Abstract
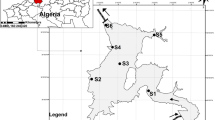
The spatial and temporal variation in the distribution, abundance and assemblage structure of zooplankton were examined in a mining-impacted stretch of river Ganga. The collection of samples has been done from three different sampling zones such as Z1 (Chandi Bridge Ghat) as reference zone, Z2 (Shyampur), and Z3 (Bisanpur) as mining-intruded area from May 2017 to April 2018. During the analysis, twenty-eight species of zooplankton kindred to four groups mainly Rotifera (ten species), Protozoa (five species), Cladocera (eight species), and Copepoda (five species) were identified. In the course of analysis, it was observed that Rotifera were dominant (43.49 %) followed by Cladocera (19.58 %), Protozoa (18.31 %), and Copepoda (18.62 %). The results showed that the distribution and abundance of zooplankton fluctuated more at Z1 (reference zone) as compared with Z2 and Z3 (mining-intruded zones). The diversity indices also indicated the higher richness, abundance, and evenness of zooplankton ranging from 3.145 to 3.180 at Z1, 3.081 to 3.129 at Z2, and 3.130 to 3.175 at Z3. The canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) showed positive and negative correlation between the zooplankton and water quality of the river Ganga. The present study shows that the anthropogenic activities such as river bed mining disturbed the water quality through enhancing the turbidity and nutrients load in the aquatic system. However, these changes in water quality significantly affected the distribution and abundance of zooplankton.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- WV:
-
water velocity
- D:
-
mean depth
- C:
-
conductivity
- WT:
-
water temperature
- TU:
-
turbidity
- TDS:
-
total dissolved solids
- DO:
-
dissolved oxygen
- BOD:
-
biochemical oxygen demand
- TH:
-
total hardness
- A:
-
alkalinity
- S:
-
salinity
- mg/L:
-
milligram per liter
- m:
-
meter
- ppm:
-
parts per million
- Aug:
-
August
- Sep:
-
September
- Oct:
-
October
- Nov:
-
November
- Dec:
-
December
- Jan:
-
January
- Feb:
-
February
- Mar:
-
March
- B1:
-
Asplanchna sp.
- B2:
-
Atrochus sp.
- B3:
-
Brachionus sp.
- B4:
-
Cephalodella sp.
- B5:
-
Colurella sp.
- B6:
-
Conochilus sp.
- B7:
-
Keratella sp.
- B8:
-
Philodina sp.
- B9:
-
Rotaria sp.
- B10:
-
Trichocerca sp.
- B11:
-
Arcella sp.
- B12:
-
Vorticella sp.
- B13:
-
Euglena sp.
- B14:
-
Paramecium sp.
- B15:
-
Zoothamnium sp.
- B16:
-
Alona sp.
- B17:
-
Alonella sp.
- B18:
-
Chydorus sp.
- B19:
-
Ceriodaphnia sp.
- B20:
-
Daphnia sp.
- B21:
-
Macrothrix sp.
- B22:
-
Pleuroxus sp.
- B23:
-
Simocephalus sp.
- B24:
-
Phyllodiaptomus sp.
- B25:
-
Mesocyclops sp.
- B26:
-
Microcyclops sp.
- B27:
-
Eucyclops sp.
- B28:
-
Cyclops sp.
References
Adeyemi SO (2012) Preliminary census of zooplankton and phytoplankton community of Ajeko Stream, Iyale, North Central Nigeria. Animal Res Int 9(3):1638–1644 https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ari/article/view/89144/78701
Akin-Oriola GA (2003) Zooplankton associations and environmental factors in Ogunpa and Ona Rivers, Nigeria. Rev Biol Trop 51(2):391–398
Almeida C, Gonzalez SO, Mallea M, Gonzalez P (2012) A recreational water quality index using chemical, physical and microbiological parameters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19(8):3400–3411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0865-5
American Public Health Association (APHA) (2012) The standard method for the examination of water and wastewater (22 editions) Washington D.C. ISBN 978-087553-013-0.
