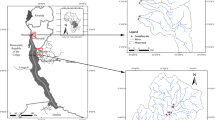
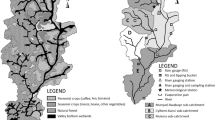
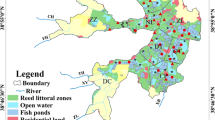
Abstract
Land uses determine water quality within riparian environments to a certain extent and directly affect human health via drinking water. The main objective of this paper is to investigate the influences of land use, both in hydrologic response units (HRUs) and 200-m-wide buffer areas, on surface water quality. The variations and interrelationships between water physicochemical properties and land uses were assessed for better management of water environment. Nitrogen was the dominant nutrient and was significantly correlated with other water quality parameters. In the HRUs and buffer areas, the dominant landscape was grassland and farmland, respectively. Total organic carbon (TOC) and dissolved oxygen (DO) had negative correlation with land use factors; nitrate nitrogen, total nitrogen, total phosphorus, electrical conductivity, and temperature, in contrast, were positively correlated with them. Industrial and residential land was the critical land use for the aquatic environment in the Dan River, indicating that point pollution should receive more attention. Vegetation area had strong regression relationships with TOC and DO. Furthermore, more specific types of land use (subcategory classification) had a greater role in water quality. The land use in buffers can act on the water body more directly and effectively.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- WQSC:
-
Water quality standard of China
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- SOC:
-
Soil organic carbon
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- PCA:
-
Pearson correlation analysis
- AN:
-
Ammonia nitrogen
- NN:
-
Nitrate nitrogen
- TN:
-
Total nitrogen
- TP:
-
Total phosphorous
- TOC:
-
Total organic carbon
- EC:
-
Electrical conductivity
- DO:
-
Dissolved oxygen
- T:
-
Temperature
- FAR:
-
Farmland
- FOR:
-
Forest
- GRA:
-
Grassland
- WAT:
-
Waters
- IRL:
-
Industrial and residential land
- BAL:
-
Bare land
- PAD:
-
Paddy field
- DRY:
-
Dry land
- HCA:
-
High coverage arbor forest
- SHR:
-
Shrub
- SPA:
-
Sparse forest
- OFL:
-
Other forest land
- HCG:
-
High coverage grassland
- MCG:
-
Medium coverage grassland
- LCG:
-
Low coverage grassland
- CAN:
-
Canal
- URB:
-
Urban
- RUR:
-
Rural
- BAR:
-
Bare lands
References
Abdul WSA (2012) Chemical safety of drinking-water: assessing priorities for risk management. Int J Environ Stud 69(06):1001
Ahearn DS, Sheibley RW, Dahlgren RA, Anderson M, Johnson J, Tate KW (2005) Land use and land cover influence on water quality in the last free-flowing river draining the western Sierra Nevada. California J Hydrol 313(3–4):234–247
Anbumozhi V, Radhakrishnan J, Yamaji E (2005) Impact of riparian buffer zones on water quality and associated management considerations. Ecol Eng 24(05):517–523
Bu HM, Meng W, Zhang Y, Wan J (2014) Relationships between land use patterns and water quality in the Taizi River basin, China. Ecol Indic 41(02):187–197
Chitapornpan S, Chiemchaisri C, Chiemchaisri W, Honda R, Yamamoto K (2013) Organic carbon recovery and photosynthetic bacteria population in an anaerobic membrane photo-bioreactor treating food processing wastewater. Bioresour Technol 141(03):65–74
De Sousa DNR, Mozeto AA, Carneiro RL, Fadini PS (2014) Electrical conductivity and emerging contaminant as markers of surface freshwater contamination by wastewater. Sci Total Environ 484(01):19–26
Dirk T, Sonja K (2014) Statistical hypothesis testing with SAS and R, Chapter 15 Tests on outliers. Wiley, Chichester, pp 219–235
Fausch KD, Baxter CV, Murakami M (2010) Multiple stressors in north temperate streams: lessons from linked forest-stream ecosystems in northern Japan. Freshw Biol 55(Supplement s1):120–134
Galbraith LM, Burns CW (2007) Linking land-use, water body type and water quality in southern New Zealand. Landsc Ecol 22(04):231–241
Haidary A, Amiri BJ, Adamowski J, Fohrer N, Nakane K (2013) Assessing the impacts of four land use types on the water quality of wetlands in Japan. Water Resour Manag 27(07):2217–2229
Kang JH, Lee SW, Cho KH, Ki SJ, Cha SM, Kim JH (2010) Linking land-use type and stream water quality using spatial data of fecal indicator bacteria and heavy metals in the Yeongsan River basin. Water Res 44(14):4143–4157
Kibena J, Nhapi I, Gumindoga W (2014) Assessing the relationship between water quality parameters and changes in landuse patterns in the upper Manyame River, Zimbabwe. Phys Chem Earth Parts 09(17):67–69 153-163
Kindler R, Siemens J, Kaiser K, Walmsley DC, Bernhofer C, Buchmann N (2011) Dissolved carbon leaching from soil is a crucial component of the net ecosystem carbon balance. Glob Chang Biol 17(02):1167–1185
Lang M, Li P, Yan X (2013) Runoff concentration and load of nitrogen and phosphorus from a residential area in an intensive agricultural watershed. Sci Total Environ 1(04):458–460 238-245
