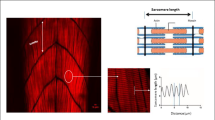
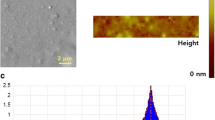
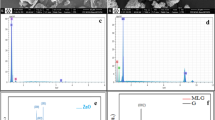
Abstract
Graphene-based nanomaterials (GBNs) have been widely used in various fields nowadays. However, they are reported to be highly toxic to some aquatic organisms. However, the multi-organ toxicity caused by pristine graphene (pG) and graphene oxide (GO) to the developing zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae or juvenile and the underlying mechanisms is not fully known. Therefore, in the present study, the effect of pG and GO with environmental concentrations (0, 5, 10, 15, 20, and 25 μg/L of pG; 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4 mg/mL of GO) on multi-organ system in developing zebrafish larvae was experimentally assessed. The pG and GO were found to accumulate in the brain tissue that also caused significant changes in the heart beat and survival rate. The sizes of hepatocytes were reduced. Altered axonal integrity, affecting axon length and pattern in “Tg(mbp:eGFP) transgenic lines” was also observed. In addition, the results indicated pathological effects in major organs and with disrupted mitochondrial structure was quite obvious. The pG and GO bioaccumulation leads to multi organ toxicity in zebrafish larvae. In future, the existence of the current study can be extrapolated to other aquatic system in general and in particularly to humans.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The obtained and analyzed data of this study are included in this article and available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Akhavan O, Ghaderi E, Akhavan A (2012) Size-dependent genotoxicity of graphene nanoplatelets in human stem cells. Biomaterials 33:8017–8025
Anzenbacher P, Anzenbacherová E (2001) Cytochromes P450 and metabolism of xenobiotics. Cell Mol Life Sci 58:737–747
Bangeppagari M, Park SH, Kundapur RR, Lee SJ (2019) Graphene oxide induces cardiovascular defects in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo model: in-vivo toxicity assessment. Sci Total Environ 673:810–820
Bianco A (2013) Graphene: safe or toxic? The two faces of the medal. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:4986–4997
Brayner R (2008) The toxicological impact of nanoparticles. Nano Today 3:48–55
Bundschuh M, Filser J, Luderwald S, Mckee MS, Metrevelis G, Schaumann GE, Schulz R, Wagner S (2018) Nanoparticles in the environment: where do we come from, where do we go to? Environ Sci Eur 30:1–17
Bussy C, Jasim D, Lozano N, Terry D, Kostarelos K (2015) The current graphene safety landscape – a literature mining exercise. Nanoscale 7:6432–6435
Chen YM, Hu XG, Sun J, Zhou QX (2016) Specific nanotoxicity of graphene oxide during zebrafish embryogenesis. Nanotoxicology 10:45–52
Chong Y, Ma Y, Shen H, Tu X, Zhou X, Xu J, Dai J, Fan S, Zhang Z (2014) The in vitro and in vivo toxicity of graphene quantum dots. Biomaterials 35:5041–5048
Chowdhury I, Duch MC, Mansukhani ND, Hersam MC, Bouchard D (2013a) Colloidal properties and stability of graphene oxide nanomaterials in the aquatic environment. Environ Sci Technol 47:6288–6296
Chowdhury SM, Lalwani G, Zhang K, Yang JY, Neville K, Sitharaman B (2013b) Cell specific cytotoxicity and uptake of graphene nanoribbons. Biomaterials 34:283–293
Dai YJ, Jia YF, Chen N, Bian WP, Li QK, Ma YB, Chen YL, Pei DS (2014) Zebrafish as a model system to study toxicology. Environ Toxicol Chem 33:11–17
Defteralí C, Verdejo R, Majeed S, Boschetti-de-Fierro A, Méndez-Gómez HR, Díaz-Guerra E, Fierro D, Buhr K, Abetz C, Martínez-Murillo R, Daniela Vuluga D, Alexandre M, Thomassin JM, Detrembleur C, Jérôme C, Abetz V, López-Manchado MA, Vicario-Abejón C (2016a) In vitro evaluation of biocompatibility of uncoated thermally reduced graphene and carbon nanotube-loaded PVDF membranes with adult neural stem cell-derived neurons and glia. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 4:94
Defteralí C, Verdejo R, Peponi L, Martín ED, Martínez-Murillo ER, López Manchado MA, Vicario-Abejón C (2016b) Thermally reduced graphene is a permissive material for neurons and astrocytes and de novo neurogenesis in the adult olfactory bulb in vivo. Biomaterials 82:84–93
Dziewiecka M, Karpeta-Kaczmarek J, Augustyniak M, Majchrzycki L, Augustyniak-Jabłokow MA (2016) Evaluation of in vivo graphene oxide toxicity for Acheta domesticus in relation to nanomaterial purity and time passed from the exposure. J Hazard Mater 305:30–40
Ersahin T, Tuncbag N, Cetin-Atalay R (2015) The PI3K/AKT/mTOR interactive pathway. Mol BioSyst 11:1946–1954
