Abstract
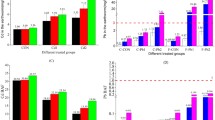
Eisenia fetida earthworms were exposed to sub-lethal levels of imidacloprid for 48 h via contact filter paper tests and soil tests. After the exposure, 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) metabolomics was used to measure earthworm sub-lethal responses by analyzing the changes in the polar metabolite profile. Maltose, glucose, malate, lactate/threonine, myo-inositol, glutamate, arginine, lysine, tyrosine, leucine, and phenylalanine relative concentrations were altered with imidacloprid exposure in soil. In addition to these metabolites (excluding leucine and phenylalanine), fumarate, ATP, inosine, betaine, scyllo-inositol, glutamine, valine, tryptophan, alanine, tyrosine, and isoleucine relative concentrations shifted with imidacloprid exposure during contact tests. Metabolite changes in E. fetida earthworms exposed to imidacloprid showed a non-linear concentration response and an upregulation in gluconeogenesis. Overall, imidacloprid exposure in soil induces a less pronounced response in metabolites glucose, maltose, fumarate, adenosine-5′-triphosphate (ATP), inosine, scyllo-inositol, lactate/threonine, and tyrosine in comparison to the response observed via contact tests. Thus, our study highlights that tests in soil can result in a different metabolic response in E. fetida and demonstrates the importance of different modes of exposure and the extent of metabolic perturbation in earthworms. Our study also emphasizes the underlying metabolic disruption of earthworms after acute sub-lethal exposure to imidacloprid. These observations should be further examined in different soil types to assess the sub-lethal toxicity of imidacloprid to soil-dwelling earthworms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baskaran S, Kookana RS, Naidu R (1999) Degradation of bifenthrin, chlorpyrifos and imidacloprid in soil and bedding materials at termiticidal application rates. Pestic Sci 55:1222–1228
Bender DA (2012) The metabolism of “surplus” amino acids. Br J Nutr 108:S113–S121
Bonmatin JM, Moineau I, Charvet R, Colin ME, Fleche C, Bengsch ER (2005) Behaviour of imidacloprid in fields. Toxicity for honey bees. In: Lichtfouse E, Schwarzbauer J, Robert D (eds) Environmental chemistry: Green chemistry and pollutants in ecosystems. Springer, pp 483–494
Bonmatin JM, Giorio C, Girolami V, Goulson D, Kreutzweiser DP, Krupke C, Liess M, Long E, Marzaro M, Mitchell EAD, Noome DA, Simon-Delso N, Tapparo A (2015) Environmental fate and exposure; neonicotinoids and fipronil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:35–67
Boroujerdi AFB, Vizcaino MI, Meyers A, Pollock EC, Huynh SL, Schock TB, Morris PJ, Bearden DW (2009) NMR-based microbial metabolomics and the temperature-dependent coral pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus. Environ Sci Technol 43:7658–7664
Brown SAE, Simpson AJ, Simpson MJ (2008) Evaluation of sample preparation methods for nuclear magnetic resonance metabolic profiling studies with Eisenia fetida. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:828–836
Brown SAE, Simpson AJ, Simpson MJ (2009) 1H NMR metabolomics of earthworm responses to sub-lethal PAH exposure. Environ Chem 6:432–440
Brown SAE, McKelvie JR, Simpson AJ, Simpson MJ (2010) 1H NMR metabolomics of earthworm exposure to sub-lethal concentrations of phenanthrene in soil. Environ Pollut 158:2117–2123
Bundy JG, Lenz EM, Bailey NJ, Gavaghan CL, Svendsen C, Spurgeon D, Hankard PK, Osborn D, Weeks JM, Trauger SA, Speir P, Sanders I, Lindon JC, Nicholson JK, Tang H (2002) Metabonomic assessment of toxicity of 4-fluoroaniline, 3,5-difluoroaniline and 2-fluoro-4-methylaniline to the earthworm Eisenia veneta (rosa): identification of new endogenous biomarkers. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1966–1972