Aswal RS, Singh P, Kamboj N, Singh R (2016) Chemometric techniques: a comparative study of drinking water sources of Dehradun and Haridwar, Uttarakhand (India). Advances in Health and Environment, Safety Select Proceedings of HSFEA, 345-352. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7122-5_33.
Bhadula S, Joshi BD (2013) Zooplankton diversity of Ganga River water with special reference to pollution status. J Environ Bio-Sci 27(1):111–114
Bhutiani R, Khanna DR, Tyagi B, Tyagi PK, Kulkarni DB (2015) Assessing environmental contamination of river Ganga using correlation and multivariate analysis. Pollution 1(3):265–273
Bhutiani R, Khanna DR, Kulkarni DB, Ruhela M (2016) Assessment of Ganga River ecosystem at Haridwar, Uttarakhand, India with reference to Water Quality Indices. Appl Water Sci 6(2):107–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0206-6
Bianchi F, Acri F, Aubry FB, Berton A, Boldrin A, Camatti E, Cassin D, Comaschi A (2003) Can plankton communities be considered as bioindicators of water quality in the lagoon of Venice? Mar Pollut Bull 46(8):964–971. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00111-5
Bruns DA (2005) Macroinvertibrate response to land cover, habitat, and water chemistry in a a mining-impacted river ecosystem: a GIS watershed analysis. Aquat Sci 67(4):403–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-005-0792-3
Dauvin JC, Thie’baut E, Wang Z (1998) Short-term changes in the mesozooplankton community in the Seine ROFI (Region of Freshwater Influence) (eastern English Channel). J Plankton Res 20(6):1145–1167
Ganesan L, Khan RA (2008) Studies on the ecology of zooplankton in a floodplain wetland of West Bengal, India. Proceeding of Taal 2007: The 12th World Lake Conferences: 67-73
Geetha Madhav V, Kondalarao B (2004) Distribution of phytoplankton in the coastal waters of east coast of India. Indian Mar Sci 30:151–160
Gophen M (2012) The ecology of Keratella cochlearis in Lake Kinneret (Israel). Open J Modern Hydrol 2(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojmh.2012.21001
Govindasamy C, Kannan L (1996) Ecology of rotifers of Pichavaram mangroves, southeast coast of India. Indian Hydrobiol 1:69–76
Gupta N, Pandey P, Hussain J (2017) Effect of physicochemical and biological parameters on the quality of river water of Narmada, Madhya Pradesh, India. Water Sci 31:11–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wsj.2017.03.002
Imoobe TOT (2011) Diversity and seasonal variation of zooplankton in Okhuo River, a tropical forest river in Edo State, Nigeria. Cent J 17(1):37–51
Imoobe TOT, Adeyinka ML (2009) Zooplankton-based assessment of the trophic state of a tropical forest river. Arch Biol Sci 61(4):733–740. https://doi.org/10.2298/ABS0904733I
Jakhar P (2013) Role of phytoplankton and zooplankton as health indicators of aquatic ecosystem (a review). Int J Innov Res Studies 2(12):490–500
Jindal R, Sharma C (2010) Studies on water quality of Sutlej River around Ludhiana with reference to physicochemical parameters. Environ Monit Assess 174:417–425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1466-8
Kamboj N, Kamboj V (2019) Water quality assessment using overall index of pollution in riverbed-mining area of Ganga-River Haridwar, India. Water Sci 33(1):65–74. https://doi.org/10.1080/11104929.2019.1626631
Kamboj N, Pandey A, Shoaib M, Kumar R (2012) Environmental impact assessment of illegal Ganga mining at Kangri Village, District Haridwar (Uttarakhand) India. J Sustain Environ Res 1:67–71
Kamboj N, Bharti M, Kamboj V, Rani A, Sharma S (2016) A comparative study of physico-chemical and bacteriological parameters of three different ritual bathing ghats of Ganga River in India. ESSENCE-Int J Environ Rehabil Conserv 7(2):46–52
