yu Y, Wang Q, Luo Z, Jiang RF, Li HF (2014) Uptake kinetics and translocation of selenite and selenate as affected by iron plaque on root surfaces of rice seedlings. Planta 241:907–916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-014-2227-7
Huang QQ, Wang Q, Luo Z, Yu Y, Jiang RF, Li HF (2015) Effects of root iron plaque on selenite and selenate dynamics in rhizosphere and uptake by rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Soil 388:255–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2329-9
Huang BF, Xin JL, Dai H, Zhou WJ (2017) Effects of interaction between cadmium (Cd) and selenium (Se) on grain yield and Cd and Se accumulation in a hybrid rice (Oryza sativa) system. J Agric Food Chem 65:9537–9546. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03316
Huang QQ, Liu YY, Xu Q, Zhao LJ, Liang XF, Xu YM (2019) Selenite mitigates cadmium-induced oxidative stress and affects Cd uptake in rice seedlings under different water management systems. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 168:486–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.10.078
Huang GX, Ding CF, Li YS, Zhang TL, Wang XX (2020) Selenium enhances Fe plaque formation by elevating the radial oxygen loss of roots to reduce cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Hazard Mater 398:122860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122860
Huang HL, Li M, Rizwan M, Dai ZH, Yuan Y, Hossain MMH, Cao MH, Xiong SL, Tu SX (2021) Synergistic effect of silicon and selenium on the alleviation of cadmium toxicity in rice plants. J Hazard Mater 401:123393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123393
Irshad MK, Chen C, Noman A, Ibrahim M, Adeel M, Shang JY (2020) Goethite-modified biochar restricts the mobility and transfer of cadmium in soil-rice system. Chemosphere 242:125152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125152
Ismael MA, Elyamine AM, Moussa MG, Cai MM, Zhao XH, Hu CX (2019) Cadmium in plants: uptake, toxicity, and its interactions with selenium fertilizers. Metallomics 11:255–277. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8mt00247a
Jing F, Chen C, Chen XM, Liu W, Hu SM, Yang ZJ, Guo BL, Xu YL, Yu QX (2020) Effects of wheat straw derived biochar on cadmium availability in a paddy soil and its accumulation in rice. Environ Pollut 257:113592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113592
Khan MIR, Nazir F, Asgher M, Per TS, Khan NA (2015) Selenium and sulfur influence ethylene formation and alleviate cadmium-induced oxidative stress by improving proline and glutathione production in wheat. J Plant Physiol 173:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2014.09.011
Khan N, Seshadri B, Bolan N, Saint CP, Kirkham MB, Chowdhury S, Yamaguchi N, Lee DY, Li G, Kunhikrishnan A, Qi F, Karunanithi R, Qiu R, Zhu YG, Syu CH (2016) Root iron plaque on wetland plants as a dynamic pool of nutrients and contaminants. Adv Agron 138:1–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.agron.2016.04.002
Kubier A, Richard T, Pichler T (2019) Cadmium in soils and groundwater: a review. Appl Geochem 108:104388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.104388
Li J, Liu JC, Yan CL, Du DL, Lu HL (2019a) The alleviation effect of iron on cadmium phytotoxicity in mangrove A. marina. Alleviation effect of iron on cadmium phytotoxicity in mangrove Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Chemosphere 226:413–420
Li HB, Zheng XW, Tao LX, Yang YJ, Gao L, Xiong J (2019b) Aeration increases cadmium (Cd) retention by enhancing iron plaque formation and regulating pectin synthesis in the roots of rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings. Rice (N Y) 12:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-019-0291-0
Liu HJ, Zhang JL, Zhang FS (2007) Role of iron plaque in Cd uptake by and translocation within rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings grown in solution culture. Environ Exp Bot 59:314–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2006.04.001
Liu JG, Cao CX, Wong MH, Zhang ZJ, Chai YH (2010) Variations between rice cultivars in iron and manganese plaque on roots and the relation with plant cadmium uptake. J Environ Sci 22:1067–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60218-7
Liu N, Jiang ZM, Li X, Liu HY, Li N, Wei SQ (2020) Mitigation of rice cadmium (Cd) accumulation by joint application of organic amendments and selenium (Se) in high-Cd-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 241:125106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125106
Nakanishi H, Ogawa I, Ishimaru Y, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2006) Iron deficiency enhances cadmium uptake and translocation mediated by the Fe2+ transporters OsIRT1 and OsIRT2 in rice. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 52:464–469. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0765.2006.00055.x
Natasha SM, Niazi NK, Khalid S, Murtaza B, Bibi I, Rashid MI (2018) A critical review of selenium biogeochemical behavior in soil-plant system with an inference to human health. Environ Pollut 234:915–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.019
Olaetxea M, Hita DD, Garcia CA, Fuentes M, Baigorri R, Mora V, Garnica M, Urrutia O, Erro J, Zamarreño AM, Berbara RL, Garcia-Mina JM (2018) Hypothetical framework integrating the main mechanisms involved in the promoting action of rhizospheric humic substances on plant root- and shoot- growth. Appl Soil Ecol 123:521–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.06.007
Ondrasek G, Rengel Z, Romic D (2018) Humic acids decrease uptake and distribution of trace metals, but not the growth of radish exposed to cadmium toxicity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 151:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.12.055
Rafiq MT, Aziz R, Yang XE, Xiao WD, Rafiq MK, Ali B, Li TQ (2014) Cadmium phytoavailability to rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown in representative Chinese soils. A model to improve soil environmental quality guidelines for food safety. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 103:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.10.016
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Rizvi H, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Hannan F, Qayyum Haffeez F, Ok YS (2016) Cadmium stress in rice: toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and management: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:17859–17879
Schnitzer M, Gupta UC (1965) Determination of acidity in soil organic matter. Soil Sci Soc Am J 29:274–277. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1965.03615995002900030016x
