Abstract
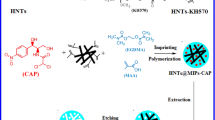
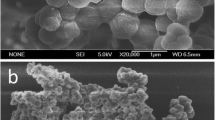
In this work, the effect of a carrier modified with a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C) on preparing multi-templates surface molecularly imprinted polymer MIP (C=C@MIP) for simultaneous detection of sulfonamides and quinolones was investigated. The results showed that the adsorption capacities of the C=C@MIP were obviously higher than those of MIP, which is the carrier without modified C=C, suggesting that C=C played a key role in preparing MIP with higher adsorption capacities. Then, C=C@MIP was used as adsorbents for solid-phase extraction (SPE) and coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the simultaneous determination of sulfonamides and quinolones in water. The method showed excellent applicability, with the adsorption capacities of 19.92, 16.38, 12.92, 18.37, 14.49, 12.01, 16.98, 23.33, and 14.29 mg/g for SDZ, STZ, SMZ, SMX, SDM, ENRO, OFL, LOME, and GATI, respectively. The spiked recoveries and relative standard deviations (RSDs) of sulfonamides and quinolones using C=C@MIP were 81.59–100.7 % and 3.75–7.37 %, respectively. The limits of detection (LODs) for SDZ, STZ, SMZ, SMX, SDM, ENRO, OFL, LOME, and GATI were 0.013, 0.012, 0.012, 0.013, 0.014, 0.012, 0.013, 0.015, and 0.015 μg/L, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcaráz MR, Bortolato SA, Goicoechea HC, Olivieri AC (2015) A new modeling strategy for third-order fast high-performance liquid chromatographic data with fluorescence detection. Quantitation of fluoroquinolones in water samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:1999–2011
Ali A, Christina SB (2020) A critical review of molecularly imprinted polymers for the analysis of organic pollutants in environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1614:460603
Antonio VHH, Javier HB, Teresa MBM, Miguel Ángel Rodríguez D (2013) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography for the simultaneous determination of 25 sulfonamide and quinolone antibiotics in water samples. J Pharm Biomed Anal 75:130–137
Dmitrienko SG, Kochuk EV, Apyari VV (2014) Recent advances in sample preparation techniques and methods of sulfonamides detection-A review Apyari. Anal Chim Acta 850:6–25
Fan YM, Zeng GL, Ma XG (2020a) Effects of prepolymerization on surface molecularly imprinted polymer for rapid separation and analysis of sulfonamides in water. J Colloid Interface Sci 571:21–29
Fan YM, Zeng GL, Ma XG (2020b) Multi-templates surface molecularly imprinted polymer for rapid separation and analysis of quinolones in water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:7177–7187
Francisco B, Beatriz A, José LT, Antonio ME (2019) Molecularly imprinted polymer-hollow fiber microextraction of hydrophilic fluoroquinolone antibiotics in environmental waters and urine samples. J Chromatogr A 1587:42–49
Gu FB, Liang M, Han DM, Wang ZH (2015) Multifunctional sandwich-like mesoporous silica-Fe3O4-graphene oxide nanocomposites for removal of methylene blue from water. RSC Adv 5:39964–39972
Guo LH, Ma XG, Xie XW (2019) Preparation of dual-dummy-template molecularly imprinted polymers coated magnetic graphene oxide for separation and enrichment of phthalate in water. Chem Eng J 2019:245–255
Han S, Li X, Wang Y, Chen SN (2015) Multifunctional imprinted polymers based on CdTe/CdS and magnetic graphene oxide for selective recognition and separation of p-t-octylphenol. Chem Eng J 271:87–95
Herrera-Herrera AV, Hernández-Borges J, Afonso MM, Palenzuela JA, Rodríguez-Delgado MÁ (2013) Comparison between magnetic and non-magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes-dispersive solid-phase extraction combined with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of sulfonamide antibiotics in water samples. Talanta 116:695–703
Huang YH, Wang YZ, Pan Q, Wang Y (2015) Magnetic graphene oxide modified with choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvent for the solid-phase extraction of protein. Anal Chim Acta 877:90–99
Kong X, Gao RX, He XW, Chen LX, Zhang YK (2012) Synthesis and characterization of the core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers (Fe3O4@MIPs) adsorbents for effective extraction and determination of sulfonamides in the poultry feed. J Chromatogr A 1245:8–16
Lang L, Dong XQ, Di JB (2018) Determination of 11 Antibiotics in Harbin Section of Songhua river by SPE-HPLC. China Water Wastewater 34(20):114–118
Li XW, He YD, Zhang W, Xu H, Huang QL, Zhou ZF, Xu LJ (2018) Pollution Status of Sulfonamides in Aquatic Environment and Its Ecotoxicological Effects on Aquatic Organisms. Eni Sci Tech 41(S1):62–6s
Lombardo-Agüí M, García-Campana AM, Cruces-Blanco C, Gámiz-Gracia L (2015) Determination of quinolones in fish by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection using QuEChERS as sample treatment. Food Control 50:864–868
Nazia T, Shahjadi K, Boris BD (2020) Perspective and application of molecular imprinting approach for antibiotic detection in food and environmental samples: A critical review. Food Control 118:107381