Laws EA, Ziemann D, Schulman D (1999) Coastal water quality in Hawaii: the importance of buffer zones and dilution. Mar Environ Res 48(1):1–21
Li S, Gu S, Liu W, Han H, Zhang Q (2008) Water quality in relation to the land use and land cover in the upper Han River basin, China. Catena 75(04):216–222
Li S, Gu S, Xiang T, Zhang Q (2009) Water quality in the upper Han River basin, China: the impacts of land use/land cover in riparian buffer zone. J Hazard Mater 165(1–3):317–324
Li S, Lu XX, He M, Zhou Y, Bei R, Li L (2011) Major element chemistry in the upper Yangtze River: a case study of the Longchuanjiang River. Geomorphology 129(1–2):29–42
Li Y, Li Y, Qureshi S, Kappas M, Hubacek K (2015) On the relationship between landscape ecological patterns and water quality across gradient zones of rapid urbanization in coastal China. Ecol Model 381:100–108
Liu X, Li Z, Li P (2015) Particle fractal dimension and total phosphorus of soil in a typical watershed of Yangtze River, China. Environ Earth Sci 73(10):6091–6099
Min K, Lehmeier CA, Ballantyne F, Tatarko A, Billings SA (2014) Differential effects of pH on temperature sensitivity of organic carbon and nitrogen decay. Soil Biol Biochem 76(05):193–200
Ouyang Y, Nkedi-Kizza P, Wu QT, Shinde D, Huang CH (2006) Assessment of seasonal variations in surface water quality. Water Res 40(20):3800–3810
Peng L, Ni BJ, Ye L, Yuan ZG (2015) The combined effect of dissolved oxygen and nitrite on N2O production by ammonia oxidizing bacteria in an enriched nitrifying sludge. Water Res 73(01):29–36
Qi F, Zhang R, Liu X, Niu Y, Zhang H, Li H, Li J, Wang B, Zhang G (2018) Soil particle size distribution characteristics of different land-use types in the Funiu mountainous region. Soil Tillage Res 184:45–51
Reilly J, Maggio P, Karp S (2004) A model to predict impervious surface for regional and municipal land use planning purposes. Environ Impact Assess Rev 24(03):363–382
Rizo-Decelis LD, Andreo B (2016) Water quality assessment of the Santiago River and attenuation capacity of pollutants downstream Guadalajara City, Mexico. River Res Appl 32(07):1505–1516
Rojas P, Andrea L (2014) Simple atmospheric dispersion model to estimate hourly ground-level nitrogen dioxide and ozone concentrations at urban scale. Environ Model Softw 59(05):127–134
Rood SB (2006) Riparia: ecology, conservation, and management of streamside communities. Bioence 56(04):353–354
Rosen MR, Lapham WW (2008) Introduction to the U.S. Geological Survey National Water-Quality Assessment (NAWQA) of ground-water quality trends and comparison to other national programs. J Environ Qual 37(05):190–198
Rothwell JJ, Dise NB, Taylor KG, Allott TEH, Scholefield P, Davies H (2010) A spatial and seasonal assessment of river water chemistry across north West England. Sci Total Environ 408(04):841–855
Saviozzi A, Levi-Minzi R, Riffaldi R (1994) The effect of forty years of continuous corn cropping on soil organic matter characteristics. Plant Soil 160(01):139–145
Scheili A, Rodriguez MJ, Sadiq R (2015) Seasonal and spatial variations of source and drinking water quality in small municipal systems of two Canadian regions. Sci Total Environ 508(01):514–524
Shen Z, Zhang Q, Yue C, Zhao J, Hu Z, Lv N, Tang Y (2006) The spatial pattern of land use/land cover in the water supplying area of the middle route of the south to north water diversion project. Acta Geograph Sin 61(04):633–644
Shull DR, Lookenbill M (2018) Biological data collection protocols. Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection, Harrisburg
Spieck Eva and Bock Eberhard (2015) Nitrifying bacteria. Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria: 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118960608.bm00016
Šraj LO, Almeida M, Inês GS, Swearer KSD, McKelvie ID (2014) Analytical challenges and advantages of using flow-based methodologies for ammonia determination in estuarine and marine waters. Trends Anal Chem 59(04):83–92
Stelzer RS, Scott JT (2018) Predicting nitrate retention at the groundwater-surface water interface in sandplain streams. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 123(09):2824–2838
Tabacchi E, Lambs L, Hélène G, Planty-Tabacchi AM, Decamps H (2000) Impacts of riparian vegetation on hydrological processes. Hydrol Process 14(703):2959–2976
Tang C, Yi Y, Yang Z, Cheng X (2014) Water pollution risk simulation and prediction in the main canal of the south-to-north water transfer project. J Hydrol 519(B27):2111–2120
Templer PH, Toll JW, Hutyra LR, Raciti SM (2015) Nitrogen and carbon export from urban areas through removal and export of litterfall. Environ Pollut 197(11):256–261
Thompson MY, Brandes D, Kney AD (2012) Using electronic conductivity and hardness data for rapid assessment of stream water quality. J Environ Manag 104(02):152–157