Sharma A, Shankhdhar D, Shankhdhar SC (2013) Enhancing grain iron concentration of rice by the application of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Plant Soil Environ 59:89–94. https://doi.org/10.17221/683/2012-PSE
Swift RS (1996) Organic matter characterization. In: Sparks DL, Bartels JM, Bigham JM (eds) Methods of soil analysis: part 3 chemical methods. Soil Sci Soc Am J 5:1011–1069. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser5.3.c35
Taylor GJ, Crowder AA (1983) Use of the DCB technique for extraction of hydrous iron oxides from roots of wetland plants. Am J Bot 70:1254–1257. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1983.tb12474.x
Wan Y, Yu Y, Wang Q, Qiao YH, Li HF (2016) Cadmium uptake dynamics and translocation in rice seedling: Influence of different forms of selenium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 133:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.07.001
Wang X, Tam NFY, Fu S, Ametkhan A, Ouyang Y, Ye ZH (2014) Selenium addition alters mercury uptake, bioavailability in the rhizosphere and root anatomy of rice (Oryza sativa). Ann Bot 114:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcu117
Wang R, Wei S, Jia PH, Liu T, Hou DD, Xie RH, Lin Z, Ge J, Qiao YB, Chang XY, Lu LL, Tian SK (2019) Biochar significantly alters rhizobacterial communities and reduces Cd concentration in rice grains grown on Cd-contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 676:627–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.133
Wang J, Li D, Lu Q, Zhang YL, Xu HJ, Wang XL, Li YT (2020) Effect of water-driven changes in rice rhizosphere on Cd lability in three soils with different pH. J Environ Sci 87:82–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.05.020
Yang WT, Zhou H, Gu JF, Zeng QR, Liao BH (2017) Influence of rapeseed cake on iron plaque formation and Cd uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings exposed to excess Cd. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 99:601–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2151-1
Yang BB, Yang C, Shao ZY, Wang H, Zan ST, Zhu M, Zhou SB, Yang RY (2019) Selenium (Se) does not reduce cadmium (Cd) uptake and translocation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) in naturally occurred Se-rich paddy fields with a high geological background of Cd. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 103:127–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02551-y
Yang L, Fan L, Huang B, Xin JL (2020) Efficiency and mechanisms of fermented horse manure, vermicompost, bamboo biochar, and fly ash on Cd accumulation in rice. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:27859–27869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09150-z
Yu Y, Wan Y, Wang Q, Li HF (2017) Effect of humic acid-based amendments with foliar application of Zn and Se on Cd accumulation in tobacco. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 138:286–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.01.011
Yu Y, Fu PN, Huang QQ, Zhang JS, Li HF (2019a) Accumulation, subcellular distribution, and oxidative stress of cadmium in Brassica chinensis supplied with selenite and selenate at different growth stages. Chemosphere 216:331–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.138
Yu RG, Jiang Q, Xv C, Li L, Bu SJ, Shi GR (2019b) Comparative proteomics analysis of peanut roots reveals differential mechanisms of cadmium detoxification and translocation between two cultivars differing in cadmium accumulation. BMC Plant Biology 19:137. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1739-5
Yu Y, Zhuang Z, Luo LY, Wang YQ, Li HF (2019c) Difference between selenite and selenate in selenium transformation and the regulation of cadmium accumulation in Brassica chinensis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:24532–24541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05705-x
Zhang LQ, Song HX, Guo YB, Fan B, Huang YT, Mao XF, Liang KH, Hu ZQ, Sun XD, Fang Y, Mei XH, Yin HQ, Li BR, Wang YT, Liu XJ, Lu BY (2020a) Benefit-risk assessment of dietary selenium and its associated metals intake in China (2017-2019): is current selenium-rich agro-food safe enough? J Hazard Mater 398:123224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123224
Zhang HY, Xie SY, Bao ZY, Tian H, Carranza EJM, Xiang W, Yao LY, Zhang H (2020b) Underlying dynamics and effects of humic acid on selenium and cadmium uptake in rice seedlings. J Soils Sediments 20:109–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02413-4
Zhao YY, Hu CX, Wu ZC, Liu XW, Cai MM, Jia W, Zhao XH (2019) Selenium reduces cadmium accumulation in seed by increasing cadmium retention in root of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Environ Exp Bot 158:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.11.017
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Test Center of Zhejiang Institute, China University of Geosciences, for element analysis support.
Funding
This work has been jointly supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41872250), the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2019CFB235), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) (Grant No. CUG170104; G1323520058), the funds of Science and Technology Research of Ankang City (AK2020FX01-9), the Young Science and Technology New Star project of Shaanxi Province (2021KJXX-98).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hongyu Zhang: conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft. Shuyun Xie: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition. Zhengyu Bao: formal analysis. Emmanuel John M. Carranza: writing—review and editing. Huan Tian: formal analysis. Changhua Wei: investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
(1) Joined application of Se, Fe, and HA inhibited shoot Cd concentrations by decreasing Cd migration.
(2) Se4+ decreased Cd uptake more effectively than Se6+ by inhibited Cd translocation in plant tissues.
(3) Iron plaque alleviated Cd uptake, but the mechanism is associated with the presence and species of Se.
(4) HA inhibited Cd uptake by reducing the bioavailability of Cd in the nutrient solution.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, ., Xie, S., Bao, Z. et al. Synergistic inhibitory effect of selenium, iron, and humic acid on cadmium uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings in hydroponic culture. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 64652–64665 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15527-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15527-5