Bundy JG, Davey MP, Viant MR (2009) Environmental metabolomics: a critical review and future perspectives. Metabolomics 5:3–21
Cang T, Dai D, Yang G, Yu Y, Lv L, Cai L, Wang Q, Wang Y (2017) Combined toxicity of imidacloprid and three insecticides to the earthworm, Eisenia fetida (Annelida, Oligochaeta). Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:8722–8730
Cox L, Koskinen WC, Celis R, Hermosin MC, Cornejo J, Yen PY (1998) Sorption of imidacloprid on soil clay mineral and organic components. Soil Sci Soc Am J 62:911–915
Craig SAS (2004) Betaine in human nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr 80:539–549
Dani VD, Simpson AJ, Simpson MJ (2018) Analysis of earthworm sublethal toxic responses to atrazine exposure using 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-based metabolomics. Environ Toxicol Chem 37:473–480
Dittbrenner N, Moser I, Triebskorn R, Capowiez Y (2011) Assessment of short and long-term effects of imidacloprid on the burrowing behaviour of two earthworm species (Aporrectodea caliginosa and Lumbricus terrestris) by using 2D and 3D post-exposure techniques. Chemosphere 84:1349–1355
Edwards CA, Bohlen PJ (1992) The effects of toxic chemicals on earthworms. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 125:23–100
EFSA (2012) Statement on the findings in recent studies investigating sub-lethal effects in bees of some neonicotinoids in consideration of the uses currently authorised in Europe. EFSA J 10:2752
Eklund M, Bauer E, Wamatu J, Mosenthin R (2005) Potential nutritional and physiological functions of betaine in livestock. Nutr Res Rev 18:31–48
Ekman DR, Teng Q, Villeneuve DL, Kahl MD, Jensen KM, Durhan EJ, Ankley GT, Collette TW (2008) Investigating compensation and recovery of fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) exposed to 17α-ethynylestradiol with metabolite profiling. Environ Sci Technol 42:4188–4194
Ekman DR, Teng Q, Villeneuve DL, Kahl MD, Jensen KM, Durhan EJ, Ankley GT, Collette TW (2009) Profiling lipid metabolites yields unique information on sex- and time-dependent responses of fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas) exposed to 17α-ethynylestradiol. Metabolomics 5:22–32
Gibbons D, Morrissey C, Mineau P (2015) A review of the direct and indirect effects of neonicotinoids and fipronil on vertebrate wildlife. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:103–118
Girolami V, Mazzon L, Squartini A, Mori N, Marzaro M, Bernardo AD, Greatti M, Giorio C, Tapparo A (2009) Translocation of neonicotinoid insecticides from coated seeds to seedling guttation drops: a novel way of intoxication for bees. J Econ Entomol 102:1808–1815
Goulson D (2013) An overview of the environmental risks posed by neonicotinoid insecticides. J Appl Ecol 50:977–987
Haskó G, Sitkovsky MV, Szabó C (2004) Immunomodulatory and neuroprotective effects of inosine. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:152–157
Horton ML, Scrimgeour KG, Perry MD, Rawn JD (2006) Principles of biochemistry. Pearson Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Lankadurai BP, Wolfe DM, Simpson AJ, Simpson MJ (2011) 1H NMR-based metabolomics of time-dependent responses of Eisenia fetida to sub-lethal phenanthrene exposure. Environ Pollut 159:2845–2851
Lankadurai BP, Simpson AJ, Simpson MJ (2012) 1H NMR metabolomics of Eisenia fetida responses after sub-lethal exposure to perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate. Environ Chem 9:502–511
Lankadurai BP, Furdui VI, Reiner EJ, Simpson AJ, Simpson MJ (2013a) 1H NMR-based metabolomic analysis of sub-lethal perfluorooctane sulfonate exposure to the earthworm, Eisenia fetida, in soil. Metabolites 3:718–740
Lankadurai BP, Nagato EG, Simpson MJ (2013b) Environmental metabolomics: an emerging approach to study organism responses to environmental stressors. Environ Rev 21:180–205
