Abstract
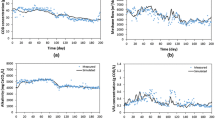
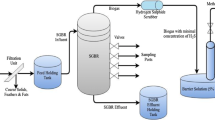
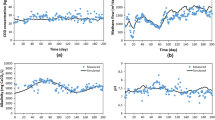
Production and consumption of confectionery products, such as chocolate, sugar, and cookies, have increased worldwide. Thus, management and treatment of confectionery effluents, as one of the most important agro-industrial wastewaters, become essential. Confectionery industries produce high-strength and highly biodegradable wastewaters that are appropriate for biological treatment prior to discharge. In this study, long-term dynamic performance of a full-scale anaerobic expanded granular sludge bed (EGSB) reactor treating confectionery effluent was simulated by using Anaerobic Digestion Model No. 1 (ADM1). Substrate fractionation was carried out based on the ADM1 state variables, and then, the model was calibrated with 300 days of operation data. The calibrated model could capture the dynamic performance of the anaerobic reactor for a long validation period of 500 days. Although the reactor was operated under highly fluctuating volumetric loading rates (VLR) between 0.2 and 5 kg chemical oxygen demand (COD)/m3 day, the model results indicated medium to high prediction accuracy for effluent COD, methane generation, total volatile fatty acids (VFA), and pH parameters. Mean relative absolute errors for COD, methane flow, VFA, and pH parameter simulations were 22%, 16%, 29%, and 1%, respectively. The study presents the applicability of ADM1 for full-scale reactors treating industrial wastewaters.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alferes J, García-Heras JL, Roca E, García C, Irizar I (2008) Integration of equalisation tanks within control strategies for anaerobic reactors. Validation based on ADM1 simulations. Water Sci Techol 57(5):747–752
Anderson GK, Yang G (1992) Determination of bicarbonate and total volatile acid concentration in anaerobic digesters using a simple titration. Water Environ Res 64(1):53–59
Antonopoulou G, Gavala HN, Skiadas IV, Lyberatos G (2012) ADM1-based modeling of methane production from acidified sweet sorghum extract in a two stage process. Bioresour Technol 106:10–19
Baeten JE, Batstone DJ, Schraa OJ, van Loosdrecht MCM, Volcke EIP (2019) Modelling anaerobic, aerobic and partial nitritation-anammox granular sludge reactors - a review. Water Res 149:322–341
Barrera EL, Spanjers H, Solon K, Amerlinck Y, Nopens I, Dewulf J (2015) Modeling the anaerobic digestion of cane molasses vinasse: extension of the Anaerobic Digestion Model No. 1 (ADM1) with sulfate reduction for a very high strength and sulfate rich wastewater. Water Res 71:42–54
Batstone DJ, Keller J (2003) Industrial application of the IWA Anaerobic Digestion Model No.1 (ADM1). Wat Sci Technol 47(12):199–206
Batstone DJ, Keller J, Angelidaki I, Kalyuzhnyi SV, Pavlostathis SG, Rozzi A, Sanders WTM, Siegrist H, Vavilin VA (2002) Anaerobic Digestion Model No.1, scientific and technical report, vol 13. IWA Publishing, London
Batstone DJ, Keller J, Blackall LL (2004) The influence of substrate kinetics on the microbial community structure in granular anaerobic biomass. Water Res 38(6):1390–1404
Beal LJ, Raman DR (2000) Sequential two-stage anaerobic treatment of confectionery wastewater. J Agric Eng Res 76(2):211–217
Boubaker F, Ridha BC (2008) Modelling of the mesophilic anaerobic co-digestion of olive mill wastewater with olive mill solid waste using Anaerobic Digestion Model no. 1 (ADM1). Bioresour Technol 99:6565–6577
CAOBISCO (2013) Statistical bulletin 2013. Brussels, Belgium
Carbonell-Barrachina AA, Garcia E, Sanchez Soriano J, Aracil P, Burlo F (2002) Effects of raw materials, ingredients, and production lines on arsenic and copper concentrations in confectionery products. J Agric Food Chem 50:3738–3742
Chen Y, Cheng JJ, Creamer KS (2008) Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: a review. Bioresour Technol 99(10):4044–4064