Kamboj V, Kamboj N, Sharma S (2017) Environmental impact of riverbed mining-a review. Int Jf Sci Res Rev 7(1):504–520
Keister JE, Bonnet D, Chiba S, Johnson CL, Mackas DL, Escribano R (2012) Zooplankton population connections, community dynamics, and climate variability. ICES J Mar Sci 69(3):347–350. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fss034
Khanna DR, Bhutiani R (2007) Laboratory manual of water and wastewater analysis. Daya Publishing House, New Delhi, pp 1–184
Khanna DR, Sarkar P, Gautam A, Bhutiani R (2007) Fish scales as bio-indicator of water quality of river Ganga. Environ Monit Assess 134:153–160
Khanna DR, Bhutiani R, Gagan M, Ginh V, Kumar D, Ahraf J (2009) A study of zooplankton with special reference to the concentration of River Ganga at Haridwar. Environ Conserv J 10(3):15–20
Khanna DR, Bhutiani R, Matta G, Singh V, Bhadauriya G (2012) Study of planktonic diversity of river Ganga from Devprayag to Roorkee, Uttarakhand (India). Environ Conserv J 13(1&2):211–217
Khattak TM, Bhatti N, Murtaza G (2005) Evaluation of algae from the effluent of Dandot Cement Company, Dandot, Pakistan. J Appl Sci Environ Manag 9:147–149 https://www.popline.org/node/260050
Kondolf GM (1997) Hungry water: effects of dams and gravel mining on river channels. Environ Manag 21:533–551
Maiti SK (2004) Handbook of methods in environmental studies Vol. 1: water and wastewater analysis. ABD Publisher. ISBN: 978-81-8577-34-07
Mohanty RK, Ambast SK, Panigrahi P, Mandal KG (2018) Water quality suitability and water use indices: useful management tools in coastal aquaculture of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 485:210–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.11.048
Molinero JC, Ibanez F, Nival P, Buecher I, Souissi S (2005) North Atlantic climate and north-western Mediterranean plankton variability. Limnol Oceanogr 50(4):1213–1220. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2005.50.4.1213
Ndour I, Berraho A, Fall M, Ettahiri O, Sambe B (2018) Composition, distribution and abundance of zooplankton and ichthyoplankton along the Senegal-Guinea maritime zone (West Africa). Egypt J Aquatic Res 44(2):109–124
Needham JG, Needham PR (1962) A guide to freshwater biology. Holden Day Ins., San Francisco (USA) 108
Ouyang Y, Higman J, Thompson J, O’Toole T, Campbell D (2002) Characterization and spatial distribution of heavy metals in sediment from cedar and Ortega rivers Basin. J Contam Hydrol 54(1-2):19–35
Padmalal D, Maya K (2014) Sand mining. Environmental impacts and selected case studies. Environ Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9144-1
Palmer CM (1972) A composite rating of algae tolerating organic pollution load. J Phycol 5:78–82
Pandey A, Upadhyay HC (2016) Studies on zooplankton diversity of western Ramganga River in Almora (Uttarakhand) India. Int J Sci Res 5(5):1192–1194
Pandey BN, Hussain S, Jha AK, Shyamanand (2004) Seasonal fluctuation of zooplankton community in relation to certain parameters of river ramjan of kishanganj, Bihar. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 3(3):325–330
Paturej E, Gutkowska A, Koszałka J, Bowszys M (2017) Effect of physicochemical parameters on zooplankton in the brackish, coastal Vistula Lagoon. Oceanologia 59(1):49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceano.2016.08.001
Peck Yen T, Rohasliney H (2013) Status of water quality subject to sand mining in the Kelantan River, Kelantan. Tropic Life Sci Res 24(1):19–34
Ramachandra TV, Rishiram R, Karthick B (2006) Zooplankton as bioindicators: hydro-biological investigations in selected Bangalore lakes. Centre of Ecological Science, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. Technical report-115: 1-116.