Villate F, Iriarte A, Uriarte I, Intxausti L, Alejandro DLS (2013) Dissolved oxygen in the rehabilitation phase of an estuary: influence of sewage pollution abatement and hydro-climatic factors. Mar Pollut Bull 70(1–2):234–246
Vosloo D, Vosloo A, Morillion EJ, Samuels JN, Sommer P (2013) Metabolic readjustment in juvenile South African abalone (Haliotis midae) acclimated to combinations of temperature and dissolved oxygen levels. J Therm Biol 38(07):458–466
Vought BM, Pinay G, Fuglsang A, Ruffinoni C (1995) Structure and function of buffer strips from a water quality perspective in agricultural landscapes. Landsc Urban Plan 31(01):323–331
Walker TR, Crittenden PD, Dauvalter VA, Jones V, Kuhry P, Loskutova O, Mikkola K (2009) Multiple indicators of human impacts on the environment in the Pechora Basin, north-eastern European Russia. Ecol Indic 9(09):765–779
Wan R, Cai S, Li H, Yang G, Li Z, Nie X (2014) Inferring land use and land cover impact on stream water quality using a Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach in the Xitiaoxi River watershed, China. J Environ Manag 133(11):1–11
Wang H, Hondzo M, Xu C, Poole V, Spacie A (2003) Dissolved oxygen dynamics of streams draining an urbanized and an agricultural catchment. Ecol Model 160(1–2):145–161
Wang S, Jin X, Pang Y, Zhao H, Zhou X, Wu F (2005a) Phosphorus fractions and phosphate sorption characteristics in relation to the sediment compositions of shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River region, China. J Colloid Interface Sci 289(02):339–346
Wang XH, Yin CQ, Shan BQ (2005b) The role of diversified landscape buffer structures for water quality improvement in an agricultural watershed, North China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 107(04):381–396
Wiesmeier M, Lützow M, Spörlein P, Geuß U, Hangen E, Reischl A, Schilling B (2015) Land use effects on organic carbon storage in soils of Bavaria: the importance of soil types. Soil Tillage Res 146(05):296–302
Wu Q, Zhang R, Huang S, Zhang H (2008) Effects of bacteria on nitrogen and phosphorus release from river sediment. J Environ Sci 20(05):404–412
Xian G, Crane M, Su J (2007) An analysis of urban development and its environmental impact on the Tampa Bay watershed. J Environ Manag 85(04):965–976
Xu J, Peng S, Yang S, Wang W (2012) Ammonia volatilization losses from a rice paddy with different irrigation and nitrogen managements. Agric Water Manag 104(03):184–192
Yamashita Y, Kloeppel BD, Knoepp J, Zausen GL, Rudolf J (2011) Effects of watershed history on dissolved organic matter characteristics in headwater streams. Ecosystems 14(07):1110–1122
You JJ, Sun L, Liu X, Hu XL, Xu Q (2019) Effects of sewage sludge biochar on soil characteristics and crop yield in loamy sand soil. Pol J Environ Stud 28(04):1–8
Zhang H, Zhang R, Qi F, Liu X, Niu Y, Fan Z, Zhang Q, Li J, Yuan L, Song Y, Yang S (2018) The CSLE model based soil erosion prediction: comparisons of sampling density and extrapolation method at the county level. Catena 165:465–472
Zhao J, Lin L, Yang K, Liu Q, Qian G (2015) Influences of land use on water quality in a reticular river network area: a case study in Shanghai, China. Landsc Urban Plan 137(12):20–29
Zhou L, Boyd CE (2015) An assessment of total ammonia nitrogen concentration in Alabama (USA) ictalurid catfish ponds and the possible risk of ammonia toxicity. Aquaculture 437(12):263–269
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Feifei Long for the help with experimental analysis. We also thank the reviewers for their useful comments.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51779204), the Shaanxi Province Innovation Talent Promotion Plan Project Technology Innovation Team (Grant No. 2018TD-037), and the Science and Technology Program of Education Department of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. GJJ170252).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Xiaojun Liu, Yi Zhang, and Peng Li. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Xiaojun Liu and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Study concept and design: Xiaojun Liu, Peng Li, and Zhanbin Li.
Analysis and interpretation of data: Xiaojun Liu, Yi Zhang, and Guoce Xu.
Drafting of the manuscript: Xiaojun Liu.
Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Peng Li and Zhanbin Li.
Statistical analysis: Xiaojun Liu.
Obtained funding: Peng Li and Zhanbin Li.
Study supervision: Peng Li and Zhanbin Li.
Experimental operation: Yuting Cheng, Tiegang Zhang and Yi Zhang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Li, Z. et al. Response of water quality to land use in hydrologic response unit and riparian buffer along the Dan River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 28251–28262 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12636-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12636-z