Chen Z, Hu D, Zhang Z, Ren N, Zhu H (2009) Modeling of two phase anaerobic process treating traditional Chinese medicine wastewater with the IWA Anaerobic Digestion Model No.1. Bioresour Technol 100:4623–4631
Dereli RK, Ersahin ME, Ozgun H, Ozturk I, Aydin AF (2010) Applicability of Anaerobic Digestion Model No 1 (ADM1) for a specific industrial wastewater opium alkaloid effluents. Chem Eng J 165(1):89–94
Dereli RK, Ersahin ME, Ozgun H, Ozturk I, Jeison D, van der Zee F, van Lier JB (2012) Potentials of anaerobic membrane bioreactors to overcome treatment limitations induced by industrial wastewaters. Bioresour Technol 122:160–170
Di Berardino S, Costa S, Converti A (2000) Semi-continuous anaerobic digestion of a food industry wastewater in an anaerobic filter. Bioresour Technol 71:261–266
Dieguez CG, Bernard O, Roca E (2013) Reducing the Anaerobic Digestion Model No. 1 for its application to an industrial wastewater treatment plant treating winery effluent wastewater. Bioresour Technol 132:244–253
El Diwani G, El Abd H, Hawash S, El Ibiari N, El Rafei S (2000) Treatment of confectionery and gum factory wastewater effluent. Adsorpt Sci Technol 18(9):813–821
Elaiuy MLC, Li Borrion A, Stegemann JA, Poggio D, Nour EAA (2018) ADM1 modelling of large-scale covered in-ground anaerobic reactor treating sugarcane vinasse. Water Sci Technol 77(5):1397–1409
El-Gohary FA, Nasr FA, Aly HI (1999) Cost-effective pre-treatment of food-processing industrial wastewater. Water Sci Technol 40(7):17–24
Ersahin ME, Dereli RK, Insel G, Ozturk I, Kinaci C (2007) Model based evaluation for the anaerobic treatment of corn processing wastewaters. Clean-Soil Air Water 35(6):576–581
Ersahin ME, Ozgun H, Dereli RK, Ozturk I (2011) Anaerobic treatment of industrial effluents: an overview of applications. In: Einschlag FSG (ed) Waste water treatment and reutilization. InTech, India, pp 3–28
Feldman, H., Flores-Alsina, X., Ramin, P., Kjellberg, K., Jeppsson, U., .Batstone, D.J., and Gernaey, K.V. (2017) Modelling an industrial anaerobic granular reactor using a multi-scale approach. Water Res, 126, 488–500
Feldman H, Flores-Alsina X, Kjellberg K, Jeppsson U, Batstone DJ, Gernaey KV (2018) Model-based analysis and optimization of a full-scale industrial high-rate anaerobic bioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 115:2726–2739
Gavala HN, Angelidaki I, Ahring BK (2003) Kinetics and modeling of anaerobic digestion process. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 81:57–93
Gernaey KV, Jeppsson U, Vanrolleghem PA, Copp JB (2014) Benchmarking of control strategies for wastewater treatment plants. IWA Publishing, London
Henze M, Gujer W, Mino T, van Loosdrecht MCM (2000) Activated sludge models ASM1, ASM2, ASM2d and ASM3. IWA scientific and technical report no. 9. IWA Publishing, London
Hinken L, Huber M, Weichgrebe D, Rosenwinkel KH (2014) Modified ADM1 for modelling an UASB reactor laboratory plant treating starch wastewater and synthetic substrate load tests. Water Res 64:82–93
Irizar I, Roche E, Beltrán S, Aymerich E, Esteban-Gutiérrez M (2018) Model-based design of a software sensor for real-time diagnosis of the stability conditions in high-rate anaerobic reactors – full-scale application to internal circulation technology. Water Res 143:479–491
Kleerebezem R, Van Loosdrecht MCM (2006) Waste characterization for implementation in ADM1. Water Sci Technol 54(4):167–174
Liu X, Xu Q, Wang D, Wu Y, Yang Q, Liu Y, Wang Q, Li X, Li H, Zeng G, Yang G (2019a) Unveiling the mechanisms of how cationic polyacrylamide affects short-chain fatty acids accumulation during long-term anaerobic fermentation of waste activated sludge. Water Res 155:142–151
Liu X, Xu Q, Wang D, Yang Q, Wu Y, Yang J, Liu Y, Wang Q, Ni BJ, Li X, Li H, Yang G (2019b) Enhanced short-chain fatty acids from waste activated sludge by heat−CaO2 advanced thermal hydrolysis pretreatment: parameter optimization, mechanisms, and implication. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:3544–3555