Rougier C, Pourriot R, Lam-Hoai T, Guiral D (2005) Ecological patterns of the rotifer communities in the Kaw River estuary (French Guiana). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 63(1):83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2004.08.023
Sahu G, Satpathy KK, Mohanty AK, Sarkar SK (2012) Variations in community structure of phytoplankton in relation to physicochemical properties of coastal waters, southeast coast of India. Indian J Geo-Marine Sci 41(3):223–241 http://hdl.handle.net/123456789/14169
Sautour B, Castel J (1995) Comparative spring distribution of zooplankton in three macrotidal European estuaries. Hydrobiologia 311:139–151
Sebastian P, Stibor H, Berger S, Diehl S (2012) Effects of water temperature and mixed layer depth on zooplankton body size. Mar Biol 159(11):2431–2440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-1931-8
Sharma A, Sharma RC, Anthwal A (2007) Monitoring phytoplankton diversity in the hill stream Chandrabhaga in Garhwal Himalayas. Life Sci J 4:80–84
Sharma RC, Singh N, Chauhan A (2016) The influence of physico-chemical parameters on phytoplankton distribution in a head water stream of Garhwal Himalayas: a case study. Egypt J Aquat Res 42:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2015.11.004
Sharma AK, Malik DS, Bargali H (2018) Status of plankton diversity in relation to water quality of Bhagirathi riverine system in Garhwal Himalaya. Int J Adv Sci Res 3(1):30–37
Singh B, Islam MR (2000) Seasonal variation in zooplankton population of two lentic bodies and Assam state zoo cum botanical garden, Guwahati, Assam. Ecol Environ Conserv 8(3):273–278
Sreebha S, Padmalal D (2011) Environmental impact assessment of sand mining from the small catchment rivers in the southwestern coast of India: a case study. Environ Manag 47:130–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-010-9571-6
Subrat Naik B, Acharya C, Mohaptra A (2005) Seasonal distribution of physico chemical parameters in effluent discharge area of Uppanar estuary, Cuddalore, southeast coast of India. J Environ Biol 26:291–297
Suresh S, Thirumala S, Ravind HB (2011) Zooplankton diversity and its relationship with physicochemical parameters in Kundavada Lake, of Davangere district, Karnataka, India. ProEnvironment 4:56–59
Ter-Braak CJF, Verdonscoht PFM (1995) Canopy correspondence analysis and related multivariate methods in aquatic ecology. Aquat Sci 57(3):255–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00877430
Thompson RM, Lake PS (2010) Reconciling theory and practice: the role of stream ecology. River Res Appl 26(1):5–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.1284
Trivedy RK, Goel PK (1986) In: Chemical and biological methods for water pollution studies. Environmental Publication, Carad
Vajravelu M, Ayyappan S, Mariyasingarayan Y (2018) Seasonal variation in environmental parameters and their impact on zooplankton species composition, abundance and density at Parangipettai coastal waters, South East Coast of Bay of Bengal. Int J Sci Advance Res Technol 4(1):42–53
Valerie D, Sautour B, Chardy P (2005) Long term changes of zooplankton varaiblity in a turbid environment: the Gironde estuary (France). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 64(2-3):171–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2005.01.014
Varadharajan D, Soundarapandian P (2013) Zooplankton abundance and diversity from Pointcalimere to Manamelkudi, South East Coast of India. J Earth Sci Clim Chang 4(5):151–161. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7617.1000151
Waidi OA, Ezekiel OA, Kehinde OA, Isaac TO, Dominic OO, Tomilola EA, Akinpelu EO (2016) The effects of environmental parameters on zooplankton assemblages in tropical coastal estuary, South-west, Nigeria. Egypt J Aquat Res 42:281–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2016.05.005
Xiong W, Ni P, Chen Y, Gao Y, Shan B, Zhan A (2017) Zooplankton community structure along a pollution gradient at fine geographical scales in river ecosystems: the importance of species sorting over dispersal. Mol Ecol 26(16):4351–4360
Xuelu GAO, Jinming S, Xuegang L (2011) Zooplankton spatial and diurnal variations in the Changjiang River estuary before operation of the Three Gorges Dam. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 29(3):591–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-011-0098-3
Younger PL, Wolkersdorfer C (2004) Mining impacts on the fresh water environment: technical and managerial guidelines for catchment scale management. Mine Water Environ 23:S2–S80
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to pay their gratitude to Gurukula Kangri Vishwavidyalaya, Haridwar, for providing the facilities for the research work.
Funding
This work is financially supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, through the INSPIRE program (Grant Number: IF160805).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamboj, V., Kamboj, N. Spatial and temporal variation of zooplankton assemblage in the mining-impacted stretch of Ganga River, Uttarakhand, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 27135–27146 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09089-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09089-1