Lenz EM, Weeks JM, Lindon JC, Osborn D, Nicholson JK (2005) Qualitative high field 1H-NMR spectroscopy for the characterization of endogenous metabolites in earthworms with biochemical biomarker potential. Metabolomics 1:123–136
Lopez-Antia A, Ortiz-Santaliestra M, Mougeot F, Mateo R (2013) Experimental exposure of red-legged partridges (Alectoris rufa) to seeds coated with imidacloprid, thiram and difenoconazole. Ecotoxicology 22:125–138
Luo Y, Zang Y, Zhong Y, Kong Z (1999) Toxicological study of two novel pesticides on earthworm Eisenia foetida. Chemosphere 39:2347–2356
McKelvie JR, Wolfe DM, Celejewski M, Simpson AJ, Simpson MJ (2010) Correlations of Eisenia fetida metabolic responses to extractable phenanthrene concentrations through time. Environ Pollut 158:2150–2157
McKelvie JR, Wolfe DM, Celejewski MA, Alaee M, Simpson AJ, Simpson MJ (2011) Metabolic responses of Eisenia fetida after sub-lethal exposure to organic contaminants with different toxic modes of action. Environ Pollut 159:3620–3626
McKelvie JR, Åslund MW, Celejewski MA, Simpson AJ, Simpson MJ (2013) Reduction in the earthworm metabolomic response after phenanthrene exposure in soils with high soil organic carbon content. Environ Pollut 175:75–81
Medrzycki P, Montanari R, Bortolotti L, Sabatini AG, Maini S, Porrini C (2003) Effects of imidacloprid administered in sub-lethal doses on honey bee behaviour. Laboratory tests. Bull Insectol 56:59–62
Moreno A, Arús C (1996) Quantitative and qualitative characterization of 1H NMR spectra of colon tumors, normal mucosa and their perchloric acid extracts: decreased levels of myo-inositol in tumours can be detected in intact biopsies. NMR Biomed 9:33–45
Nelson DL, Lehninger AL, Cox MM (2012) Lehninger principles of biochemistry. W.H. Freeman, New York
Nemeth-Konda L, Füleky G, Morovjan G, Csokan P (2002) Sorption behaviour of acetochlor, atrazine, carbendazim, diazinon, imidacloprid and isoproturon on Hungarian agricultural soil. Chemosphere 48:545–552
Newsholme P, Procopio J, Lima MMR, Pithon-Curi TC, Curi R (2003) Glutamine and glutamate—their central role in cell metabolism and function. Cell Biochem Funct 21:1–9
OECD (1984) Test no. 207: Earthworm, acute toxicity tests. OECD Publishing, Paris
Oliver DP, Kookana RS, Quintana B (2005) Sorption of pesticides in tropical and temperate soils from Australia and the Philippines. J Agric Food Chem 53:6420–6425
Pisa LW, Amaral-Rogers V, Belzunces LP, Bonmatin JM, Downs CA, Goulson D, Kreutzweiser DP, Krupke C, Liess M, McField M, Morrissey CA, Noome DA, Settele J, Simon-Delso N, Stark JD, Van Der Sluijs JP, Van Dyck H, Wiemers M (2015) Effects of neonicotinoids and fipronil on non-target invertebrates. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:68–102
Pollak P (2011) Fine chemicals: the industry and the business. Second edition. Wiley, pp 312
Ratriyanto A, Mosenthin R, Bauer E, Eklund M (2009) Metabolic, osmoregulatory and nutritional functions of betaine in monogastric animals. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 22:1461–1476
Semple KT, Doick KJ, Jones KC, Burauel P, Craven A, Harms H (2004) Defining bioavailability and bioaccessibility of contaminated soil and sediment is complicated. Environ Sci Technol 38:228A–231A
Shafy A, Molini V, Cortes-Morichetti M, Hupertan V, Lila N, Chachques JC (2012) Comparison of the effects of adenosine, inosine, and their combination as an adjunct to reperfusion in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction. ISRN Cardiol 2012:1–9
Simpson AJ, Brown SA (2005) Purge NMR: effective and easy solvent suppression. J Magn Reson 175:340–346
Simpson MJ, McKelvie JR (2009) Environmental metabolomics: new insights into earthworm ecotoxicity and contaminant bioavailability in soil. Anal Bioanal Chem 394:137–149