Mottet A, François E, Latrille E, Steyer JP, Déléris S, Vedrenne F, Carrère H (2010) Estimating anaerobic biodegradability indicators for waste activated sludge. Chem Eng J 160(2):488–496
Ozgun H, Karagul N, Dereli RK, Ersahin ME, Coskuner T, Ciftci DI, Ozturk I, Altinbas M (2012) Confectionery industry: a case study on treatability-based effluent characterization and treatment system performance. Water Sci Technol 66(1):15–20
Ozkan-Yucel UG, Gökçay CF (2010) Application of ADM1 model to a full-scale anaerobic digester under dynamic organic loading conditions. Environ Technol 31(6):633–640
Patwardhan AD (2008) Industrial waste water treatment. Prentice Hall of India Private Limited, New Delhi
Poggio D, Walker M, Nimmo W, Ma L, Pourkashanian M (2016) Modelling the anaerobic digestion of solid organic waste – substrate characterisation method for ADM1 using a combined biochemical and kinetic parameter estimation approach. Waste Manag 53:40–54
Reichert P, Ruchti J, Simon W (1998) Aquasim 2.0, Swiss Federal Institute for Environmental Science and Technology (EAWAG), Duebendorf, Switzerland
Reichert P, Borchardt D, Henze M, Rauch W, Shanahan P, Somlyody L, Vanrolleghem PA (2001) River water quality model no.1. IWA Publishing, London
Rönner-Holm SGE, Zak A, Holm NC (2012) Comparison of different conditions, substrates and operation modes by dynamic simulation of a full-scale anaerobic SBR plant. Water Sci Technol 65(3):558–566
Siegrist H, Vogt D, Garcia-Heras JL, Gujer W (2002) Mathematical model for meso- and thermophilic anaerobic sewage sludge digestion. Environ Sci Technol 36:1113–1123
Silva F, Nadais H, Prates A, Arroja L, Capela I (2009) Modelling of anaerobic treatment of evaporator condensate (EC) from a sulphite pulp mill using the IWA anaerobic digestion model no. 1 (ADM1). Chem Eng J 148:319–326
Sötemann SW, Ristow NE, Wentzel MC, Ekama GA (2005) A steady state model for anaerobic digestion of sewage sludges. Water SA 31(4):511–528
Speece RE (1996) Anaerobic biotechnology for industrial wastewaters. Archae Press, USA
Statista (2018) Food report 2018 – confectionery. Statista Consumer Market Outlook – Segment Report (Analyst: Madeleine Brinckmann). Hamburg, Germany
Sun H, Guo J, Wu S, Liu F, Dong R (2017) Development and validation of a simplified titration method for monitoring volatile fatty acids in anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag 67:43–50
van Ginkel SW, Oh S, Logan BE (2005) Biohydrogen gas production from food processing and domestic wastewaters. Int J Hydrog Energy 30:1535–1542
van Lier JB, van der Zee FP, Frijters CTMJ, Ersahin ME (2015) Celebrating 40 years anaerobic sludge bed reactors for industrial wastewater treatment. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 14:681–702
Wang D, Liu Y, Ngo HH, Zhang C, Yang Q, Peng L, He D, Zeng G, Li X, Ni BJ (2017) Approach of describing dynamic production of volatile fatty acids from sludge alkaline fermentation. Bioresour Technol 238:343–351
Wanner O, Morgenroth E (2004) Biofilm modeling with AQUASIM. Water Sci Technol 49(11–12):137–144
Wojdalski J, Grochowicz J, Drózdz B, Bartoszewska K, Zdanowska P, Kupczyk A, Ekielski A, Florczak I, Hasny A, Wójcik G (2015) Energy efficiency of a confectionery plant – case study. J Food Eng 146:182–191
Yingthavorn N, Rakmak N, Kongjan P, Siripatanaa C (2016) Mathematical modeling of existing two stage anaerobic digestion process for palm oil mill wastewater. J Teknol 78(10–4):21–26
Zhang Y, Piccard S, Zhou W (2015) Improved ADM1 model for anaerobic digestion process considering physico-chemical reactions. Bioresour Technol 196:279–289
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 66 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dereli, R.K. Modeling long-term performance of full-scale anaerobic expanded granular sludge bed reactor treating confectionery industry wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 25037–25045 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05739-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05739-1