Fernandes AL, Nascimento JP, Santos AP, Furtado CA, Romano LA, da Rosa CA, Monserrat JM, Ventura-Lima J (2018) Assessment of the effects of graphene exposure in Danio rerio: a molecular, biochemical and histological approach to investigating mechanisms of toxicity. Chemosphere 210:458–466
Giese B, Klaessig F, Park B, Ralf K, Steinfeldt M, Wigger H, Gleich A, Gottschalk F (2018) Risks, release and concentrations of engineered nanomaterial in the environment. Sci Rep 8:1565
Guo X, Mei N (2014) Assessment of the toxic potential of graphene family nanomaterials. J Food Drug Anal 22:105–115
He JH, Guo SF, Zhu F, Zhu JJ, Chen YX, Huang CJ, Gao JM, Dong QX, Xuan YX, Li CQ (2013) A zebrafish phenotypic assay for assessing drug induced hepatotoxicity. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 67:25–32
He K, Chen G, Zeng G, Peng M, Huang Z, Shi J, Huang T (2017) Stability, transport and ecosystem effects of graphene in water and soil environments. Nanoscale 9:5370–5388
Jasim DA, Boutin H, Fairclough M, Ménard-Moyon C, Prenant C, Bianco A, Kostarelos K (2016) Thickness of functionalized graphene oxide sheets plays critical role in tissue accumulation and urinary excretion: a pilot PET/CT study. Appl Mater Today 4:24–30
Kanungo J, Lantz S, Paule MG (2011) In vivo imaging and quantitative analysis of changes in axon length using transgenic zebrafish embryos. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33:618–623
Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I (2019) Nanoparticles: properties, applications and toxicities. Arab J Chem 7:908–931
Kurantowicz N, Strojny B, Sawosz E, Jaworski S, Kutwin M, Grodzik M, Wierzbicki M, Lipińska L, Mitura K, Chwalibog A (2015) Biodistribution of a high dose of diamond, graphite, and graphene oxide nanoparticles after multiple intraperitoneal injections in rats. Nanoscale Res Lett 10:398
Li S, Pan X, Wallis LK, Fan Z, Chen Z, Diamond SA (2014) Comparison of TiO2 nanoparticle and graphene-TiO2 nanoparticle composite phototoxicity to Daphnia magna and Oryzias latipes. Chemosphere 12:62–69
Lim MH, Jeung IC, Jeong J, Yoon SJ, Lee SH, Park J, Kang YS, Lee H, Park YJ, Lee HG, Lee SJ, Han BS, Song NW, Lee SC, Kim JS, Bae KH, Min JK (2016) Graphene oxide induces apoptotic cell death in endothelial cells by activating autophagy via calcium-dependent phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinases. Acta Biomater 46:191–203
Lu CJ, Jiang XF, Junaid M, Ma YB, Jia PP, Wang HB, Pei DS (2017a) Graphene oxide nanosheets induce DNA damage and activate the base excision repair (BER) signaling pathway both in vitro and in vivo. Chemosphere 184:795–805
Lu K, Dong S, Petersen EJ, Niu J, Chang X, Wang P, Lin S, Gao S, Mao L (2017b) Biological uptake, distribution, and depuration of radio-labeled graphene in adult zebrafish: effects of graphene size and natural organic matter. ACS Nano 11:2872–2885
Manjunatha B, Park SH, Kim K, Kundapur RR, Lee SJ (2018a) In vivo toxicity evaluation of pristine graphene in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:12821–12829
Manjunatha B, Park SH, Kim K, Kundapur RR, Lee SJ (2018b) Pristine graphene induces cardiovascular defects in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryogenesis. Environ Pollut 243:246–254
Meyers TR, Hendricks JD (1982) A summary of tissue lesions in aquatic animals induced by controlled exposures to environmental contaminants, chemotherapeutic agents, and potential carcinogens. Mar Fish Rev 44:1–17
Modi A, Verma SK, Bellare J (2017) Graphene oxide nanosheets and d-alpha-tocopheryl ultrafiltration in polyethersulfone polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) doping improves biocompatibility and ultrafiltration in polyethersulfone hollow fiber membranes. J Colloid Interface Sci 504:86–100
Mu S, Li G, Liang Y, Wu T, Ma D (2017) Hyper branched polyglycerol-modified graphene oxide as an efficient drug carrier with good biocompatibility. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 78:639–646
Osterauer R, Köhler H, Triebskorn R (2010) Histopathological alterations and induction of hsp70 in ramshorn snail (Marisa cornuarietis) and zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos after exposure to PtCl2. Aquat Toxicol 99:100–107
Ren C, Hu X, Li X, Zhou Q (2016) Ultra-trace graphene oxide in a water environment triggers Parkinson’s disease-like symptoms and metabolic disturbance in zebrafish larvae. Biomaterials 93:83–94
Saburi E, Islami M, Hosseinzadeh S, Moghadam AS, Mansour RN, Azadian E, Joneidi Z, Nikpoor AR, Ghadiani MH, Khodaii Z, Ardeshirylajimi A (2019) In vitro osteogenic differentiation potential of the human induced pluripotent stem cells augments when grown on graphene oxide-modified nanofibers. Gene 696:72–79