Strange K, Morrison R, Heilig CW, DiPietro S, Gullans SR (1991) Upregulation of inositol transport mediates inositol accumulation in hyperosmolar brain cells. Am J Phys Cell Phys 260:C784–C790
Suchail S, Guez D, Belzunces LP (2001) Discrepancy between acute and chronic toxicity induced by imidacloprid and its metabolites in Apis mellifera. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2482–2486
Tang R, Ding C, Dang F, Ma Y, Wang J, Zhang T, Wang X (2018) NMR-based metabolic toxicity of low-level Hg exposure to earthworms. Environ Pollut 239:428–437
Tomizawa M, Casida JE (2005) Neonicotinoid insecticide toxicology: mechanisms of selective action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 45:247–268
Tuffnail W, Mills GA, Cary P, Greenwood R (2009) An environmental 1H NMR metabolomic study of the exposure of the marine mussel Mytilus edulis to atrazine, lindane, hypoxia and starvation. Metabolomics 5:33–43
van der Sluijs JP, Simon-Delso N, Goulson D, Maxim L, Bonmatin JM, Belzunces LP (2013) Neonicotinoids, bee disorders and the sustainability of pollinator services. Curr Opin Environ Sustain 5:293–305
Wang Y, Cang T, Zhao X, Yu R, Chen L, Wu C, Wang Q (2012) Comparative acute toxicity of twenty-four insecticides to earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 79:122–128
Wang J, Wang G, Zhu L (2016) DNA damage and oxidative stress induced by imidacloprid exposure in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 144:510–517
Whitfield Åslund ML, Simpson AJ, Simpson MJ (2011) 1H NMR metabolomics of earthworm responses to polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) exposure in soil. Ecotoxicology 20:836–846
Whitfield Åslund ML, McShane H, Simpson MJ, Simpson AJ, Whalen JK, Hendershot WH, Sunahara GI (2012) Earthworm sub-lethal responses to titanium dioxide nanomaterial in soil detected by 1H NMR metabolomics. Environ Sci Technol 46:1111–1118
Whitfield Åslund M, Stephenson GL, Simpson AJ, Simpson MJ (2013) Comparison of earthworm responses to petroleum hydrocarbon exposure in aged field contaminated soil using traditional ecotoxicity endpoints and 1H NMR-based metabolomics. Environ Pollut 182:263–268
Yuk J, Simpson MJ, Simpson AJ (2011) 1-D and 2-D NMR metabolomics of earthworm responses to sub-lethal trifluralin and endosulfan exposure. Environ Chem 8:281–294
Yuk J, Simpson MJ, Simpson AJ (2012) Coelomic fluid: a complimentary biological medium to assess sub-lethal endosulfan exposure using 1H NMR-based earthworm metabolomics. Ecotoxicology 21:1301–1313
Yuk J, Simpson MJ, Simpson AJ (2013) 1-D and 2-D NMR-based metabolomics of earthworms exposed to endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate in soil. Environ Pollut 175:35–44
Zang Y, Zhong Y, Luo Y, Kong ZM (2000) Genotoxicity of two novel pesticides for the earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 108:271–278
Zhang Q, Zhang B, Wang C (2014) Ecotoxicological effects on the earthworm Eisenia fetida following exposure to soil contaminated with imidacloprid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:12345–12353
Acknowledgments
We extend our gratitude to Dr. Ronald Soong for technical assistance and valuable discussions.
Funding
We thank the National Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada Strategic Partnership Grant (STPGP 494273-16) for funding this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1.77 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dani, V.D., Lankadurai, B.P., Nagato, E.G. et al. Comparison of metabolomic responses of earthworms to sub-lethal imidacloprid exposure in contact and soil tests. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 18846–18855 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05302-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05302-y