Niharika K, Nazim FI, Songita S, Ram P, Hemen S (2021) Environmental antibiotics and resistance genes as emerging contaminants: Methods of detection and bioremediation. Curr Res Microb Sci 2:100027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crmicr.2021.100027
Peng YL (2018) Investigation and Study on Antibiotic Abuse. J Guiyang Uni Chin Med 40(5):81–85
Rocha DG, Santos FA, Silva JC, Augusti R, Faria AF (2015) Multiresidue determination of fluoroquinolones in poultry muscle and kidney according to the regulation 2002/657/EC. A systematic comparison of two different approaches: liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry or tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1379:83–91
Shi XZ, Meng Y, Liu JH, Sun AL, Li DX, Yao CX, Lu Y, Chen J (2011) Group-selective molecularly imprinted polymer solid-phase extraction for the simultaneous determination of six sulfonamides in aquaculture products. J Chromatogr B 879:1071–1076
Sun HW, Qiao FX (2008) Recognition mechanism of water-compatible molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and determination of nine quinolones in urine by high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1212:1–9
Sun L, Chen LG, Sun X, Du XB, Yue YS, He DQ, Xu HY, Zeng QL, Wang H, Ding L (2009) Analysis of sulfonamides in environmental water samples based on magnetic mixed hemimicelles solid-phase extraction coupled with HPLC-UV detection. Chemosphere 77:1306–1312
Supuran CT, Casini A, Scozzafava A (2003) Protease inhibitors of the sulfonamide type: Anticancer, antiinflammatory, and antiviral agents. Med Res Rev 23(5):535–558
Tang YW, Liu H, Gao JW, Liu XY, Gao X, Lu XN, Fang GZ, Wang JP, Li JR (2018) Upconversion particle@Fe3O4@molecularly imprinted polymer with controllable shell thickness as high-performance fluorescent probe for sensing quinolones. Talanta 181:95–103
Wang ZM, Wang WD, Coombs N, Soheilnia N, Ozin GA (2010) Graphene oxide-periodic mesoporous silica sandwich nanocomposites with vertically oriented channels. J Acs Nano 4:437–7450
Wojciech B, Ewa A, Justyna Z, Andrzej S (2011) Effects of the presence of sulfonamides in the environment and their influence on human health. J Hazard Mater 196:1–15
Xie XW, Ma XG, Guo LH (2019) Novel magnetic multi-templates molecularly imprinted polymer for selective and rapid removal and detection of alkylphenols in water. Chem Eng J 357:56–65
Xu J, Hu P, Lu JP, Guo CS (2018) Pollution characteristics and control measures of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in the aquatic environment. Sci Technol Rev 36(15):13–23
Zeng GL, Liu YY, Ma XG, Fan YM (2021) Fabrication of magnetic multi-template molecularly imprinted polymer composite for the selective and efficient removal of tetracyclines from water. Front Environ Sci Eng 15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-021-1395-5
Zhang ZC, Cheng HF (2019) Recent development in sample pretreatment and detection methods for the determination of quinolones in environmental matrices. Environ Chem 38(1):1–22
Zhang MY, Ma XG, Li J, Huang RF, Guo LH, Zhang XF, Fan YM, Zeng GL (2019) Enhanced removal of As (III) and As (V) from aqueous solution using ionic liquid-modified magnetic graphene oxide. Chemosphere 234:196–203
Zhao XL, Wang JY, Wang JP, Wang S (2018) Development of water-compatible molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the detection of six sulfonamides in animal-derived foods. J Chromatogr A 1574:9–17
Zhou QX, Fang Z (2015) Highly sensitive determination of sulfonamides in environmental water samples by sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate enhanced microsolid phase extraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 141:170–174
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the Foundation of Guangxi Science and Technology of Base & Talent Special Program (AD20159067 ) and Guilin University of Technology (GUTQDJJ2019130).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yizhen Xie: conceptualization, methodology, software, investigation, writing—original draft, data curation.
Qiuyi Li: validation, formal analysis, visualization.
Lulu Qin: validation, formal analysis, visualization.
Xiaobin Zhou: validation, formal analysis, visualization.
Yinming Fan: validation, formal analysis, visualization, resources, writing—review and editing, supervision, data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Yes. Our study does not involve human subjects.
Consent to participate
Yes.
Consent to publish
Yes.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ester Heath
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 393 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Y., Li, Q., Qin, L. et al. Multi-templates surface molecularly imprinted polymer for simultaneous and rapid determination of sulfonamides and quinolones in water: effect of carbon-carbon double bond. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 54950–54959 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14794-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14794-6