Sánchez-González S, Diban N, Bianchi F, Ye H, Urtiaga A (2018) Evidences of the effect of GO and rGO in PCL membranes on the differentiation and maturation of human neural progenitor cells. Macromol Biosci 18:e1800195
Sawosz E, Jaworski S, Kutwin M, Hotowy A, Wierzbicki M, Grodzik M, Kurantowicz N, Strojny B, Lipińska L, Chwalibog A (2014) Toxicity of pristine graphene in experiments in a chicken embryo model. Int J Nanomedicine 9:3913–3922
Souza JP, Baretta JF, Santos F, Paino IMM, Zucolotto V (2017) Toxicological effects of graphene oxide on adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 186:11–18
Strojny B, Sawosz E, Grodzik M, Jaworski S, Szczepaniak J, Sosnowska M, Wierzbicki M, Kutwin M, Orlińska S, Chwalibog A (2018) Nanostructures of diamond, graphene oxide and graphite inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 enzymes and downregulate their genes in liver cells. Int J Nanomedicine 13:8561–8575
Sun J, Zhou Q, Hu X (2019) Integrating multi-omics and regular analyses identifies the molecular responses of zebrafish brains to graphene oxide: perspectives in environmental criteria. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 180:269–279
Szmidt M, Sawosz E, Urbańska K, Jaworski S, Kutwin M, Hotowy A, Wierzbicki M, Grodzik M, Lipińska L, Chwalibog A (2016) Toxicity of different forms of graphene in a chicken embryo model. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:19940–19948
Tabish TA, Pranjol MZI, Jabeend F, Abdullah T, Latif A, Khalid A, Ali M, Hayat H, Winyard PG, Whatmore JL, Zhang S (2018) Investigation into the toxic effects of graphene nanopores on lung cancer cells and biological tissues. Appl Mater Today 12:389–401
van Leeuwen LM, Evans RJ, Jim KK, Verboom T, Fang X, Bojarczuk A, van der Sar AM (2018) A transgenic zebrafish model for the in vivo study of the blood and choroid plexus brain barriers using claudin 5. Biol Open 7(2):bio030494
Vliegenthart AD, Tucker CS, Del Pozo J, Dear JW (2014) Zebrafish as model organisms for studying drug-induced liver injury. Br J Clin Pharmacol 78:1217–1227
Xu M, Zhu J, Wang F, Xiong Y, Wu Y, Wang Q, Weng J, Zhang Z, Chen W, Liu S (2016) Improved in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of graphene oxide through surface modification: poly (acrylic acid)-functionalization is superior to PEGylation. ACS Nano 10:3267–3281
Zhang J, Liss M, Wolburg H, Blasig IE, Abdelilah-Seyfried S (2012) Involvement of claudins in zebrafish brain ventricle morphogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1257(1):193–198
Zhang X, Zhou Q, Zou W, Hu X (2017) Molecular mechanisms of developmental toxicity induced by graphene oxide at predicted environmental concentrations. Environ Sci Technol 51:7861–7871
Zhao Y, Wang X, Wu Q, Li Y, Wang D (2015) Translocation and neurotoxicity of CdTe quantum dots in RMEs motor neurons in nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Hazard Mater 283:480–489
Zhao J, Cao XS, Wang ZY, Dai YH, Xing BS (2016) Mechanistic understanding toward the toxicity of graphene-family materials to freshwater algae. Water Res 111:18–27
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Korea Research Fellowship (Brain Pool Program) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (grant no. 2016H1D3A1938252).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bangeppagari Manjunatha: investigation, visualization, conceptualization, data curation, methodology, validation, formal analysis, writing - original draft, writing - review and editing, funding acquisition. Eunseok Seo: TEM analysis. Sung Ho Park: zebrafish sources. Rajesh R. Kundapur: formal analysis. Sang Joon Lee: project administration, writing – review and editing, funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experiments using zebrafish were performed according to the animal protocol approved by the Animal Care and Ethics Committee from POSTECH (POSTECH-2019-0059), South Korea.
Consent for publication
Not applicable to this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 60 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manjunatha, B., Seo, E., Park, S.H. et al. Pristine graphene and graphene oxide induce multi-organ defects in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae/juvenile: an in vivo study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 34664–34675 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13058-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13058-7